NameNodes have scalability limits because of the metadata overhead comprised of inodes (files and directories) and file blocks, the number of Datanode heartbeats, and the number of HDFS RPC client requests. The common solution is to split the filesystem into smaller subclusters, HDFS Federation, and provide a federated view ViewFs. The problem is how to maintain the split of the subclusters (e.g., namespace partition), which forces users to connect to multiple subclusters and manage the allocation of folders or files to them.
Key Advantages of Router-based Federation:
Scalability:
- Router-based federation can handle more namespaces and storage than ViewFs.
- It efficiently distributes client requests across multiple namespaces, improving load management.
Fault Isolation:
- In case of a namespace failure, the rest of the system remains unaffected.
- This isolation ensures continuous availability even in the event of individual failures, unlike ViewFs, where a failure in one mount point could potentially impact the entire system.
Distributed Namespace:
- Router-based federation allows the namespace to be distributed across multiple NameNodes.
- This distribution helps in balancing loads, enhancing performance, and improving reliability.
Security:
- Provides a unified Access Control List (ACL) across namespaces.
- Offers enhanced security features compared to ViewFs, ensuring robust data protection mechanisms.
Flexibility:
- Namespaces can be dynamically added or removed without affecting the system’s overall performance.
- This flexibility allows administrators to scale and manage the system seamlessly without downtime.
Routing Policies:
- Supports multiple routing policies, such as local, random, and hash-based, enabling better load distribution across NameNodes.
- Customizable routing policies ensure that resources are optimally utilized.
High Availability (HA):
- Supports High Availability configurations, enhancing system reliability and accessibility.
- ViewFs lacks native support for HA, making router-based federation more robust for critical deployments.
Example flow
The simplest configuration deploys a Router on a machine not shared with NameNode (configuration conflict when shared with NN host HDFS-17356 ). The Router monitors the local NameNode and heartbeats the state to the State Store. When a regular DFS client contacts any of the Routers to access a file in the federated filesystem, the Router checks the Mount Table in the State Store (i.e., the local cache) to find out which subcluster contains the file. Then, it checks the Membership table in the State Store (i.e., the local cache) for the NameNode responsible for the subcluster. After it has identified the correct NameNode, the Router proxies the request. The client accesses DataNodes directly.
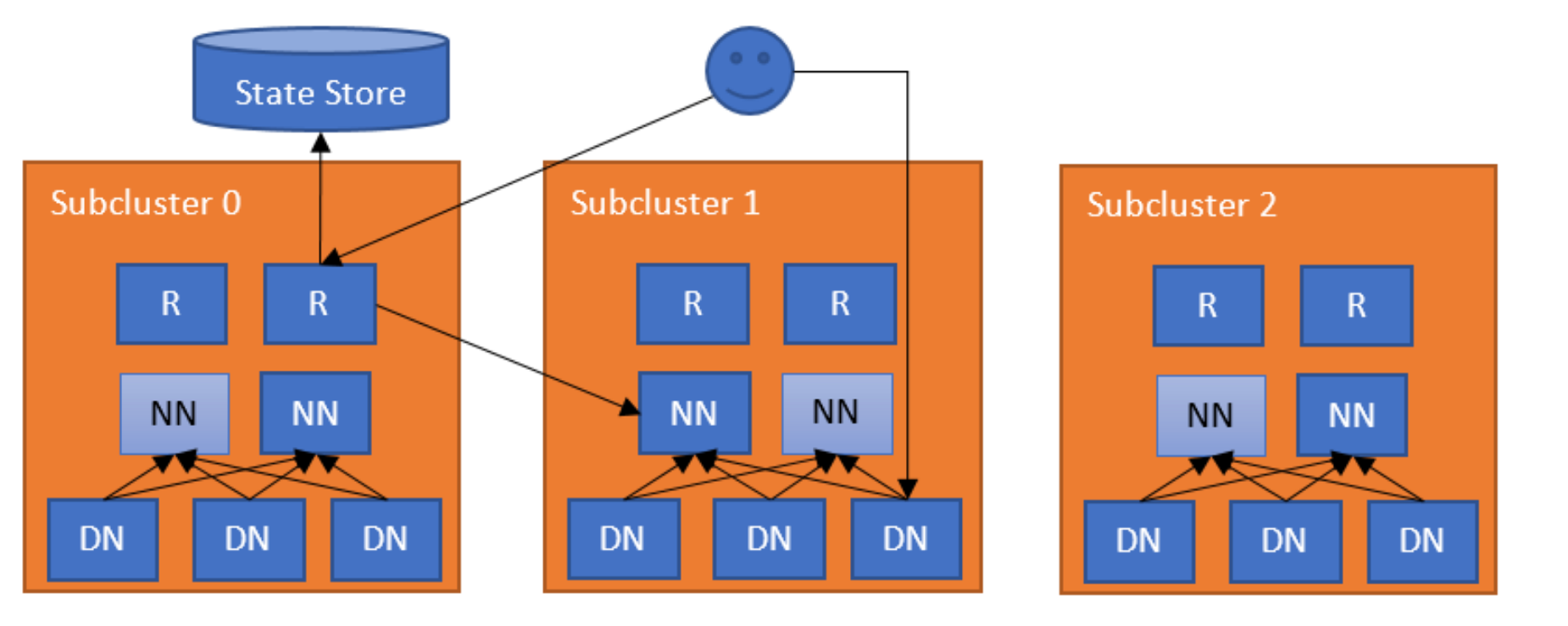
Deployment
By default, the Router is ready to take requests and monitor the NameNode in the local machine. It needs to know the State Store endpoint by setting dfs.federation.router.store.driver.class. The rest of the options are documented in hdfs-rbf-default.xml.
