Getting Started
Introduction to Acceldata SDK
Acceldata SDK includes APIs that allow for fine-grained end-to-end tracking and visibility of Python data pipelines.
Installation
The following Python modules must be installed in the environment:
Install acceldata-sdk
pip install acceldata-sdkPrerequisites
To make calls to ADOC, API keys are required.
Creating an API Key
You can generate API keys in the ADOC UI's Admin Central by visiting the API Keys section.
Before using acceldata-sdk calls, make sure you have your API keys and ADOC URL handy.
TORCH_CATALOG_URL - URL of the torch catalogueTORCH_ACCESS_KEY - API access key generated from torchTORCH_SECRET_KEY - API secret key generated from torchFeatures Provided by Acceldata SDK
Pipeline: Represents an execution of a data pipelineSpan: Logical collection of various tasksJob: Logical representation of a taskEvent: An event can contain arbitrary process or business data and is transmitted to the ADOC system for future tracking against a Pipeline execution
Minimum Instrumentation Required
Step 1. Create Pipeline and Pipeline Run
A pipeline should be created and a new pipeline run should be started before beginning the data processing code.
You must provide the pipeline_uid, which will be updated in ADOC to track the data pipeline execution.
torch_credentials = { 'url': torch_url, 'access_key': torch_access_key, 'secret_key': torch_secret_key }torch_client = TorchClient(**torch_credentials)meta = PipelineMetadata(owner='sdk/pipeline-user', team='TORCH', codeLocation='...')pipeline_name_ = pipeline_namepipeline = CreatePipeline( uid=pipeline_uid, name=pipeline_name_, description=f'The pipeline {pipeline_name_} has been created from torch-sdk', meta=meta, context={'pipeline_uid': pipeline_uid, 'pipeline_name': pipeline_name_})pipeline_res = torch_client.create_pipeline(pipeline=pipeline)print('pipeline id :: ', pipeline_res.id)pipeline_run = pipeline_res.create_pipeline_run()global pipeline_run_idpipeline_run_id = pipeline_run.idspan_name_ = f'{pipeline_uid}.span'global parent_span_contextparent_span_context = pipeline_run.create_span(uid=span_name_)Tracking Each Task
You must add more instrumentation to the code to allow ADOC to provide a fine-grained view of the data pipeline, as described in the sections below.
Tracking Each Task Using Jobs
Before each function is executed, a job_uid, input, output, and metadata should be passed as arguments to make each task visible as a job in the ADOC pipeline. The task's inputs should be described in the inputs list, and the task's output assets should be represented in the outputs list. A corresponding span can be created in addition to a job to populate the timeline and allow events to be associated with tasks.
def athena_to_redshift(job_uid, inputs, outputs, metadata, context_job, span_uid): span_uid_temp = span_uid pipeline = torch_client.get_pipeline(pipeline_uid) pipeline_run = pipeline.get_run(pipeline_run_id) job = CreateJob( uid=job_uid, name=f'{job_uid} Job', version=pipeline_run.versionId, description=f'{job_uid} created using torch job decorator', inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, meta=metadata, context=context_job ) job = pipeline.create_job(job) parent_span_context1 = pipeline_run.get_root_span() associated_job_uids = [job_uid] if span_uid is None: span_uid_temp = job_uid span_context = parent_span_context1.create_child_span( uid=span_uid_temp, context_data={ 'time': str(datetime.now()) }, associatedJobUids=associated_job_uids) ...Getting the UID of the Asset to be Used in the Input and Output List
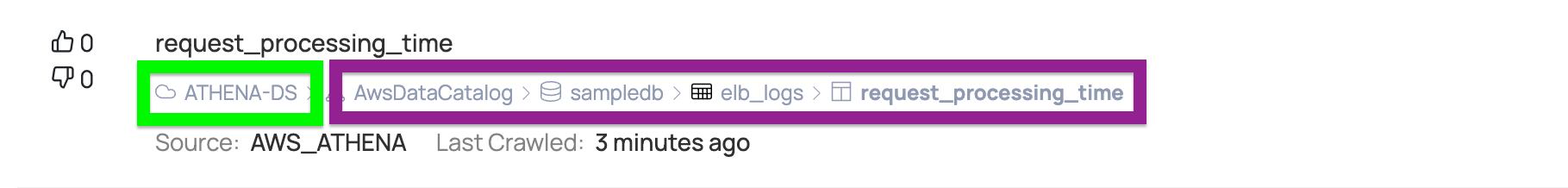
To get the UID of an asset, you must first open an asset in the ADOC UI. A path to the asset is shown in the asset under the Asset name, as shown in the image above. The first part highlighted in green is the data source name, and the remaining items can be used as asset names by using a period as a field separator. The DataSource name in this example is ATHENA-DS, and the asset name is AwsDataCatalog.sampledb.elb_logs.request processing time.
This asset can be used as an input with the following syntax: inputs=[Node(asset_uid='ATHENA-DS.AwsDataCatalog.sampledb.elb_logs.request_processing_time')],
Subdividing a Task into Multiple Spans
You can represent a single task with multiple steps in multiple child spans with create_child_span and send events for those child spans. To create a child span, you must first get the parent span context, which returns us to the root span. You must use the parent span context to call create child span, and it will appear as child span in the ADOC pipelines view.
def athena_to_redshift():... parent_span_context = span_context athena_result_span = parent_span_context.create_child_span( uid="athena.finance.approved_result", context_data={'client_time': str(datetime.now())} ) ... athena_result_span.send_event( GenericEvent( context_data={ 'client_time': str(datetime.now()) }, event_uid="finance.athena.approved_result" ) ) athena_result_span.end( context_data={'client_time': str(datetime.now())} ) .... redshift_upload_span = parent_span_context.create_child_span( uid="redshift.data.approved_upload", context_data={'client_time': str(datetime.now())} ) ... redshift_upload_span.send_event( GenericEvent( context_data={ 'client_time': str(datetime.now()) }, event_uid="finance.redshift.approved_upload" ) ) redshift_upload_span.end( context_data={'client_time': str(datetime.now())} )Linking a Task with Another Task
In previous examples, each pipeline job takes an asset as input and produces another asset as output, which the next job will use as input. Acceldata-sdk uses these to connect jobs in the ADOC pipeline UI. However, there may be times when a task does not produce another asset as an output. In such cases, you can provide a job_uid as output instead of an asset to link the next job.
def syncoperator_result():outputs=[Node(job_uid='quality.customers.athena')]job = CreateJob( uid=job_uid, name=f'{job_uid} Job', pipeline_run_id=pipeline_run.versionId, description=f'{job_uid} created using torch job decorator', inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, meta=metadata, context=context_job ) ...Conclusion
In this how-to guide, we explored using Acceldata SDK APIs to provide visibility to python data pipelines in ADOC pipelines UI.