MongoDB
This section provides a step-by-step guide on integrating MongoDB with Acceldata's Data Observability Cloud (ADOC). MongoDB, a popular NoSQL database, can be monitored and managed efficiently using ADOC's comprehensive tools.
Prerequisites
- A running MongoDB instance.
- Access credentials for MongoDB.
- ADOC installed and set up.
Add as Data Source
Navigate and select the Register icon from the left pane.
In the Data Source tab click on the Add Data Source button.
Select MongoDB from the list of available data sources.
Enter the MongoDB connection details:
- Host: The address of the MongoDB Server
- Port: The Port number of MongoDB
- Username : Your MongoDB username
- Password : Your MongoDB password
Click on Test Connection to verify the details
Click Next. The Observability Setup page is displayed.
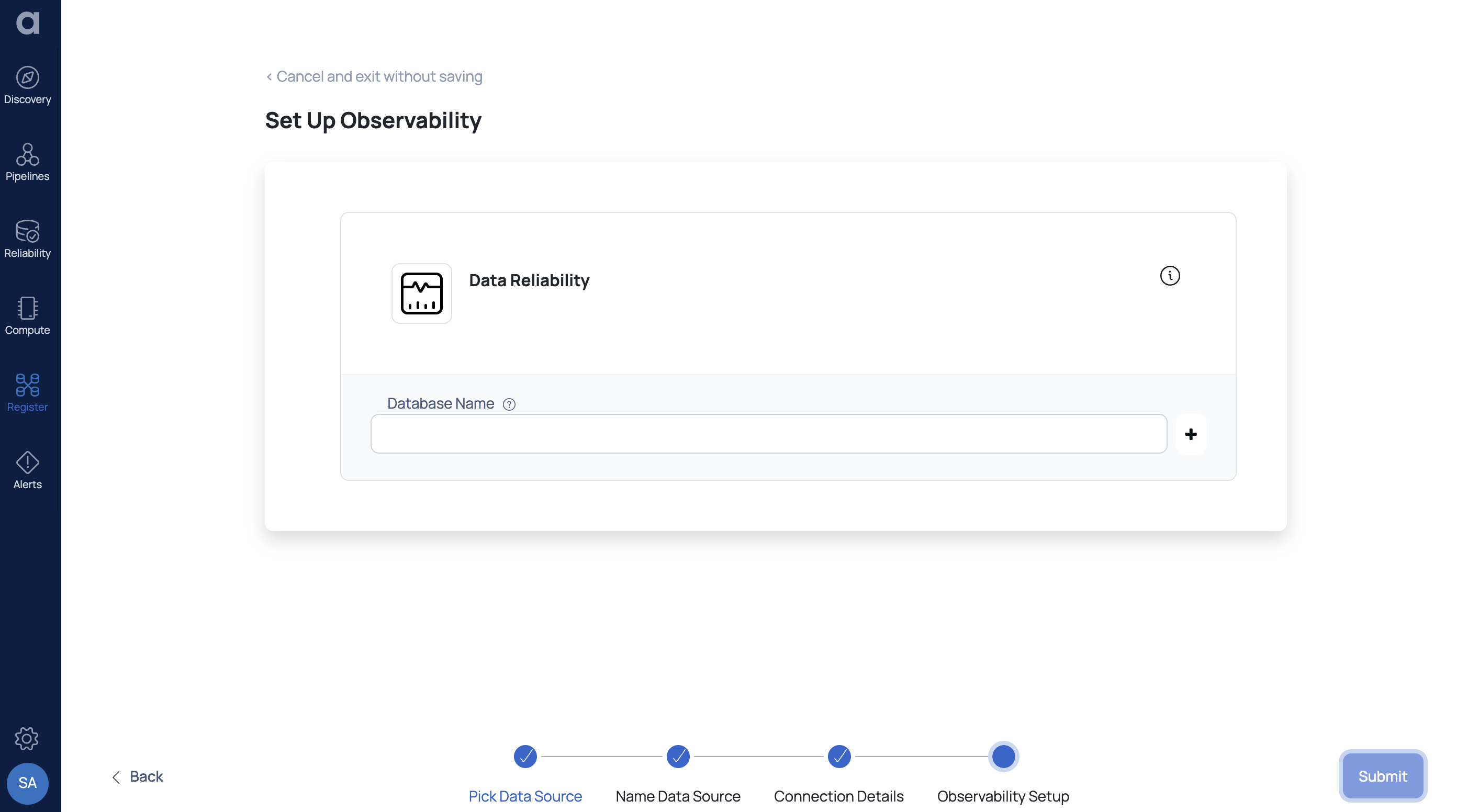
- Provide the Database Name of the MongoDB databases to be monitored by ADOC. To add multiple databases, click +.
- Enable Crawler Execution Schedule: Turn on this toggle switch to select a time tag and time zone to schedule the execution of crawlers for Data Reliability.
- Click Submit to complete the integration process.
You have successfully integrated MongoDB with ADOC. You can now monitor and manage your MongoDB data efficiently using ADOC’s powerful observability tools.
