Installing Dataplane - Managed ADOC
Dataplane V1 has been deprecated. Its visibility is now managed by a feature flag, which, when deactivated, prevents users from creating new Dataplane V1 instances. The UI has transitioned to the Nextgen Dataplane for a more streamlined experience. While existing Dataplane V1 instances can still be deleted, upgrading is no longer supported.
What is Data Plane
The Data Plane facilitates smooth data transfer between various software systems. In Acceldata Data Observability Cloud (ADOC), the Data Plane is a crucial component to leverage Data Reliability for a data source. Once you install a Data Plane in ADOC, you can reuse it for creating multiple data sources thereafter. You only need to install the Data Plane once.
Key Highlights:
- A Data Plane integrates with your chosen cloud environment .
- It enables data processing, crawler operations, and observability features within ADOC.
Compatibility Metrics
The ADOC Control Plane version 3.2.0 maintains backward compatibility with Data Plane versions 2.12.X, 3.0.X, and 3.1.X, ensuring seamless integration and upgrade flexibility
Supported Cloud Providers
| Cloud Provider Supported | AWS | Azure | GCS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spark Types (version - 32) | YuniKorn | YuniKorn | YuniKorn |
| Spark Types (version - 32) | Databricks | Databricks | Dataproc |
Spark Version
| Data Plane Environments | YuniKorn | Dataproc |
|---|---|---|
_Spark version_ | 32 | |
| AWS | NA | |
| GCS | ||
| Azure | NA |
For optimal performance and stability of the Data Plane, ADOC requires Kubernetes version 1.25 as the minimum and supports up to version 1.27. Ensure your environment meets these version requirements before proceeding with Data Plane installation.
Data Plane and Data Sources
Data Planes process and evaluate data, while Data Sources represent the various external systems or storage services from which data is obtained. By installing and configuring the Data Plane, you enable analysis, crawling, and observability features on these Data Sources within ADOC.
Prerequisites for Data Plane Installation
