Microsoft | Azure MSSQL
Azure MSSQL is a fully managed, cloud-based relational database service that provides the capabilities of SQL Server in the cloud. It is a fully managed, scalable, and secure database service that allows you to create, deploy, and manage relational databases in the cloud.
Azure MSSQL in ADOC
ADOC provides data reliability capability for data stored in your Azure MSSQL data source. To use this functionality, you must either create or use an existing Data Plane to add Azure MSSQL as a Data source in ADOC. You can examine the details of your Azure MSSQL data on ADOC's Data Reliability tab after adding Azure MSSQL as a Data Source.
For all Azure-related services provided in ADOC, users who wish to learn more about Service Principal support and its configuration can refer to our detailed guide. Visit the Service Principal Support for Azure Data Sources page for comprehensive instructions and information.
Add Azure MSSQL as a Data Source
To add Azure MSSQL as a Data source:
- Click Register from the left pane.
- Click Add Data Source.
- Select the Azure MSSQL Data Source. The Data source basic Details page is displayed.
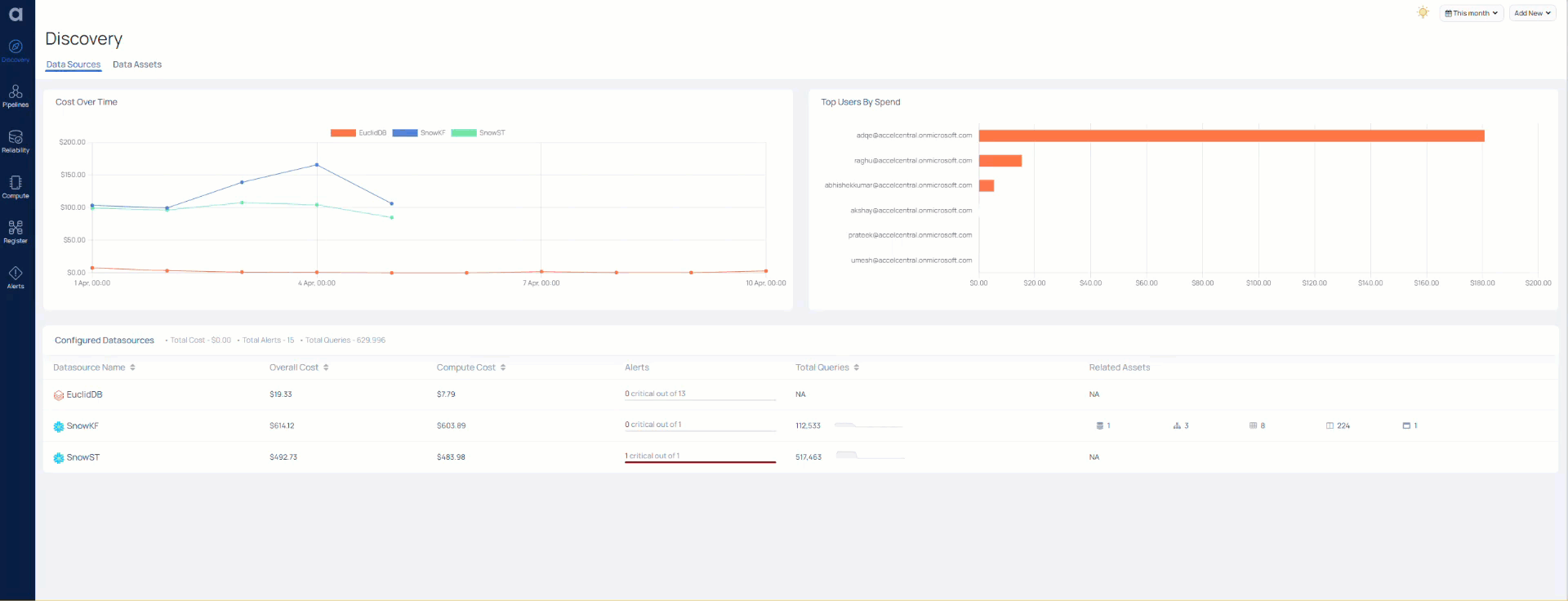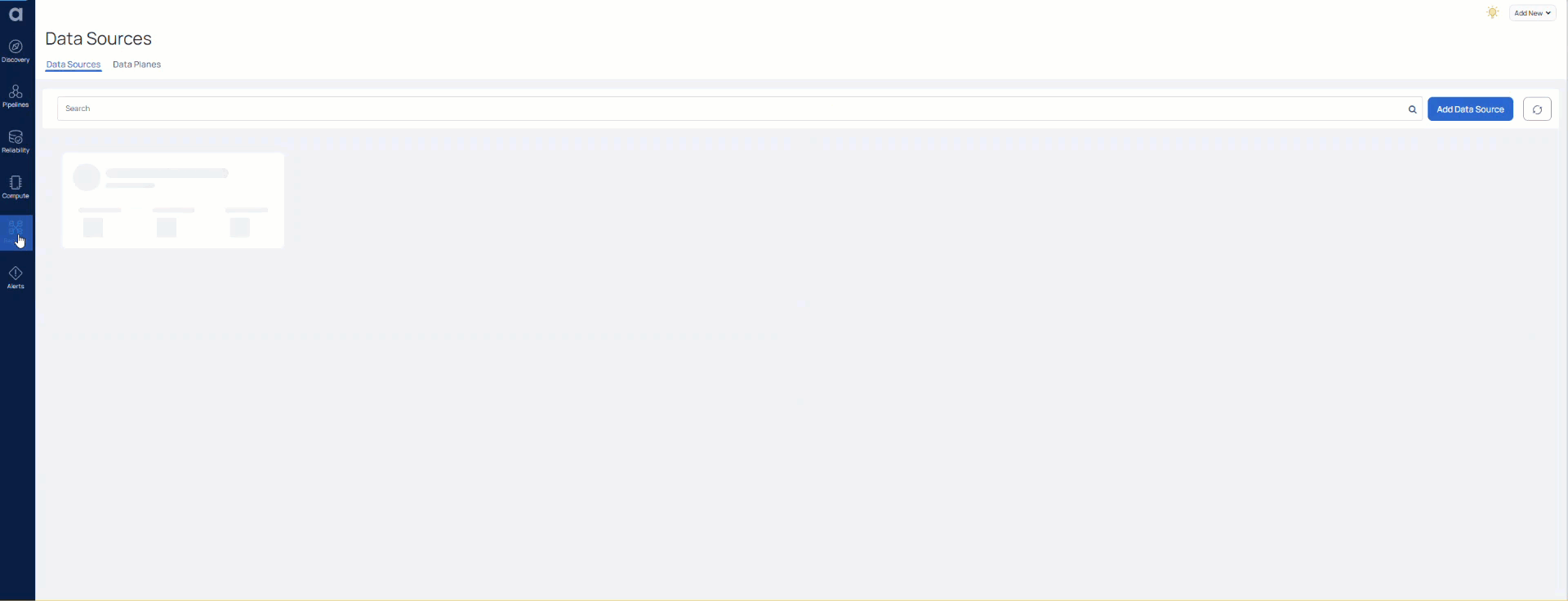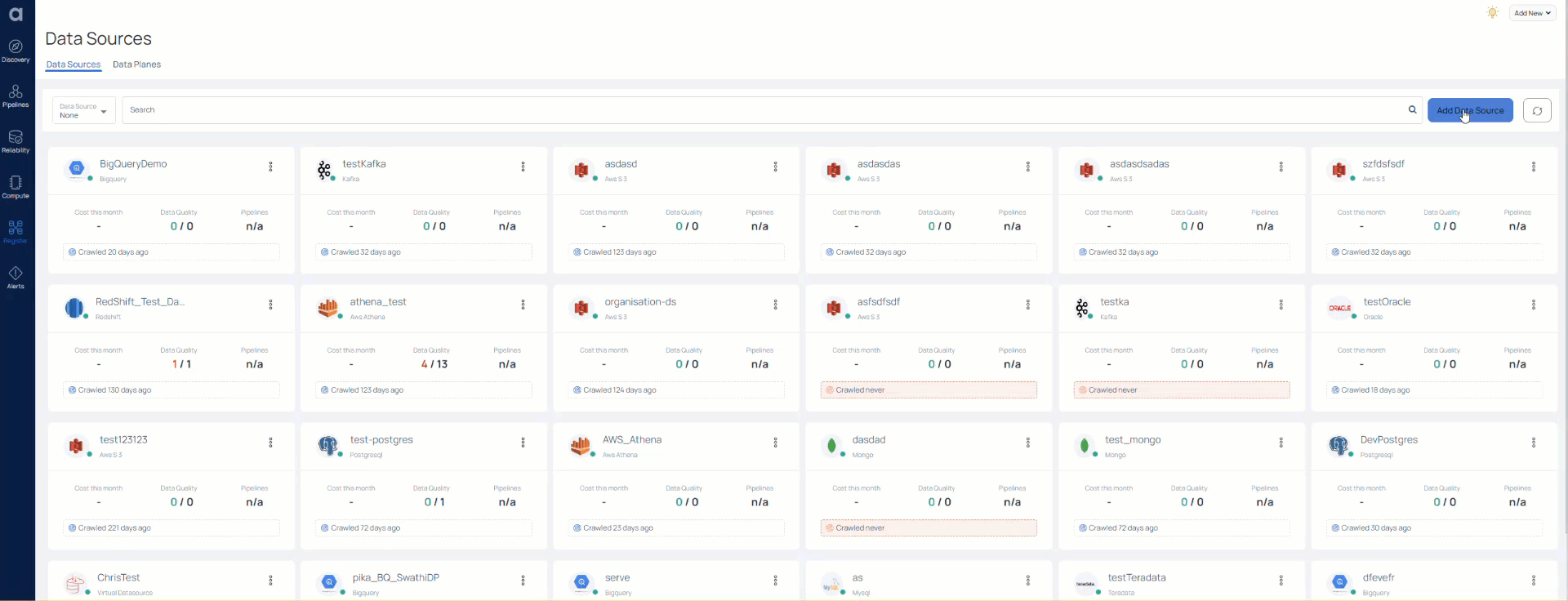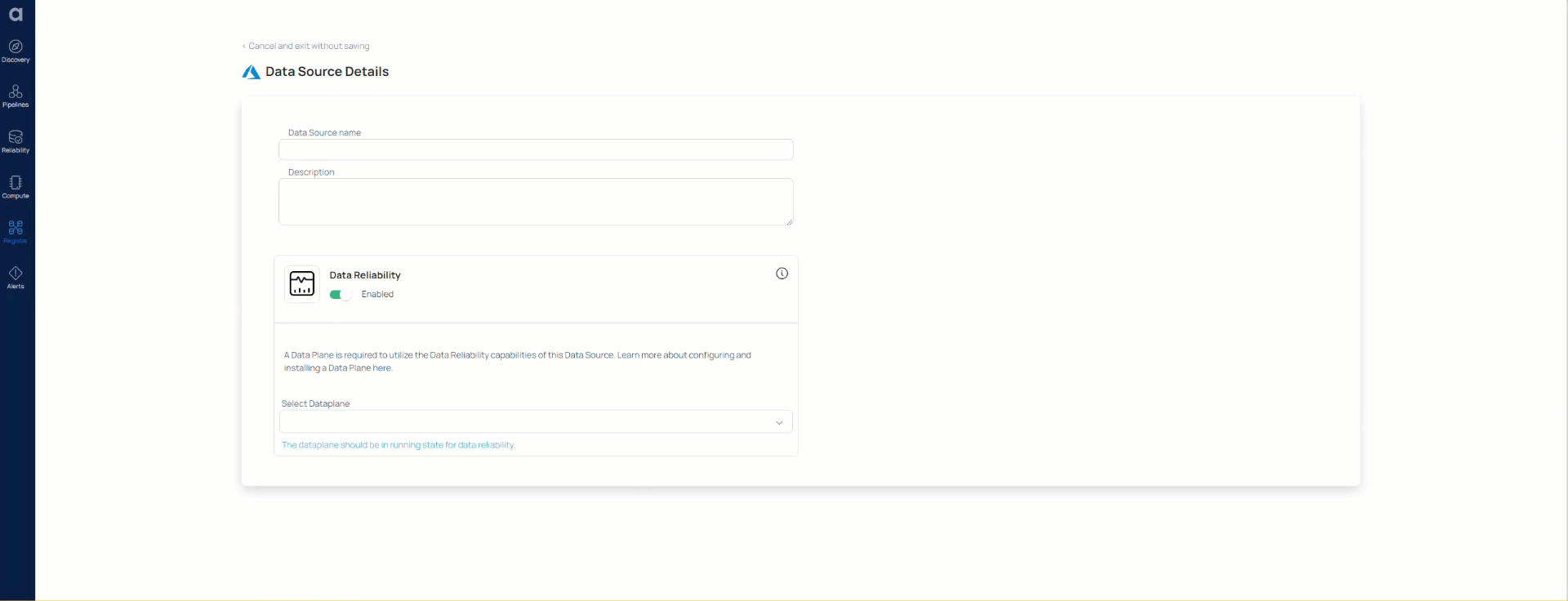
- Enter a name for the data source in the Data Source name field.
- (Optional) Enter a description for the Data Source in the Description field.
- Enable the Data Reliability capability by toggling the switch.
- Select a Data Plane from the Select Data Plane drop-down menu. To create a new Data Plane, click Setup Dataplane.
- Click Next. The Azure MSSQL Connection Details page is displayed.

- Enter your account JDBC URL in the JDBC URL field.
- Enter your JDBC username in the JDBC Username filed.
- Enter the JDBC password in the JDBC Password field.