Managing Multiple Routers in HDFS Router-Based Federation
To manage multiple Routers, the user needs to install the Router on hosts that do not have NameNodes. Follow these detailed steps:
Steps:
Cluster Setup:
- Ensure that you have a minimum 6-node Ambari cluster.
- Install the HDFS service and enable High Availability (HA).
- Add at least one additional namespace (there must be at least two namespaces).
Router Installation:
- Add 2 Routers to the cluster on nodes that do not have NameNodes.
Automatic Configuration in
core-site.xml: The following configurations will be automatically added to thecore-site.xmlof the selected hosts during Router installation (this is managed byparams_linux.py):- fs.defaultFS:
ns-fed - hadoop.zk.address:
zk_quorum
- fs.defaultFS:
Automatic Configuration in
hdfs-site.xml: The following configurations will be automatically added to Customhdfs-site.xml:
<configuration> <property> <name>dfs.nameservices</name> <value>ns0,ns1,ns2,ns3,ns-fed</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.ha.namenodes.ns-fed</name> <value>r1,r2</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.namenode.rpc-address.ns-fed.r1</name> <value>router1:rpc-port</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.namenode.rpc-address.ns-fed.r2</name> <value>router2:rpc-port</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.client.failover.proxy.provider.ns-fed</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.ConfiguredFailoverProxyProvider</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.client.failover.random.order</name> <value>true</value> </property></configuration>Key Consideration: This setup ensures that the NameNode is not restarted, preventing any configuration conflicts. Only the configuration files of the Router hosts will be affected.
Steps to Configure Router Federation:
- Enable NN HA.
- Adding additional nodes to the cluster provides an option to add routers on those hosts.
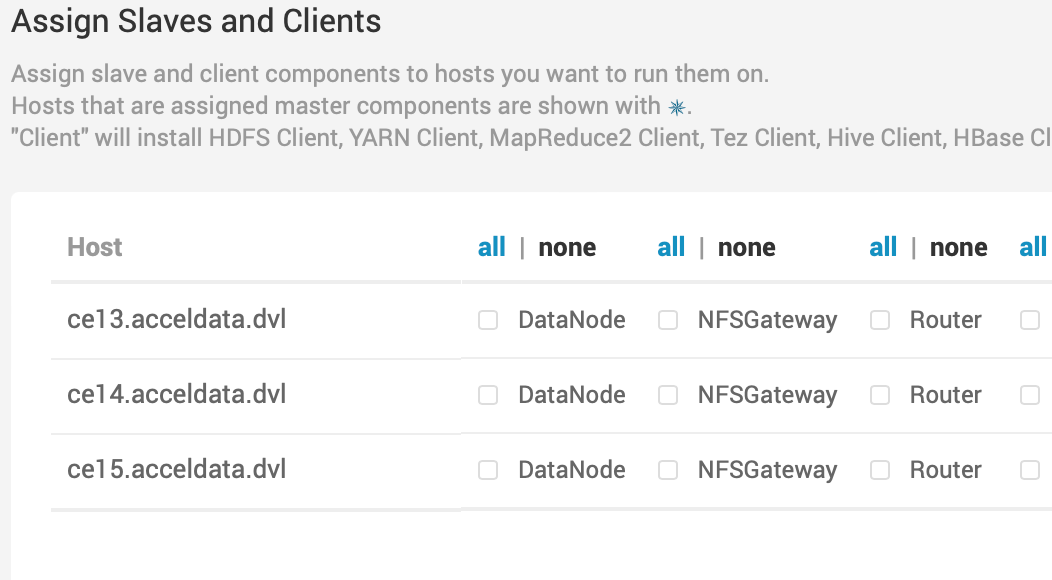
- Add at least one additional namespace (must have at least two namespaces).
