Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Types of Certificates
A comprehensive overview of the various types of digital certificates utilized for secure communications within ODP and Hadoop environments, specifically focusing on self-signed certificates, CA-signed certificates, and internal CA certificates.
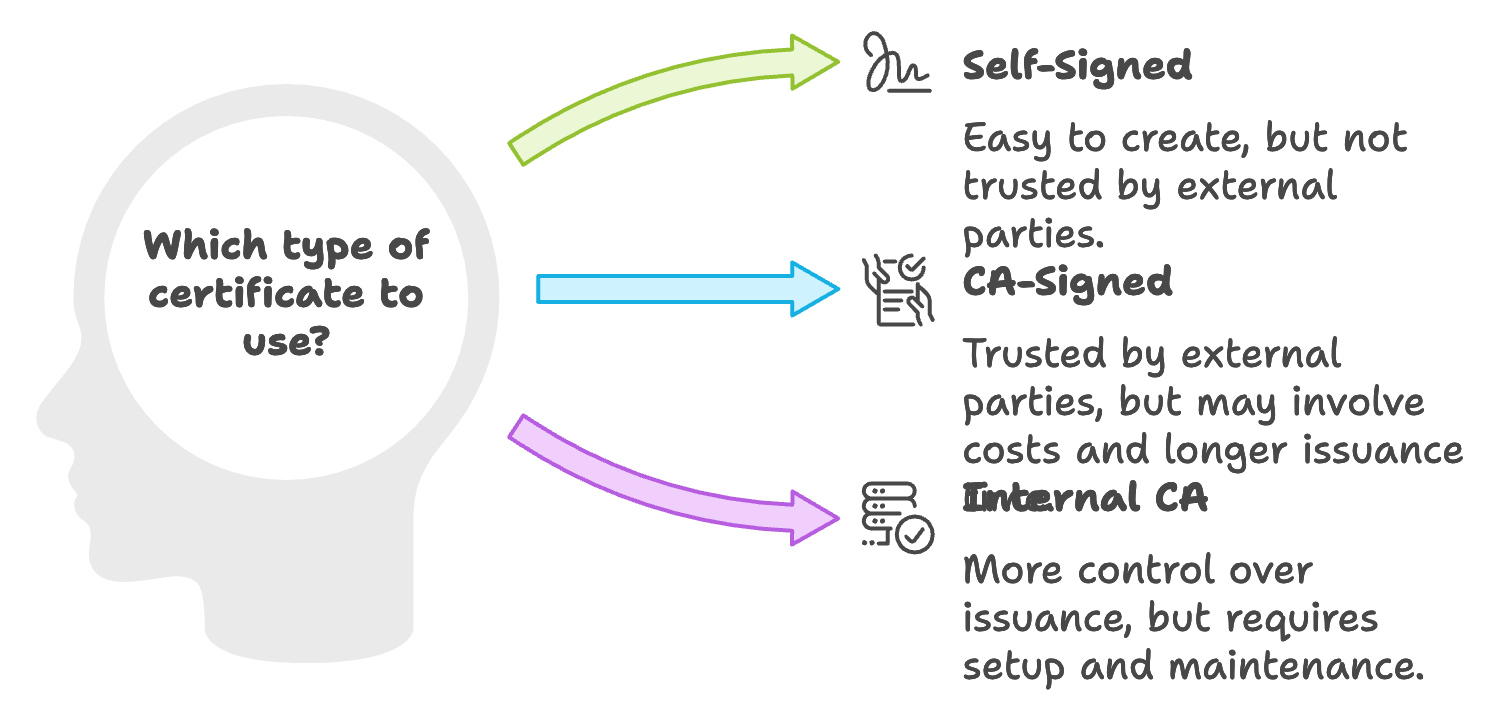
Self-Signed Certificates
Definition:
A self-signed certificate is a digital certificate that is signed by the same entity that created it, utilizing its private key.
Use Cases:
- Internal Communications: Commonly employed within private networks to secure data transmission.
- Development Environments: Suitable for testing and staging setups where external dependencies are not feasible.
Testing Scenarios: Ideal for applications requiring SSL/TLS encryption without relying on external authorities.
Downsides:
- Untrusted by External Clients: These certificates are not automatically recognized by external systems; manual addition to truststores is necessary.
Increased Risk of Attacks: More vulnerable to Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks due to lack of external validation.
Management Tools:
- OpenSSL: Utilized for the creation and management of self-signed certificates within ODP/Hadoop infrastructures.
- Keytool: A Java-based utility for managing keys and certificates pertinent to Hadoop applications.
CA-Signed Certificates
Definition:
The CA-signed certificates are issued by recognized Certificate Authorities (CAs), providing trusted verification of identity across systems.
Use Cases:
Secure Public Communications: Critical for establishing HTTPS connections on web interfaces and APIs.