Before installing the Data Plane, ensure you have the following roles, permissions, and setup ready. This will streamline the installation process and help prevent configuration issues later.
Quick Reference Table
| Cloud Provider | Roles/Permissions Required | Setup Steps | Additional Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| AWS | Permissions for managing EKS clusters (via UI or Examples of actions:
|
|
|
Minimum IAM Privileges to Create a Cluster on AWS
These policies ensure you have the necessary permissions to create and manage EKS clusters, including actions like cluster creation, updates, IAM role management, and auto-scaling.
Data Plane List View Page
The Data Plane list view displays all the Data Planes created in ADOC. All the values are present in a table. The table has the following columns.

| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the Data Plane |
| Status | The current status of the Data Plane. This can be Installing or Running. |
| Data Source Associated | Displays the number of data sources linked to the data plane. |
| Cloud Provider | The cloud service provider for the Data Plane. This can be AWS, GCP, or Azure. |
| Region | The region in which the Data Plane is deployed. |
| Description | The Data Plane description provided by you. |
| URL | The URL of the Data Plane installation. |
| Version | the current version of the Data Plane. |
| Updated At | The date and time when the Data Plane was last updated. |
| Action | The actions you can perform on the Data Plane. This can be Delete, View Logs or Upgrade Pipeline. |
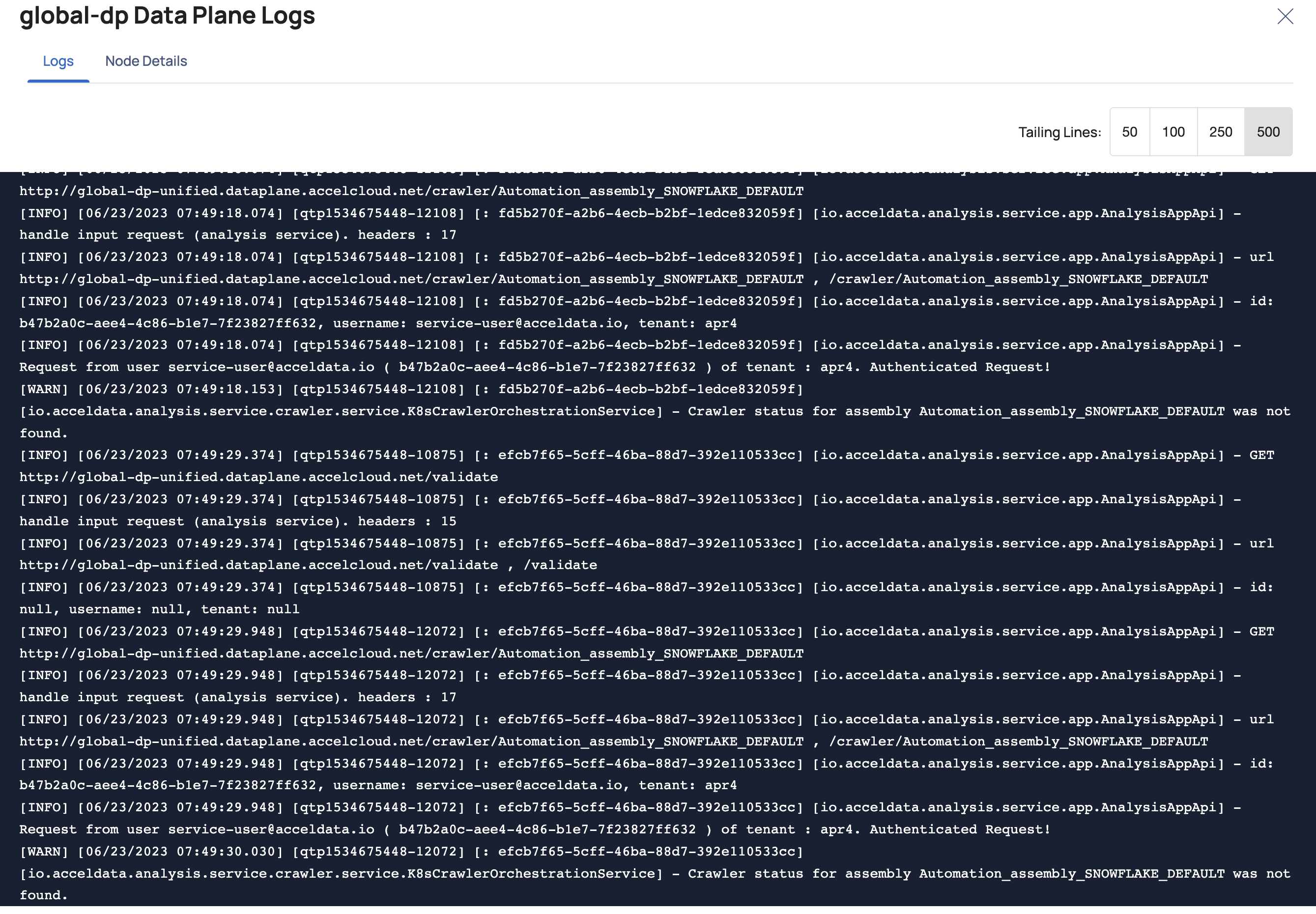
Viewing Data Plane Logs
ADOC allows you to view the following logs by clicking the vertical ellipsis icon and clicking View Logs:
Crawler: Once you start crawlers for a Snowflake or Databricks data source, you can see the current logs that are being generated by the analysis service that is operating on the data plane side. You will also be able to view the running logs on data sources that are generated by the crawlers by clicking on the vertical ellipsis icon and selecting View Crawler Logs.
Spark job logs can be monitored only if the data plane is deployed with Spark on K8s. Jobs running on Databricks, Dataproc or on Hadoop can not be monitored.