Control Plane Concurrent Connections and Queueing Mechanism
The ADOC Control Plane (CP) now supports a queueing mechanism for managing concurrent connections at the data source level. This feature is aimed at controlling and optimizing the execution of jobs, thereby preventing overload on customer databases and improving system performance and reliability. This guide provides an overview of how concurrent job execution is managed and queued, as well as details on the configuration process for manual and scheduled executions.
Key Features
- Concurrency Control at Datasource Level: Define the maximum number of concurrent jobs allowed for a specific data source.
- Queueing Mechanism for Jobs: Introduce a queueing mechanism to manage jobs that exceed the configured concurrency limit, ensuring smooth execution without overloading the database.
- Support for Multiple Job Types: Currently supports data quality, reconciliation, and profiling jobs.
- Flexibility in Slot Allocation: Users can set the number of available slots as per their performance needs.
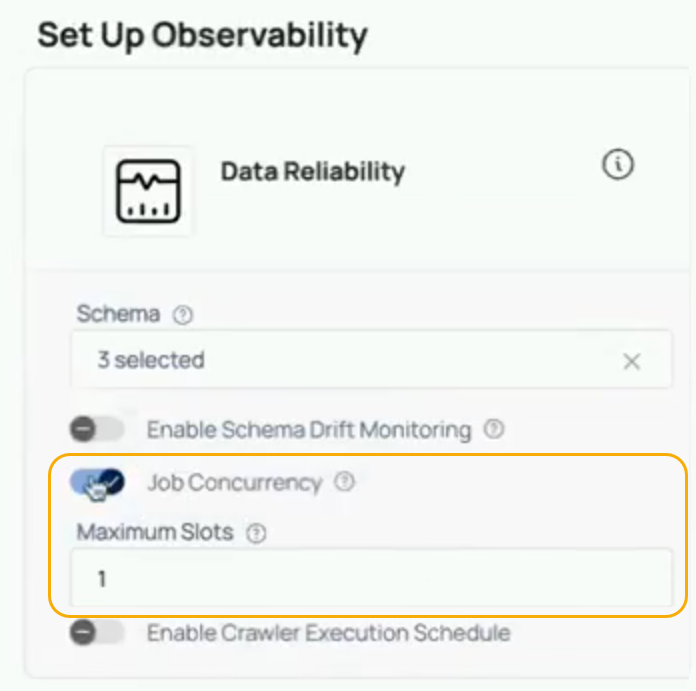
Concurrency Control and Queueing Mechanism
Why Concurrency Control is Needed?
Previously, no concurrency control existed to manage numerous jobs on the Control Plane. This meant that users may submit a huge number of jobs at once, potentially overflowing their database and causing performance issues or even system breakdowns. The new concurrency management technique ensures that only a fixed number of jobs can run concurrently, with additional jobs queued.
The concurrency control and queueing mechanism has been implemented for SAP Hana data sources. The new feature allows users to set the maximum number of concurrent jobs for a particular data source. If the number of jobs triggered exceeds the defined limit, the remaining jobs are queued until a slot becomes available.
How the Mechanism Works
- Job Slots: Users can define the number of slots available for concurrent job execution for a given data source. For example, if a data source is configured with a maximum of 5 concurrent jobs, only five jobs will run simultaneously.
- Queueing Mechanism: If more than five jobs are triggered, the excess jobs are moved to a queue and marked as "waiting." As soon as a running job completes, a slot is freed, and a job from the queue is picked for execution.
- Slot Monitoring: A background service continuously monitors the availability of job slots, checking every minute to see if a queued job can be started.
Configuration
Setting Concurrent Job Limits
When configuring a new data source or editing an existing one, users have the option to enable job concurrency control. By default, this setting is disabled, but it can be enabled, and users can set the Maximum Slots to define how many jobs can run concurrently.
Steps to Configure Job Concurrency:
- Navigate to the data source configuration page.
- Enable Job Concurrency Control by toggling the setting.
- Enter the number of slots (e.g., 1, 5, 10) that should be available for concurrent job execution.
- Save the configuration.
- Slot Setting: Suppose a user sets the Maximum Slots to 1 for a particular data source.
- Job Submission: The user then triggers three profiling jobs simultaneously.
- Queueing: Only one job will start immediately. The remaining two jobs are queued, and their status is shown as waiting.
- Slot Release: Once the first job completes, a slot is released, and the next job in the queue is started.
Benefits
- Prevents Overload: By limiting the number of concurrent jobs, the feature helps prevent overloading of customer databases, thus maintaining performance and avoiding potential crashes.
- Flexible Configuration: Users can adjust the number of concurrent slots based on their performance needs, giving them control over the workload being processed.
- Scalable: While this feature is currently implemented for SAP Hana data sources, it can be extended to other data sources such as Snowflake with minimal changes.
The queueing method for concurrent connections at the data source level is critical for maintaining system stability and optimal performance when dealing with multiple task executions. By restricting the amount of concurrent jobs and implementing a queueing system, the Control Plane may effectively manage workloads without overflowing the database.