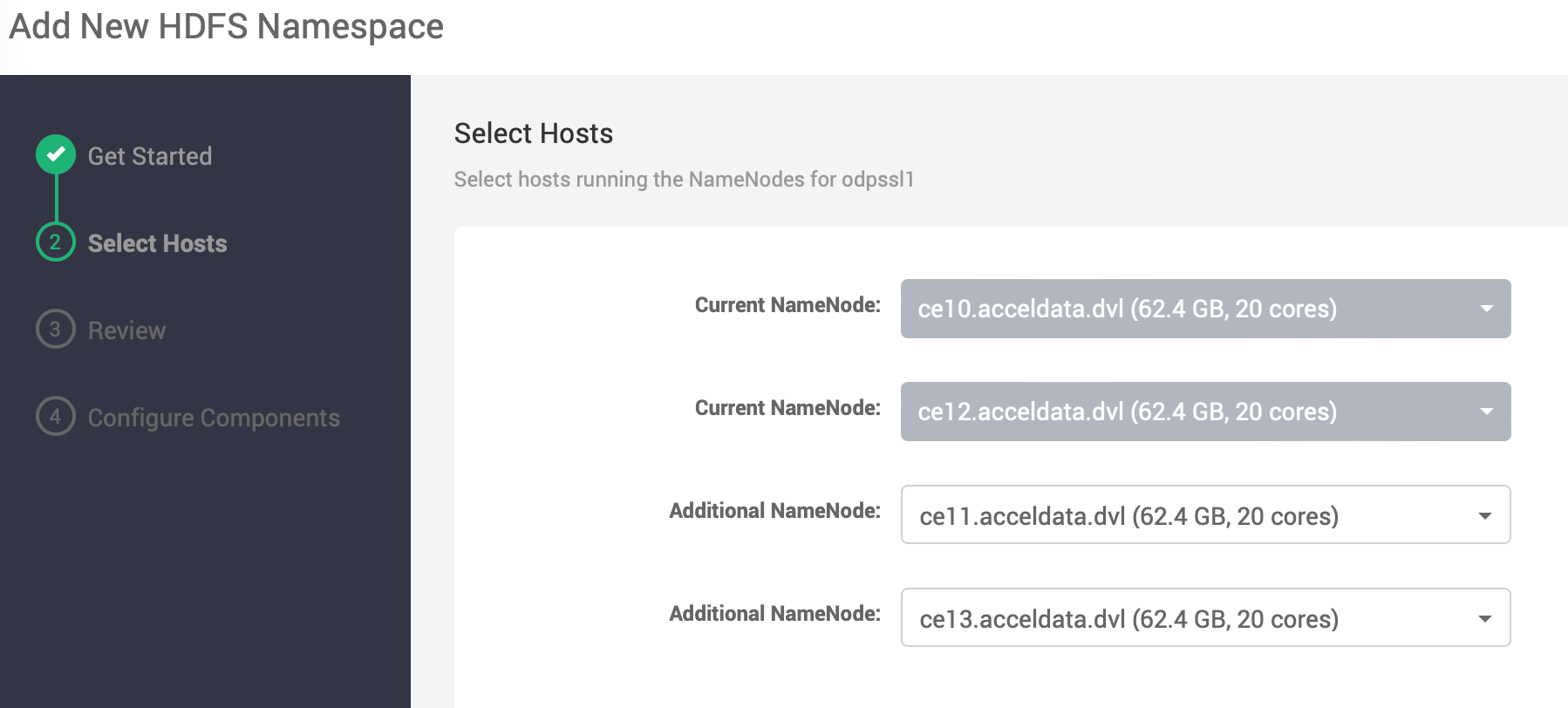
- Select additional NNs for new namespace.
