Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Key Concepts: Keystore and Truststore
Keystore
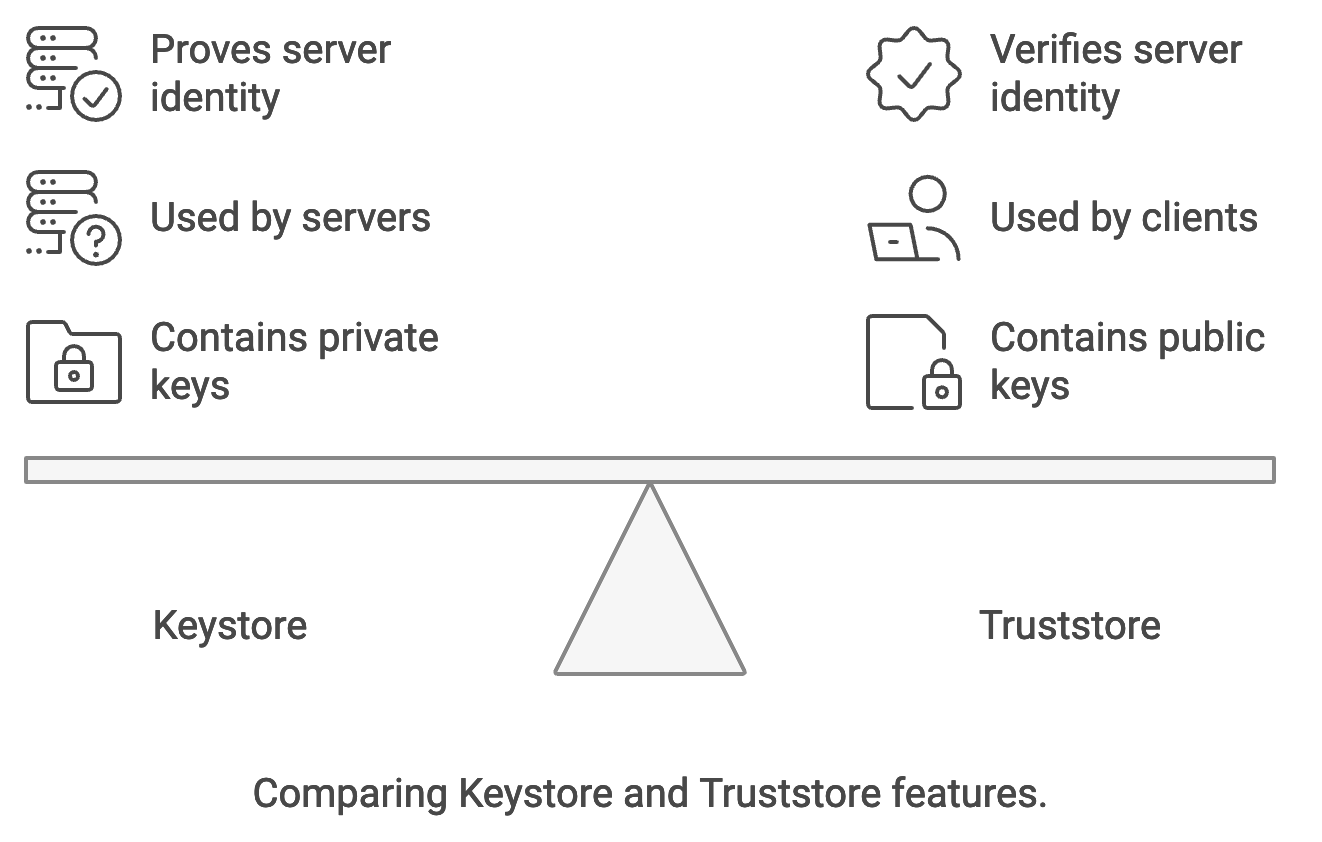
A keystore is a secure file that holds a server's private keys and corresponding certificates. It is primarily used by servers to authenticate themselves to clients during secure communications. The keystore typically employs a password to protect its contents and can contain various types of keys and certificates, including:
- Private Keys: These are secret keys used for encrypting data and signing certificates. The private key must remain confidential and should not be shared. - Public Key Certificates: These certificates contain the public key associated with the private key, along with metadata about the key, such as the issuing Certificate Authority (CA), the validity period, and the entity it represents.
Truststore
A truststore is a secure file that contains trusted certificates from external sources, such as Certificate Authorities (CAs). It is used by clients to verify the identity of servers they connect to. The truststore ensures that clients can trust the certificates presented by the servers, protecting against man-in-the-middle attacks and other security vulnerabilities. Like keystores, truststores also have a password to secure their contents.
Keystore vs. Truststore
| Feature | Keystore | Truststore |
|---|---|---|
| Contains | Private keys and corresponding public key certificates | Trusted public key certificates |
| Used by | Servers to authenticate themselves to clients | Clients to verify server identity |
| Purpose | Proves server identity | Verifies server identity |
| Security Role | Ensures confidentiality of private keys | Ensures trust in external certificates |
| Management | Managed by server administrators | Managed by client administrators |
| File Extension | Commonly .jks (Java KeyStore) | Commonly .jks |