Open Source Data Platform (ODP) is an open-source implementation of Apache Hadoop Distribution, built and provided as a single installation package by Acceldata. ODP is a software framework consisting of libraries and integration of the latest upstream code from Apache projects to assist data-driven enterprises in their data ingestion, storage, computing, and security endeavors. Deployment and cluster management in ODP is provided using Ambari. Besides, additional components can also be added to the stack using custom Ambari management packs.
ODP also comes with Acceldata's Pulse support to allow enterprises with complete solutions for the management and observability of their data and data-driven operations.
Features of ODP
- ODP is completely open-source - built and tested by Acceldata using the latest upstream code.
- Easy to deploy version-controlled repository of community-driven open source stack components for Enterprises.
- A simple, cost-effective, scalable data platform solution.
- ODP uses the same stack deployed by various top organizations.
- Provide enterprises to continue with their Big Data Hadoop journey.
- ODP supports public, private, and hybrid environments to meet the changing requirements of enterprises.
- Provides agility to run multiple instances of the same or different version of any open source component seamlessly through mpacks.
- Enterprises may couple ODP implementation with a customer support team having deep experience supporting huge clusters.
ODP Architecture
The following image displays the architecture of ODP.
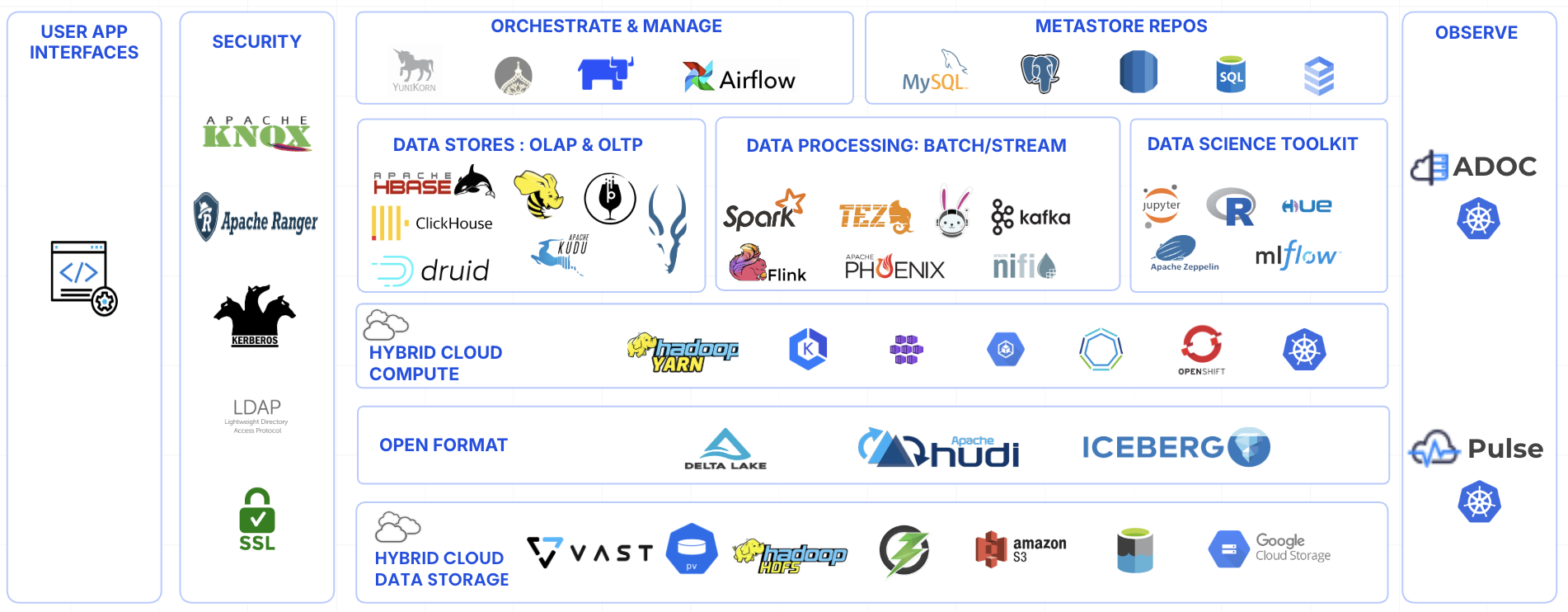
Open Source Data Platform Specifications
Component Versions
This section provides a list of the official Apache component versions for the Open Source Data Platform (ODP). To ensure that you are working with the most recent stable software available, you must be familiar with the latest Apache component versions in ODP. Additionally, you should be aware of the available Technical Preview components and use them only in a testing environment.