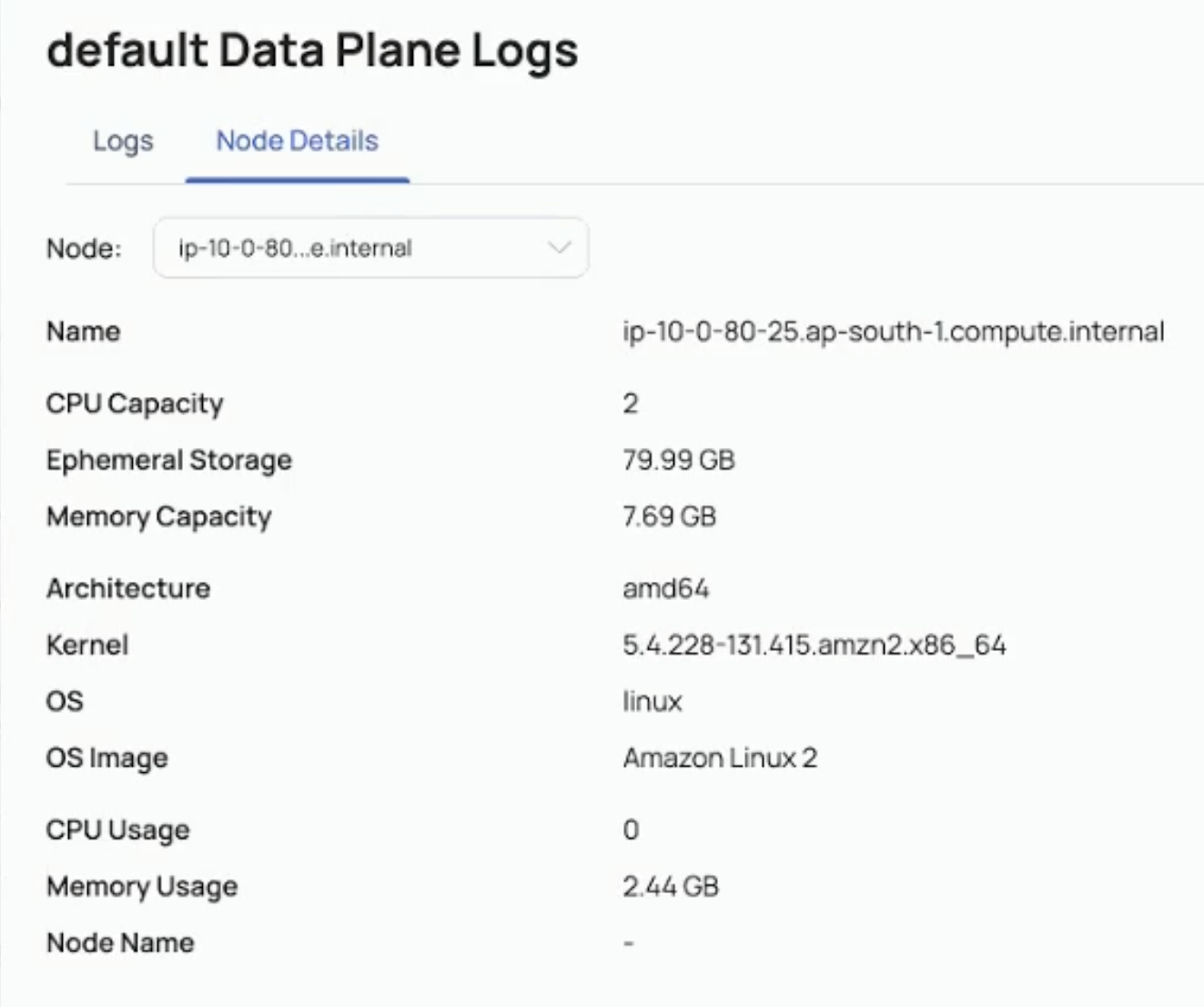
Node Detail: The selected node's CPU capacity, ephemeral storage, memory capacity, architecture, kernel, OS, OS image, and CPU usage are collected by Kubernetes for analysis of our pipeline during runtime.
To access the node detail logs, ensure that the Kubernetes monitoring service is operational and that you have the necessary user access to retrieve the node details from the service.
Deleting Data Plane
ADOC allows you to delete data planes. When you delete a data plane, the data plane data is only deleted from the ADOC environment. However, the data plane entries are still available on AWS/Azure. You must manually go to AWS/Azure and delete the data plane.
To delete data plane:
- Click Register from the left pane.
- Click Data Plane.
- Click the delete icon for the data plane you want to delete.
- Confirm the delete operation on the pop-up window. This deletes the data plane record from ADOC.
