Overview
Migrating data between Hadoop clusters located in different Kerberos realms requires establishing cross-realm authentication. This comprehensive guide provides detailed, step-by-step instructions for the following scenarios:
- Scenario 1: Cross-Realm Trust Between Clusters with Both MIT KDCs
- Scenario 2: Cross-Realm Trust Between an MIT KDC and an Active Directory KDC
- Scenario 3: Cross-Realm Trust Between Clusters with Both Active Directory KDCs
- Scenario 4: Data Migration Between Secure and Unsecure Clusters
Follow the instructions provided on this page to set up cross-realm trusts, configure Kerberos and Hadoop settings, and perform data migration using distcp.
Prerequisites
Administrative Access:
- For MIT KDCs: Root or administrative access to both KDC servers.
- For Active Directory Domains: Domain Administrator privileges.
Network Connectivity:
- Ensure all clusters and their respective KDCs or domain controllers can communicate over the network.
Consistent User and Group Identities:
- Usernames and group names should be consistent across clusters for seamless access control.
DNS Configuration:
- Proper DNS setup for name resolution between clusters and KDCs.
Time Synchronization:
- All systems must have synchronized clocks (use NTP) to prevent Kerberos authentication failures.
Configure and Validate the DNS Settings
The correct DNS configuration is crucial for Kerberos authentication and Hadoop operations.
Configure the DNS Forwarding or Conditional Forwarders
On each domain controller and KDC:
Active Directory Domain Controllers:
- DNS Forwarding:
- Open DNS Manager.
- Right-click on the DNS server and select Properties.
- Go to the Forwarders tab and add the IP address of the DNS server from the other domain.
- DNS Forwarding:
Conditional Forwarders:
- In DNS Manager, expand the server and right-click Conditional Forwarders.
- Select New Conditional Forwarder.
- Enter the domain name of the other realm and the IP address of its DNS server.
MIT KDC Servers:
Update
/etc/resolv.conf:- Add the nameserver entries for the other realm's DNS servers.
Configure DNS Zones:
- Modify your DNS server to include zones for the other domain, if applicable.
Validate the DNS Resolution
On a node in each domain:
- Test Forward Lookup
nslookup hostname.otherdomain.com- Replace
hostname.otherdomain.comwith an actual hostname from the other domain. - Verify that it resolves to the correct IP address.
- Test Reverse Lookup
nslookup IP_ADDRESS- Replace
IP_ADDRESSwith the IP address of a host in the other domain. - Verify that it resolves to the correct hostname.
Verify Network Connectivity
- Ping Test
ping hostname.otherdomain.com- Port Connectivity: Test the connectivity to critical ports (For example, Kerberos port 88):
nc -zv hostname.otherdomain.com 88For a cross-realm trust to function properly, both Key Distribution Centers (KDCs) must have the same krbtgt principal and password, and must be configured to use the same encryption type.
Scenario 1: Cross-Realm Trust Between Clusters with Both MIT KDCs
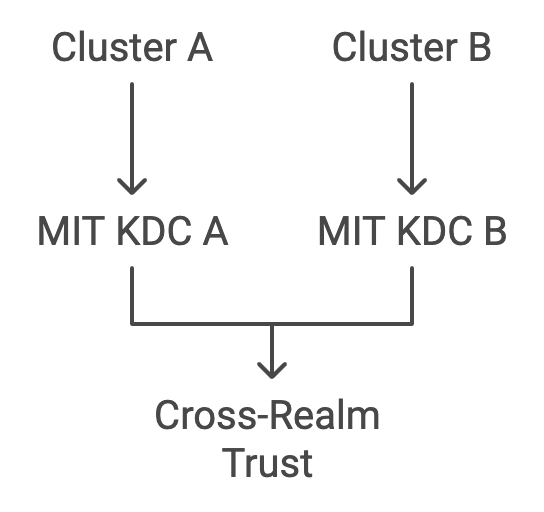
Configure each MIT KDC Servers
On MIT KDC Server A (REALM_A.COM):
- Create Cross-Realm Principal:
kadmin.local -q "addprinc krbtgt/REALM_B.COM@REALM_A.COM"On MIT KDC Server B (REALM_B.COM):
- Create Cross-Realm Principal:
kadmin.local -q "addprinc krbtgt/REALM_A.COM@REALM_B.COM"Edit /etc/krb5.conf on both KDCs:
- Add the following configurations:
[realms] REALM_A.COM = { kdc = kdc1.realm_a.com admin_server = kdc1.realm_a.com } REALM_B.COM = { kdc = kdc1.realm_b.com admin_server = kdc1.realm_b.com }[domain_realm] .realm_a.com = REALM_A.COM realm_a.com = REALM_A.COM .realm_b.com = REALM_B.COM realm_b.com = REALM_B.COM[capaths] REALM_A.COM = { REALM_B.COM = . } REALM_B.COM = { REALM_A.COM = . }- Explanation:
- The
[capaths]section defines the authentication paths between realms. - The dot (
.) indicates a direct trust relationship.