- Click Test Connection. If your credentials are valid, you receive a Connected message. If you get an error message, validate the credentials you entered.
- Click Next. The Observability Setup page is displayed.
- Choose the required options on the Observability setup page,
- Enable Crawler Execution Schedule: Turn on this toggle switch to select a time tag and time zone to schedule the execution of crawlers for Data Reliability.
- Click Submit.
Azure MSSQL is now added to ADOC as a Data Source.
Azure Managed Identities provide a secure and automated way to access Azure services, including Azure MSSQL. They eliminate the need to manage credentials manually, thus enhancing security and simplifying access control for Azure MSSQL databases in cloud environments.
Configuring Azure Managed Identities for Azure MSSQL Access
Configuring Azure Managed Identities in ADOC for Azure MSSQL involves the following steps:
1. Configure Managed Identity in Azure:
1.1. In the Azure portal, navigate to the Azure SQL Database.
1.2. Under 'IAM' (Identity and Access Management), add a new role assignment.
1.3. Assign roles like 'SQL DB Contributor' to the Managed Identity.
2. Integrate Managed Identity with ADOC:
2.1. In ADOC, when adding Azure MSSQL as a data source, opt for Managed Identity authentication.
2.2. Provide the Managed Identity details as required in the ADOC configuration setup.
Configuring Azure Managed Identities to Add Azure MSSQL as Data Source
To utilize Azure Managed Identities for Azure MSSQL in ADOC:
1. Data Source Registration:
1.1. Navigate to the Data Source section in ADOC.
1.2. Click on the Add Data Source button and select Azure MSSQL.
1.3. In the authentication section, select the option to use Azure Managed Identity.
2. Configuration Details:
- Enter the required Managed Identity information, such as Tenant ID and Azure Client ID.
- Check that the Managed Identity you have chosen has the relevant permissions on the Azure MSSQL database.