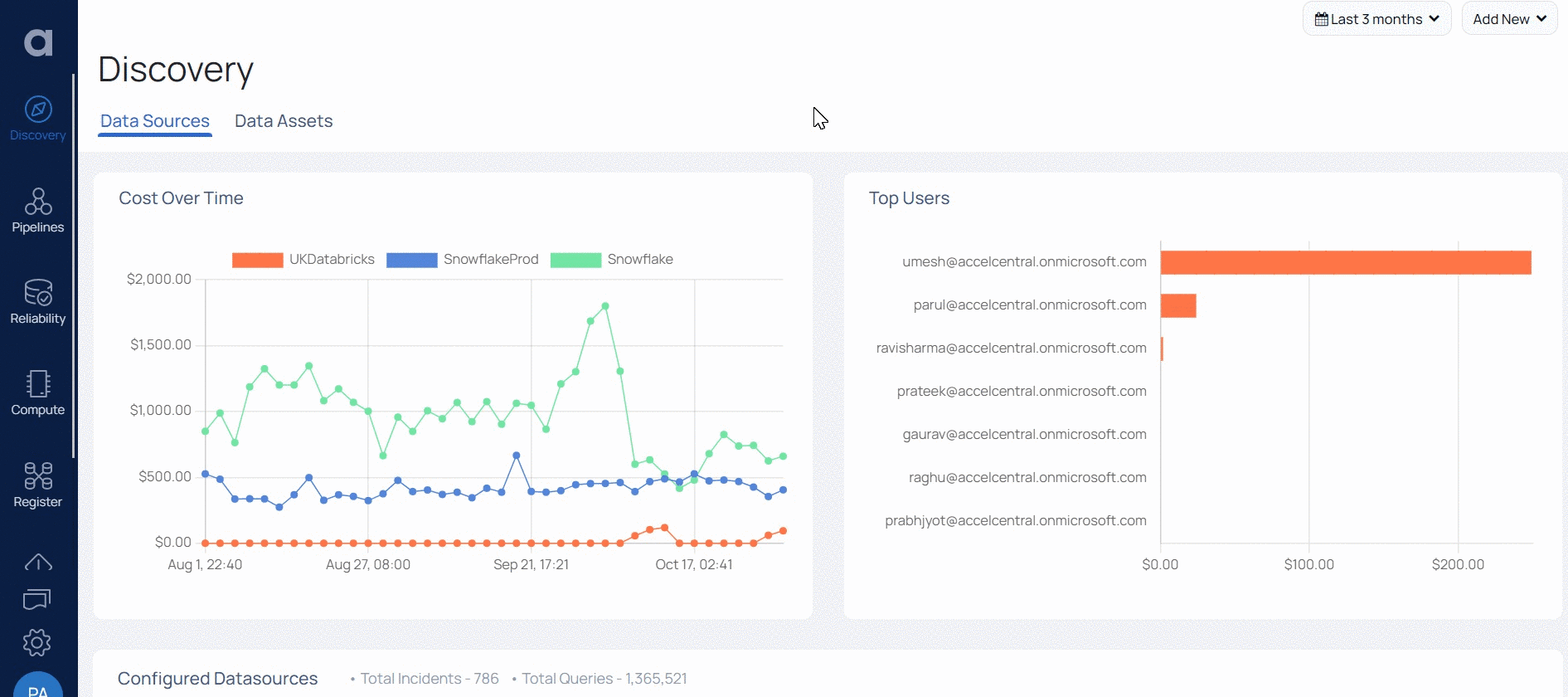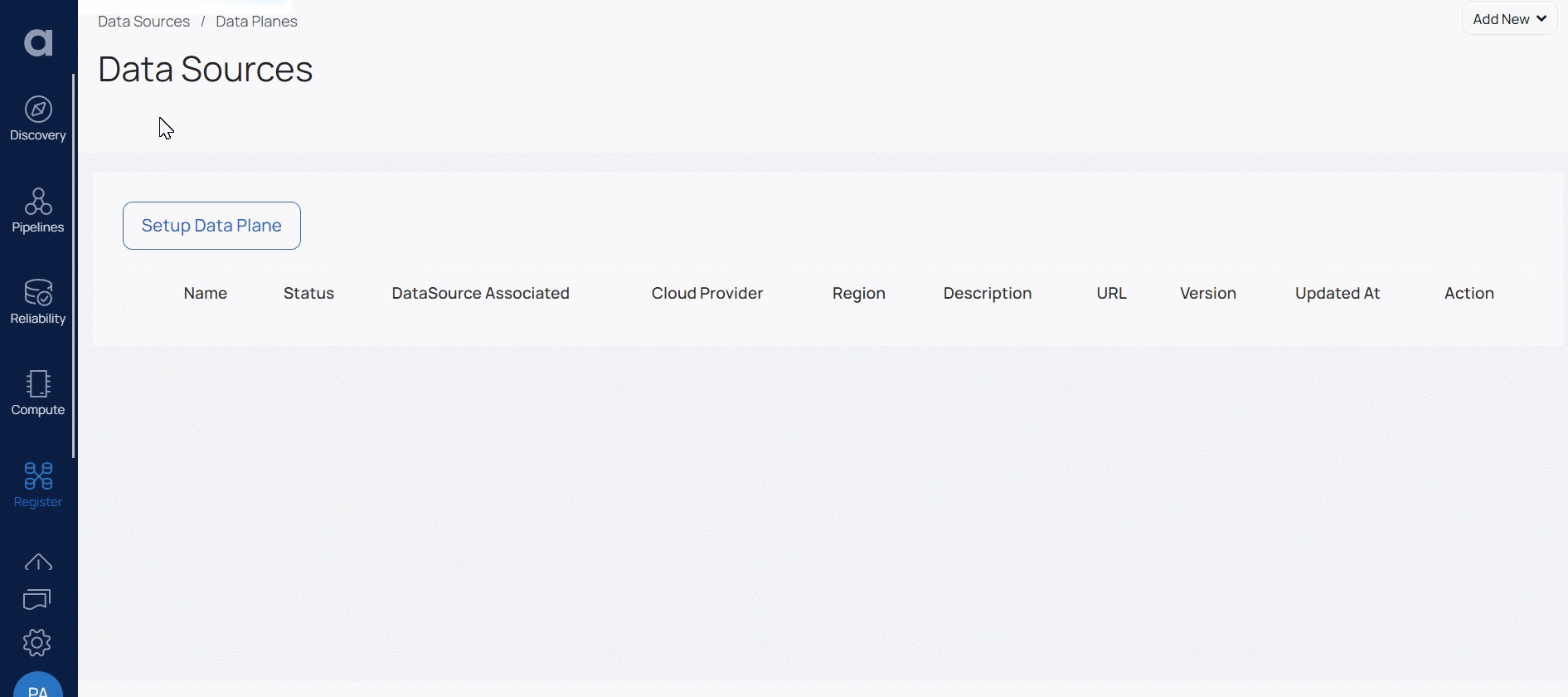