- Provide a new path for storing the edits under the new journal node edits directory
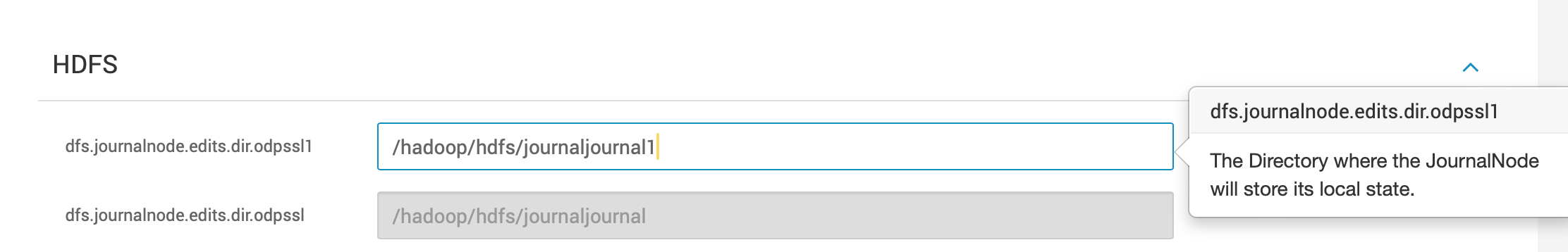
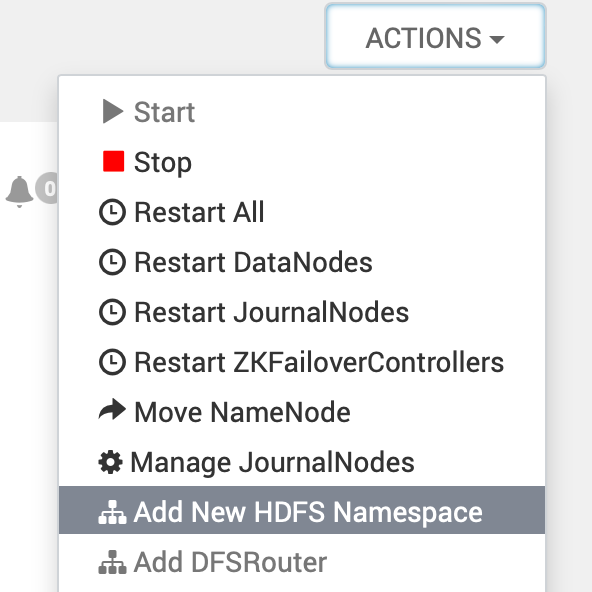
- A new HDFS Namespace is being deployed.
- Run the below to update
journalnode.pyon all the journal nodes; otherwise, the journal node start fails.
sudo sed -i 's/params\.jn_edits_dirs/list(params.jn_edits_dirs)/g' /var/lib/ambari-agent/cache/stacks/ODP/3.0/services/HDFS/package/scripts/journalnode.py- DataNodes are not started after getting stopped as part of all services thus, NN start fails.
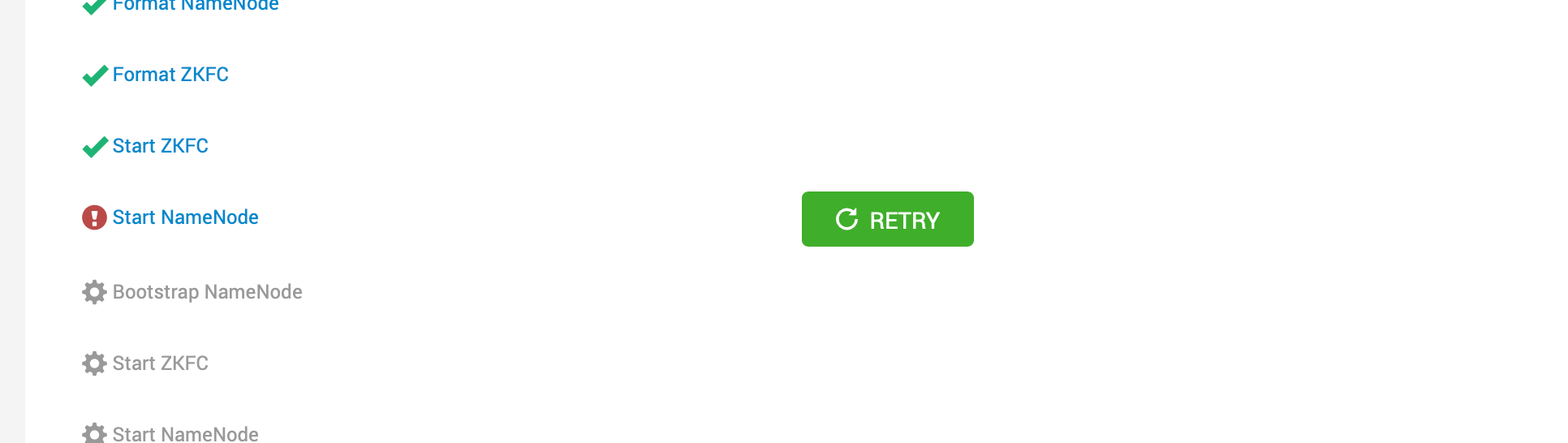
- Stop the the Ambari operation for NN start and start back the DNs from the other Ambari terminal.