The Acceldata approach is to provide patches only when necessary to ensure the interoperability of components. Unless you are explicitly directed by Acceldata Support to install a patch, each of the ODP components should remain at the following package version levels to ensure a certified and supported copy of ODP.
Below is the ODP-3.3.6.x Support Matrix with officially supported Apache component versions.
| COMPONENTS | OS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Service | Version | RHEL 8/9 | Ubuntu 20/22 |
| Ambari | 3.0.0.0-1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Airflow (mpack) | 2.8.3 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Cruise Control + Kafka 2 | 2.5.84 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Cruise Control + Kafka 3 (mpack) | 2.5.137 | ✅ | ✅ |
| ClickHouse | 25.5.4.38 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Druid | 29.0.1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Flink | 1.19.1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Hadoop | 3.3.6 | ✅ | ✅ |
| HBase | 2.6.2 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Hive | 4.0.1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Httpfs (mpack) | 2.7.1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Hue (mpack) | 4.11.0 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Impala (mpack) | 4.4.1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Infra Solr | 3.0.0.0-1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Isilon (mpack) | 1.0.3 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Jupyterhub | 5.2.1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Kafka 2 | 2.8.2 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Kafka 3 (mpack) | 3.7.2 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Knox | 2.0.0 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Kudu | 1.17.0 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Livy | 0.8.0 | ✅ | ✅ |
| MLflow | 3.1.0 | ✅ | ✅ |
| NiFi (mpack) | 1.27.8 | ✅ | ✅ |
| NiFi Registry (mpack) | 1.27.8 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Oozie | 5.2.1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Ozone (mpack) | 1.4.1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Phoenix | 5.2.1 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Pinot | 1.4.0 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Ranger | 2.5.0 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Schema Registry (mpack) | 1.0.0 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Spark 3 (mpack) | 3.5.5 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Sqoop | 1.4.8 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Tez | 0.10.4 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Trino | 472 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Zeppelin | 0.12.0 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Zookeeper | 3.8.4 | ✅ | ✅ |
| ODP-UTILS | 1.1.0.22 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Spark3-warehouse-connector | 1.0.0 | ✅ | ✅ |
Java Certifications
By default, OpenJDK11 does not enable support for weaker encryption types. It has been deprecated from JDK8 onwards, For more information, see the Release notes for Red Hat build of OpenJDK 8.0.392.
| Name | Status |
|---|---|
| Java | JDK 11 and JDK 17 |
| Azul JDK | 11.0.24+8 (completed) |
Supported Databases
| Service | Version |
|---|---|
| MySQL | 8.x |
| PostgreSQL | 15.7 |
| MariaDB | 10.3, 10.11 |
| OracleDB | 19c and above |
ODP Process Methodology
ODP process
ODP Migration Options
Acceldata supports three types of migrations for ODP. The three migration methods are described as follows.
In-Place Upgrade
This is the fastest migration process and does not require you to uninstall the existing version. You can start this migration process without saving data beyond normal precautions.
In-place upgrade
Side-car Upgrade
You can use the side-car migration technique when you have tight service-level agreements (SLAs) that preclude an extended. This process minimizes downtime on individual workloads while providing a straightforward roll-back mechanism on a per-workload basis.
Side-car upgrade
Forklift Upgrade
Forklift upgrade requires major changes to your existing IT infrastructure. Forklift upgrades are a result of relatively minor enhancements that cannot be implemented piece by piece due to legacy systems. In such cases, the hardware and software needs to be updated simultaneously, creating a job so large that it requires a metaphorical forklift to carry it out.
Forklift upgrade
The content here and henceforth is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purposes only, and may not be incorporated into any contract.