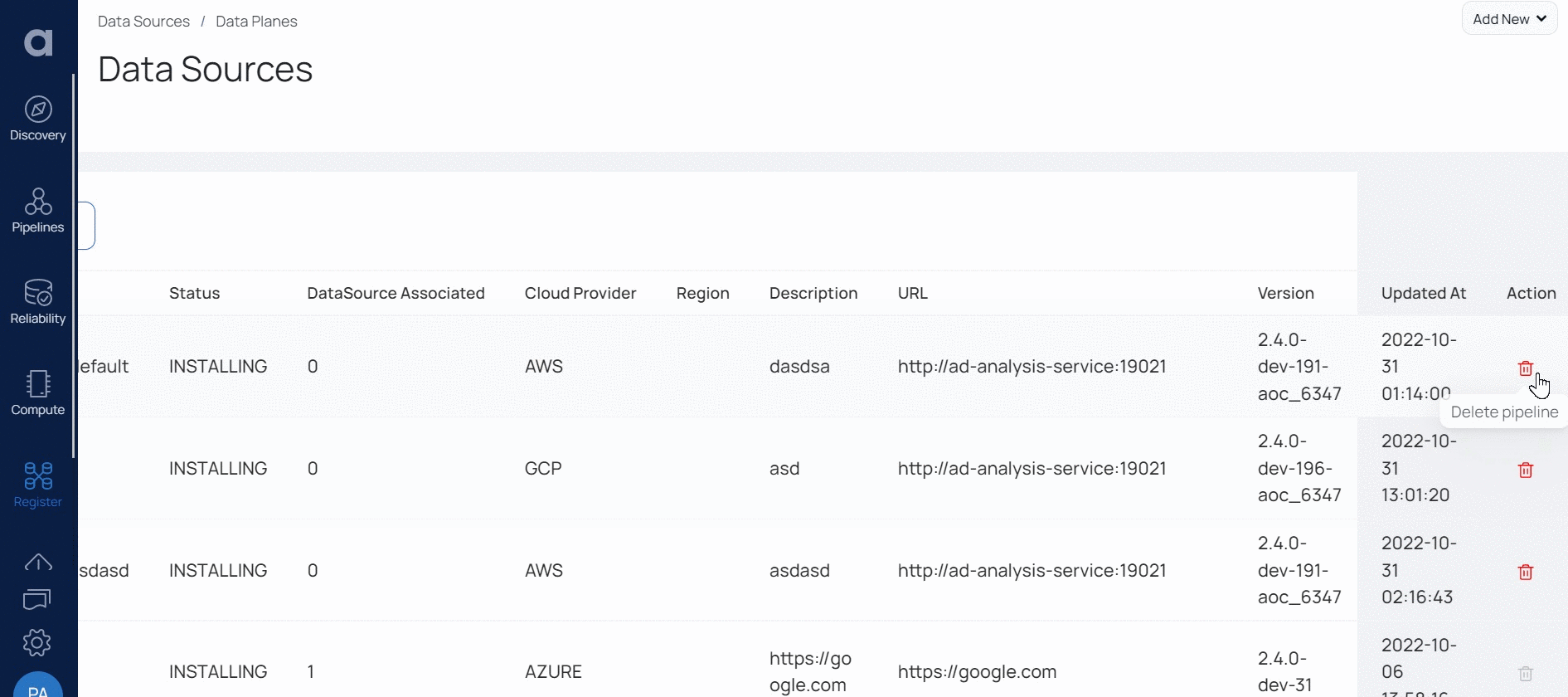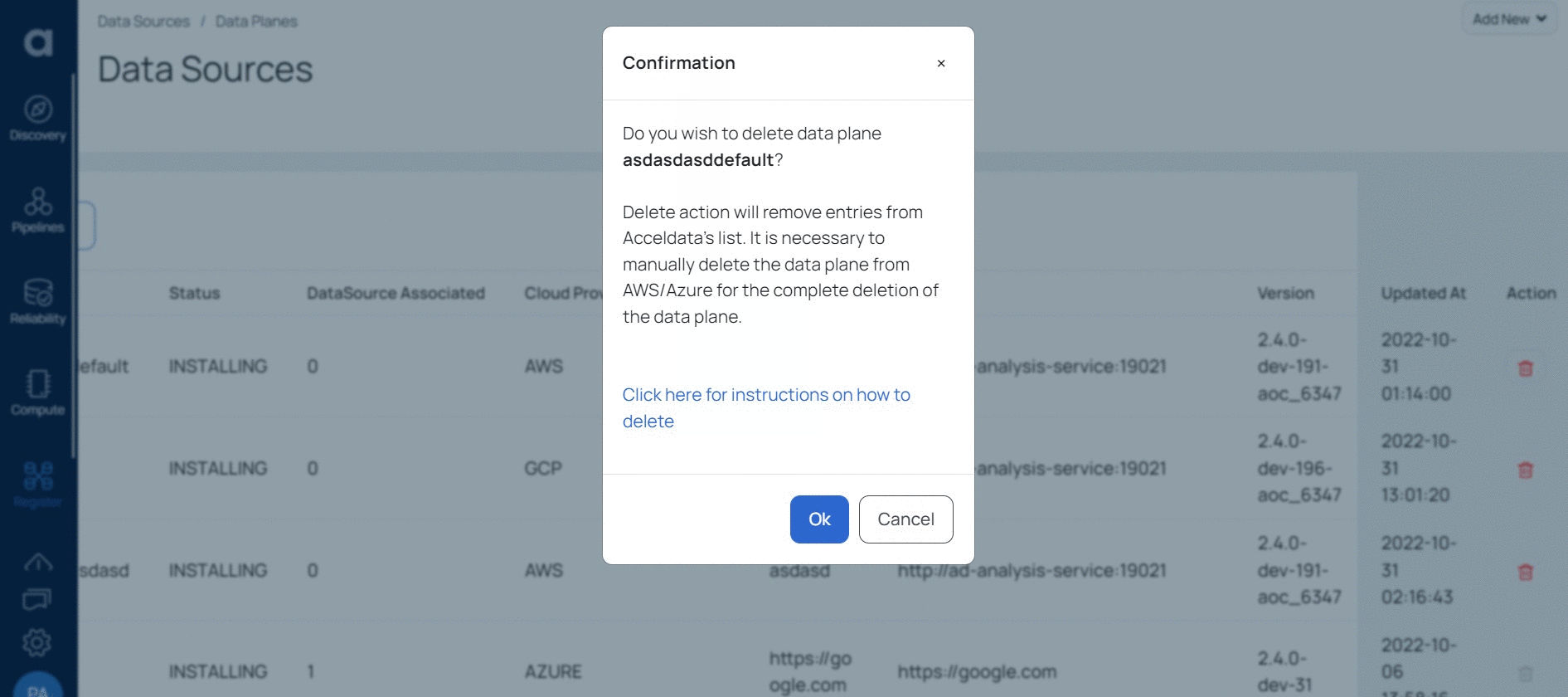
You must now navigate to Azure/AWS and delete the data plane from there to completely remove the data plane.