Permissions and Roles for Azure MSSQL Access
To ensure a seamless integration of Azure MSSQL with Azure Managed Identities:
- Assign roles to the Managed Identity such as SQL DB Contributor or SQL Server Contributor.
- These roles can be configured in the Azure portal's Access Control (IAM) settings for the SQL database.
Permissions for Data Cadence/Freshness Metrics Collection for SQL Server
To enable the collection of Data Cadence and Freshness metrics for SQL server assets, specific permissions must be granted to the database user in Azure MSSQL. These permissions are necessary to ensure that ADOC can effectively gather and evaluate Data Freshness policies.
Required Permissions
Replace <dbUser>and <dbscema> with the actual user and schema names in your SQL Server environment, then execute the following SQL command:
-- Grant permission to the user to view database state information.GRANT VIEW DATABASE STATE TO <dbUser>;-- Grant SELECT permissions on system views for metadata access.GRANT SELECT ON sys.tables TO <dbUser>; -- Access to user tablesGRANT SELECT ON sys.schemas TO <dbUser>; -- Access to schemasGRANT SELECT ON sys.indexes TO <dbUser>; -- Access to indexesGRANT SELECT ON sys.partitions TO <dbUser>; -- Access to partitionsGRANT SELECT ON sys.allocation_units TO <dbUser>; -- Access to allocation units-- Create a role for database read access.CREATE ROLE dbDataReader;-- Add user to the role for consolidated permissions management.ALTER ROLE dbDataReader ADD MEMBER <dbUser>;-- Grant read access to all tables in the 'dbSchema' schema to the role.GRANT SELECT ON SCHEMA::<dbSchema> TO dbDataReader;-- Grant the role permission to view database state information.GRANT VIEW DATABASE STATE TO dbDataReader;Verification Steps
After assigning these permissions, sign in as <dbUser> and perform a sample data query to verify that cadence metrics collection is functioning as expected.
ADOC does not presently support Azure SQL flavors.
Troubleshooting and FAQs for Azure Managed Identities
1. Managed Identity Not Recognized in Azure MSSQL
Issue: The managed identity is not authenticated by Azure MSSQL.
Solution: Verify that the managed identity has been assigned the correct roles (like 'SQL DB Contributor') in Azure's IAM settings. Also, ensure that the identity is correctly configured in ADOC's data source settings.
2. Permission Denied Error
Issue: Receiving a permission denial error when accessing Azure MSSQL.
Solution: Check if the managed identity has adequate permissions on the Azure MSSQL database. If necessary, adjust the role assignments in the Azure portal.
3. Connectivity Issues in ADOC
Issue: Unable to establish a connection between ADOC and Azure MSSQL using Managed Identity.
Solution: Confirm that the network settings and firewall rules in Azure allow connections from ADOC. Ensure that the ADOC environment has internet access to communicate with Azure services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What roles are necessary for a managed identity to access Azure MSSQL in ADOC?
Typically, roles like 'SQL DB Contributor' or 'SQL Server Contributor' are required. The exact role depends on the level of access needed for Azure MSSQL.
Q2: How do I configure Azure Managed Identity in ADOC for Azure MSSQL?
In ADOC, add Azure MSSQL as a data source and select the option to use Azure Managed Identity for authentication. Provide the relevant managed identity details, such as the Azure client ID and tenant ID.
Q3: Can I use the same managed identity for multiple Azure services in ADOC?
Yes, a user-assigned managed identity can be shared across multiple Azure services and resources, including Azure MSSQL.
Q4: What should I do if my managed identity is not recognized by Azure MSSQL?
Ensure that the managed identity is correctly assigned to the Azure MSSQL database in the Azure portal and that all necessary permissions are granted. Also, check if the managed identity details in ADOC are accurate.
Q5: Where can I find detailed logs for troubleshooting Azure Managed Identity issues in ADOC?
Check the ADOC logs for any errors or messages related to Azure MSSQL connectivity. Additionally, the Azure portal provides auditing and logging features for tracking managed identity activities.