- The
Scenario 2: Cross-Realm Trust Between an MIT KDC and an Active Directory KDC
Configure the Active Directory Domain Controller
On the AD Domain Controller (ADDOMAIN.COM):
Create a User for Cross-Realm Trust:
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Create a user named
krbtgt/MITREALM.COM. - Set a strong password and select Password never expires.
- Uncheck User must change password at next logon.
Map the MIT Realm to the AD Domain:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Run the following command and
ktpass /out krbtgt_MITREALM.COM.keytab /princ krbtgt/MITREALM.COM@ADDOMAIN.COM /mapuser krbtgt/MITREALM.COM /pass * /crypto ALL /ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL- Enter the password when prompted.
- Copy the Keytab to the MIT KDC Server:
- Transfer
krbtgt_MITREALM.COM.keytabsecurely to the MIT KDC server.
- Transfer
Configure the MIT KDC Server
On the MIT KDC Server (MITREALM.COM):
- Create the Trust Principal:
kadmin.local -q "addprinc krbtgt/ADDOMAIN.COM@MITREALM.COM"- Use the same password set on the AD side.
- Import the Keytab from AD:
ktutil ktutil: rkt krbtgt_MITREALM.COM.keytab ktutil: wkt /etc/krb5.keytab ktutil: quit- Verify the Keytab Entries:
klist -k- Update
/etc/krb5.conf:- Add the AD realm under
[realms]and update[capaths].
- Add the AD realm under
Scenario 3: Cross-Realm Trust Between Clusters with Both Active Directory KDCs
Types of Trust
- External Trust: Domain-to-domain trust outside the forest.
- Forest Trust: Trust between two AD forests, allowing all domains within to trust each other.
Trust Direction and Authentication Scope
Trust Direction:
- One-Way Trust: Only one domain trusts the other.
- Two-Way Trust: Both domains trust each other.
Authentication Scope:
- Forest-Wide Authentication: All users can authenticate.
- Selective Authentication: Only specified users/groups can authenticate.
Choose the Appropriate Trust Type
- Recommended: Two-Way Forest Trust with Forest-Wide Authentication.
Create a Two-Way Forest Trust
Option A: Using GUI (Active Directory Domains and Trusts)
On the Domain Controller of DOMAIN_A.COM:
Open Active Directory Domains and Trusts:
- Navigate to Start > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Domains and Trusts.
Create New Trust:
- Right-click
DOMAIN_A.COM> Properties > Trusts tab > New Trust.
- Right-click
Follow the Wizard:
- Enter
DOMAIN_B.COMas the trust name. - Select Forest Trust.
- Choose Two-way trust.
- Select Both this domain and the specified domain.
- Choose Forest-wide authentication.
- Set a secure trust password.
- Complete the wizard.
- Enter
Repeat the steps on DOMAIN_B.COM Domain Controller.
Option B: Using the Command-Line (netdom)
On DOMAIN_A.COM Domain Controller:
- Run the below command and enter passwords when prompted.