Delete Data Plane on AWS
For an AWS data plane, you must delete the following entries.
- Delete Load Balancer
- Delete Stack
- Delete the YAML file from S3 bucket and any other files created in the S3 bucket by data plane.
Delete Data Plane on Azure
For an Azure data plane, you must delete the following entries.
- Delete the data plane resources from resource group.
- Delete the YAML file from Azure storage account container and any other files created in the container by data plane.
Network Connectivity for Data Plane
User data sources must be configured to provide seamless integration of ADOC with the data plane and control planes.
Control Plane Connectivity
Presently, the Control Planes can only connect to the Data Sources via the Internet. As a result, to establish connectivity you must whitelist the IP address.
Whitelisting the IP Address
Data Sources (Snowflake & Databricks only) must allow connections for the following Control plane IP addresses to enable compute service.
| IP ADDRESS |
|---|
| 3.17.21.244 |
| 3.18.178.29 |
| 18.216.209.216 |
Ensure to whitelist the IP addresses before the Control plane initiates connections.
Whitelisting in Snowflake Configuration
Snowflake accounts can only be accessed from known IP addresses, depending on the networking policy configuration in the Snowflake service.
To configure the control plane address to the user's Snowflake account, see the Snowflake Documentation.
| IP ADDRESS |
|---|
| 3.17.21.244 |
| 3.18.178.29 |
| 18.216.209.216 |
Data Plane Environment
The Data plane is installed in the user’s environment. Hence, it can be installed in the existing or the new Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Ensure that VPC’s that produce Data plane resources must connect to the data sources.
VPC Connectivity Options
- VPC Peering
- AWS Private Link or VPC Endpoint
VPC Peering
If the data sources are located in a VPC other than the Data Plane VPC, VPC peering must be configured as described in the AWS Documentation.
VPC peering requires IP address ranges that are not overlapping.
When constructing a new VPC, ensure that the IP address ranges do not overlap.
AWS Private Link or VPC Endpoint
You cannot connect to some of the data sources with VPC Endpoints. In such circumstances, either a New VPC Endpoint can be built in Data Plane's VPC or VPC peering must be created between Data Plane's VPC and the existing VPC where VPC Endpoint is already configured.
Dataplane Observability
From ADOC V3.0 introduces enhanced visibility and observability within the data plane. This includes integration with the Spark history server, offering a comprehensive view of data operations and resource utilization.
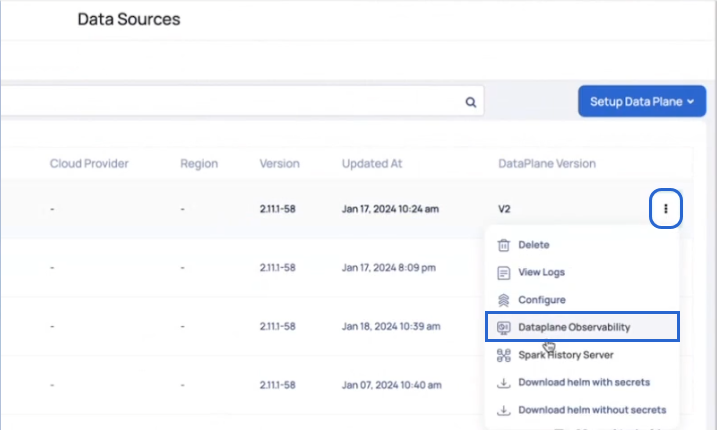
When you click the Data Observability option, a new window opens that presents a dashboard with graphs, real-time data, and status of several components, including Spark operators and analysis clients.