Benefits:
- Trusted by Clients and Browsers: Automatically recognized by most clients and browsers, eliminating the need for manual trust configuration.
- Validation Levels: Offers varying levels of validation (Domain, Organization, and Extended) to ensure the identity of entities.
Downsides:
- Cost: Typically involves a purchase, which may present a financial consideration for organizations.
- Management Overhead: Requires continuous renewal and lifecycle management to maintain certificate validity.
Common Certificate Authorities:
- DigiCert: Provides high-assurance certificates and scalable public key infrastructure (PKI) solutions.
- GlobalSign: Offers a variety of digital certificates and comprehensive PKI services suitable for enterprise environments.
- Let’s Encrypt: A free CA offering automated SSL/TLS certificates, beneficial for development and testing phases.
Management Tools:
- Certbot: A tool for obtaining certificates from Let’s Encrypt, facilitating secure communications within Hadoop environments.
- AWS Certificate Manager: A service for managing SSL/TLS certificates within AWS infrastructure that may host Hadoop clusters.
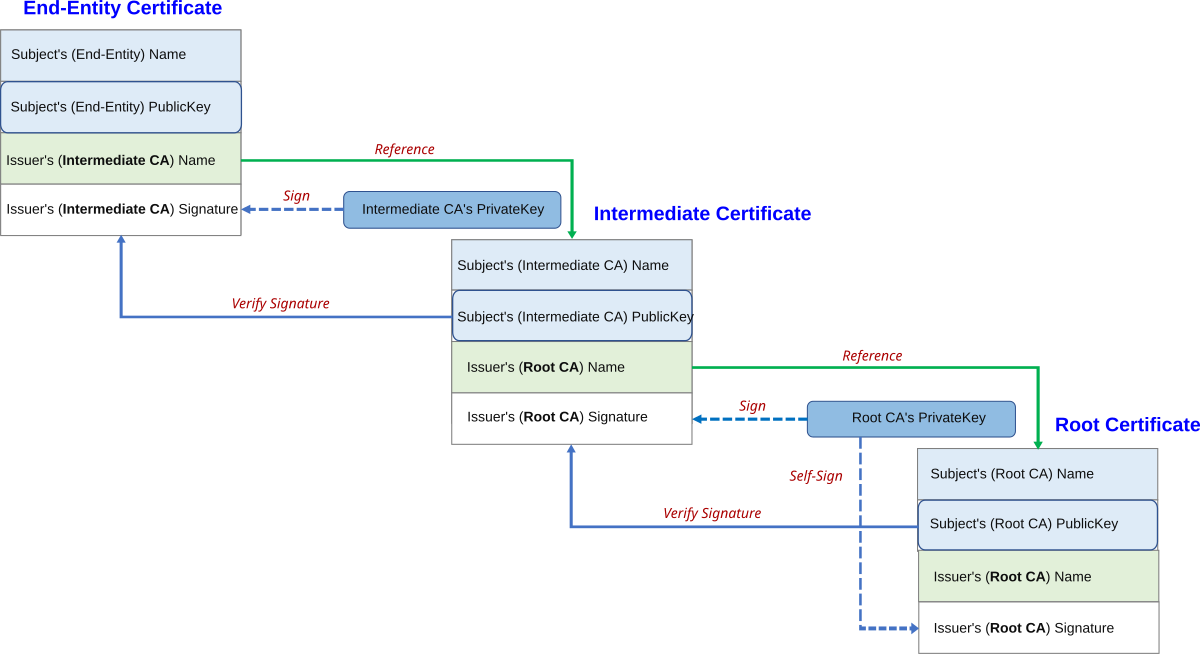
Internal CA Certificates
Definition:
The Internal CA certificates are issued by a Certificate Authority that is managed within the organization, enabling control over certificate issuance processes.
Use Cases:
- Internal Communications: Essential for securing connections for internal applications and services within the ODP/Hadoop ecosystem.
- Development and Testing Environments: Provides flexibility and control without reliance on external Certificate Authorities.
Benefits:
- Cost-Effective: Helps reduce costs associated with acquiring external certificates.
- Greater Control and Flexibility: Allows organizations to tailor certificate policies to meet specific operational needs.
Downsides:
- Trust Management Required: External systems must be configured to recognize and trust the internal CA.
- Limited Recognition: Not automatically acknowledged in public systems, potentially hindering external communications.
Management Tools:
OpenSSL: A primary tool for creating and managing internal CA certificates within ODP/Hadoop environments.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate type of certificate—self-signed, CA-signed, or internal CA—depends on specific security requirements and the operational context of ODP and Hadoop environments. A thorough understanding of the benefits, downsides, and management tools associated with each certificate type is essential for effective certificate management and ensuring secure communications across systems.