netdom trust DOMAIN_A.COM /Domain:DOMAIN_B.COM /Add /TwoWay /ForestTrust /Transitive:Yes /UserD:DOMAIN_B\Administrator /PasswordD:* /UserO:DOMAIN_A\Administrator /PasswordO:* /PasswordT:*On DOMAIN_B.COM Domain Controller:
netdom trust DOMAIN_B.COM /Domain:DOMAIN_A.COM /Add /TwoWay /ForestTrust /Transitive:Yes /UserD:DOMAIN_A\Administrator /PasswordD:* /UserO:DOMAIN_B\Administrator /PasswordO:* /PasswordT:*Option C: Using PowerShell
On DOMAIN_A.COM Domain Controller:
$TrustPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString "YourTrustPassword" -AsPlainText -Force New-AdForestTrust -Name "DOMAIN_B.COM" -SourceForest "DOMAIN_A.COM" -TargetForest "DOMAIN_B.COM" -TrustType Forest -Direction Bidirectional -ForestTransitive $true -TrustPassword $TrustPassword -AuthenticationType ForestOn DOMAIN_B.COM Domain Controller:
$TrustPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString "YourTrustPassword" -AsPlainText -Force New-AdForestTrust -Name "DOMAIN_A.COM" -SourceForest "DOMAIN_B.COM" -TargetForest "DOMAIN_A.COM" -TrustType Forest -Direction Bidirectional -ForestTransitive $true -TrustPassword $TrustPassword -AuthenticationType ForestValidate and Confirm the Trust
Using GUI:
- On both domain controllers:
- Active Directory Domains and Trusts > Right-click domain > Properties > Trusts tab > Select trust > Properties > Validate.
Using Command-Line (netdom)
On DOMAIN_A.COM:
netdom trust DOMAIN_A.COM /Domain:DOMAIN_B.COM /Verify /UserD:DOMAIN_B\Administrator /PasswordD:* /UserO:DOMAIN_A\Administrator /PasswordO:*On DOMAIN_B.COM:
netdom trust DOMAIN_B.COM /Domain:DOMAIN_A.COM /Verify /UserD:DOMAIN_A\Administrator /PasswordD:* /UserO:DOMAIN_B\Administrator /PasswordO:*Using PowerShell
On DOMAIN_A.COM*: *
Get-ADTrust -Identity "DOMAIN_B.COM" | Format-List Name, TrustType, TrustDirection, IsForestTrust, IsActiveOn DOMAIN_B.COM:
Get-ADTrust -Identity "DOMAIN_A.COM" | Format-List Name, TrustType, TrustDirection, IsForestTrust, IsActiveScenario 4: Data Migration Between Secure and Unsecure Clusters
When migrating data between a secure (Kerberos-enabled) and an unsecure Hadoop cluster, specific configurations are required.
Configure the Unsecure Cluster
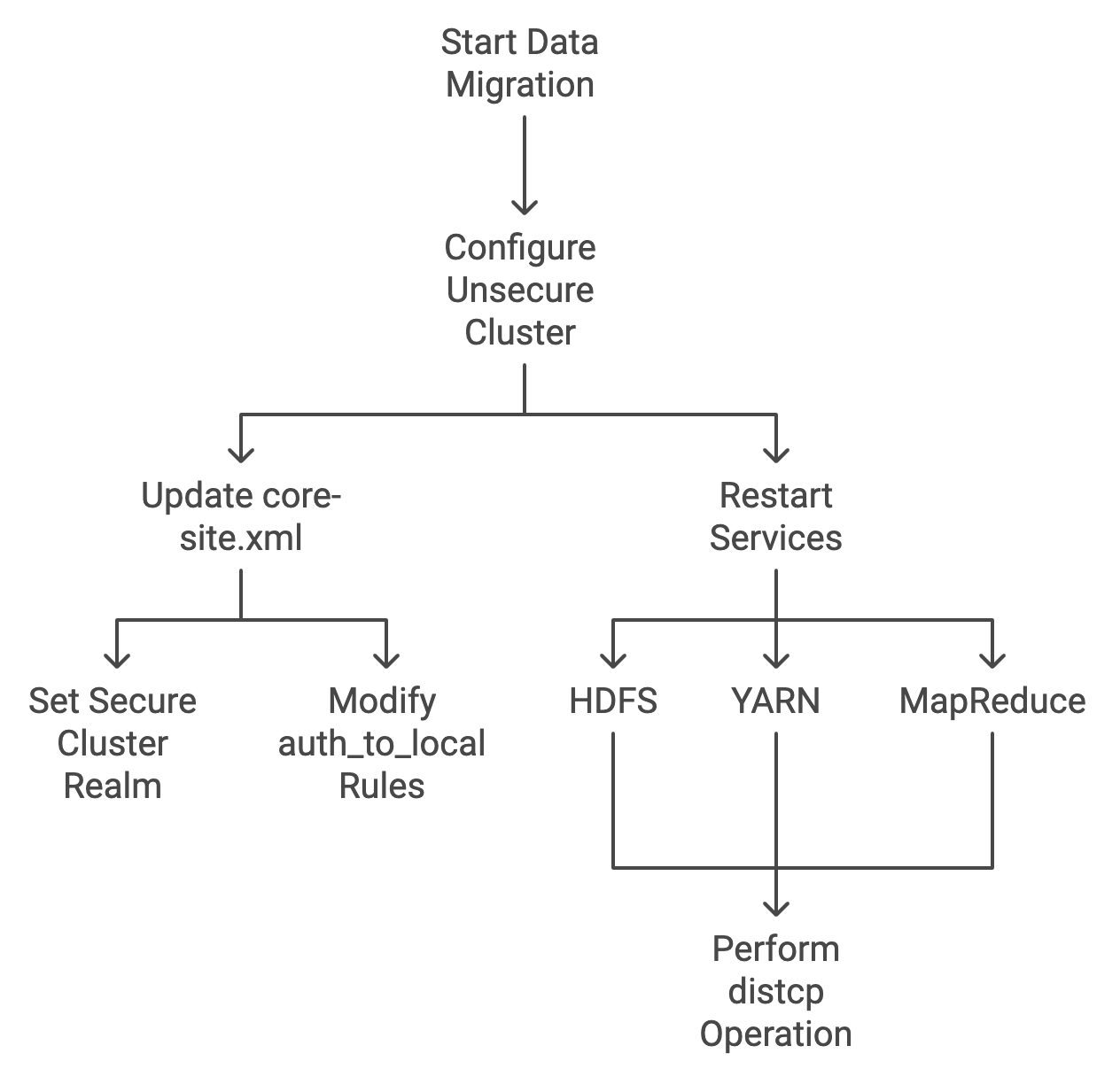
Replace SECURE_REALM.COM with your secure cluster's realm name.
Update the core-site.xml
Add the following properties:
- Set the Secure Cluster Realm:
<property> <name>hadoop.registry.kerberos.realm</name> <value>SECURE_REALM.COM</value></property>- Modify hadoop.security.auth to local Rules.
<property> <name>hadoop.security.auth_to_local</name> <value> RULE:[2:$1/$2@$0](.*@SECURE_REALM\.COM)s/(.*)@SECURE_REALM\.COM// RULE:[1:$1@$0](.*@SECURE_REALM\.COM)s/(.*)@SECURE_REALM\.COM// DEFAULT </value></property>Restart Affected Services
- Restart the HDFS, YARN, and MapReduce services.
Perform the distcp Operation
From the Secure Cluster to the Unsecure Cluster:
hadoop distcp -D ipc.client.fallback-to-simple-auth-allowed=true \ hdfs://secure-namenode.securecluster.com:8020/path/to/source \ hdfs://unsecure-namenode.unsecurecluster.com:8020/path/to/destinationExplanation:
- The
-D ipc.client.fallback-to-simple-auth-allowed=trueflag allows the secure cluster to communicate with the unsecure cluster using simple authentication.
Common Steps for All Scenarios
Configure Kerberos (krb5.conf) on All Cluster Nodes
On all nodes in both Clusters, update /etc/krb5.conf to recognize all involved realms.
Sample /etc/krb5.conf :
[libdefaults] default_realm = LOCALREALM.COM dns_lookup_kdc = true dns_lookup_realm = false forwardable = true default_ccache_name = /tmp/krb5cc_%{uid} renew_lifetime = 7d ticket_lifetime = 24h udp_preference_limit = 1[realms] REALM_A.COM = { kdc = kdc1.realm_a.com admin_server = kdc1.realm_a.com default_domain = realm_a.com } REALM_B.COM = { kdc = kdc1.realm_b.com admin_server = kdc1.realm_b.com default_domain = realm_b.com } ADDOMAIN.COM = { kdc = ad-dc.addomain.com admin_server = ad-dc.addomain.com default_domain = addomain.com } MITREALM.COM = { kdc = kdc.mitrealm.com admin_server = kdc.mitrealm.com default_domain = mitrealm.com }[domain_realm] .realm_a.com = REALM_A.COM realm_a.com = REALM_A.COM .realm_b.com = REALM_B.COM realm_b.com = REALM_B.COM .addomain.com = ADDOMAIN.COM addomain.com = ADDOMAIN.COM .mitrealm.com = MITREALM.COM mitrealm.com = MITREALM.COM[capaths] REALM_A.COM = { REALM_B.COM = . ADDOMAIN.COM = . MITREALM.COM = . } REALM_B.COM = { REALM_A.COM = . ADDOMAIN.COM = . MITREALM.COM = . } ADDOMAIN.COM = { MITREALM.COM = . REALM_A.COM = . REALM_B.COM = . } MITREALM.COM = { ADDOMAIN.COM = . REALM_A.COM = . REALM_B.COM = . }Update the Hadoop Configuration
Modify **core-site.xml:** Add or update the hadoop.security.auth_to_local property.