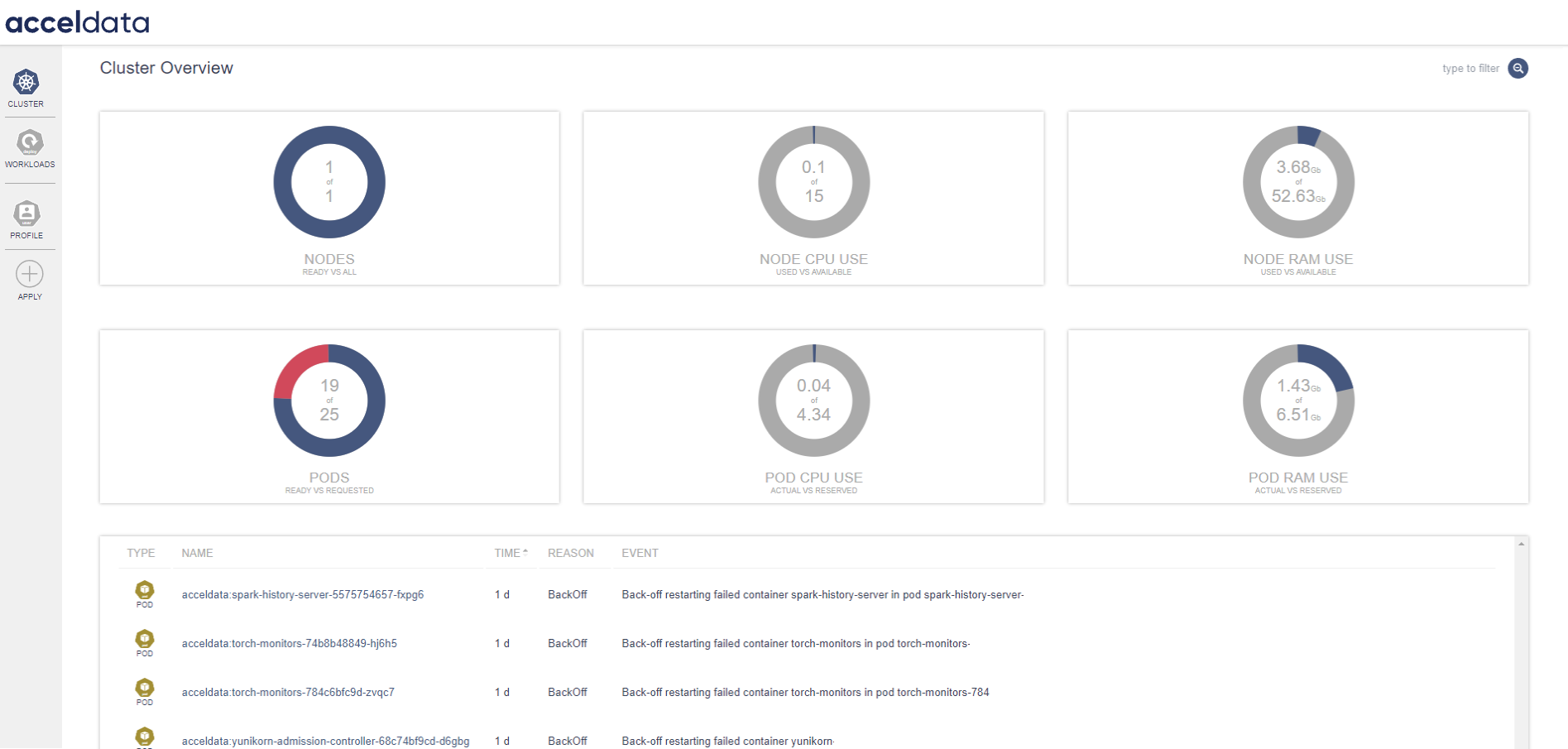
For more detailed information see Dataplane Observability Dashboard.