<property> <name>hadoop.security.auth_to_local</name> <value> RULE:[1:$1@$0](.*@REALM_A\.COM)s/@REALM_A\.COM// RULE:[1:$1@$0](.*@REALM_B\.COM)s/@REALM_B\.COM// RULE:[1:$1@$0](.*@ADDOMAIN\.COM)s/@ADDOMAIN\.COM// RULE:[1:$1@$0](.*@MITREALM\.COM)s/@MITREALM\.COM// DEFAULT </value></property>Update hdfs-site.xml:Add the following property.
<property> <name>dfs.namenode.kerberos.principal.pattern</name> <value>*</value></property>Synchronize Time Across Clusters
- Ensure that all systems use NTP or similar services for time synchronization.
Restart Hadoop Services
- Restart the Hadoop services on all clusters to apply new configurations.
Verification Steps
Test Kerberos Authentication
On a Node in Each Cluster:
- Obtain a Kerberos Ticket:
kinit user@LOCALREALM.COM- Access HDFS on the Other Cluster:
hdfs dfs -ls hdfs://namenode.otherrealm.com:8020/Expected Result: You must see the content of the HDFS directory without authentication errors.
Troubleshooting
- Check Kerberos Tickets
klistReview the Hadoop Logs
- Check the logs under
/var/log/hadoop/for errors.
- Check the logs under
Common Issues
- Clock skew between servers.
- Incorrect
krb5.confconfigurations. - Firewall blocking necessary ports.
Performing the Data Migration
Run distcp Between Clusters
- For Secure Clusters:
hadoop distcp \ hdfs://namenode.sourcecluster.com:8020/path/to/source \ hdfs://namenode.targetcluster.com:8020/path/to/destination- For Secure to Unsecure Cluster (Scenario 4):
hadoop distcp -D ipc.client.fallback-to-simple-auth-allowed=true \ hdfs://secure-namenode.securecluster.com:8020/path/to/source \ hdfs://unsecure-namenode.unsecurecluster.com:8020/path/to/destinationAdditional Options:
- If experiencing issues, force Kerberos to use TCP by adding to
/etc/krb5.conf:
[libdefaults] udp_preference_limit = 1Verify Data Migration
- Use
hdfs dfs -lsto check the destination directory. - Verify file integrity and permissions.
Summary of Steps
DNS Configuration:
- Configure DNS forwarding or conditional forwarders.
- Validate DNS resolution and network connectivity.
Establish Cross-Realm Trust:
- Scenario 1: Configure cross-realm principals on MIT KDCs.
- Scenario 2: Set up trust between AD DC and MIT KDC.
- Scenario 3: Create a two-way forest trust between AD domains.
- Scenario 4: Configure an unsecure cluster to accept connections from the secure cluster.
Kerberos Configuration:
- Update
/etc/krb5.confwith realm and KDC details. - Define
[capaths]for authentication paths.
- Update
Hadoop Configuration:
- Modify
core-site.xmlandhdfs-site.xmlwith necessary properties. - Distribute configurations across all nodes.
- Modify
Time Synchronization:
- Ensure all systems have synchronized clocks using NTP.
Restart Services:
- Restart Hadoop services to apply changes.
Verification:
- Test Kerberos authentication.
- Access HDFS across clusters.
Data Migration:
- Use
hadoop distcpfor data transfer. - Verify successful data migration.
- Use
This guide assumes familiarity with Kerberos and Hadoop administration. Always ensure you have backups before making significant changes to production systems. Consult with your organization's security policies before implementing cross-realm trusts.