- Bootstrap Standby fails if “
/hadoop/hdfs/namenode/“ contains any files or folder.
Perform the below step on the NameNode which needs bootstrap and continue.
rm -rf /hadoop/hdfs/namenode/*Continue once all the steps are completed.
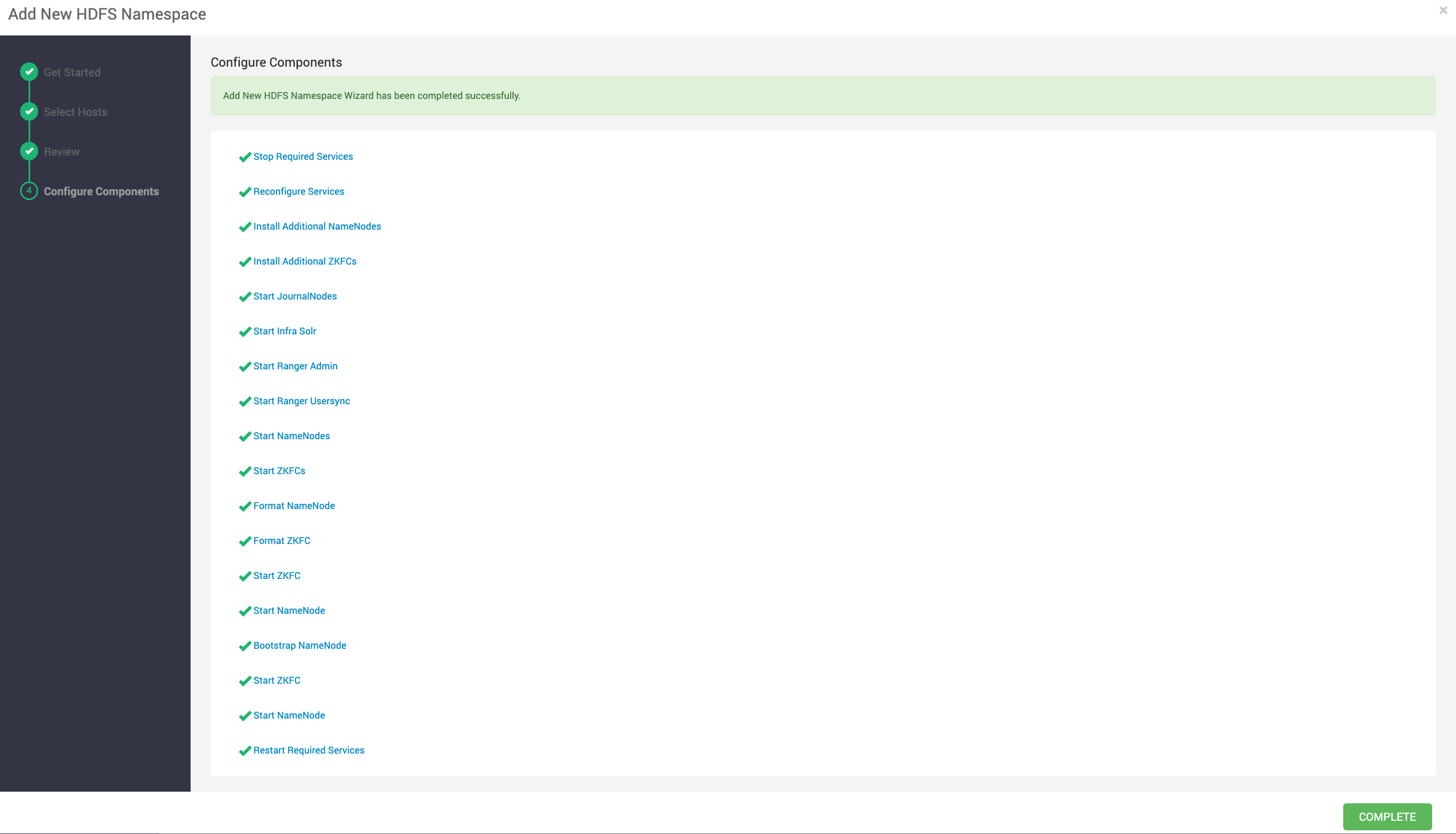
- After all the service restart, confirm on the HDFS summary page that we have two HDFS namespace.
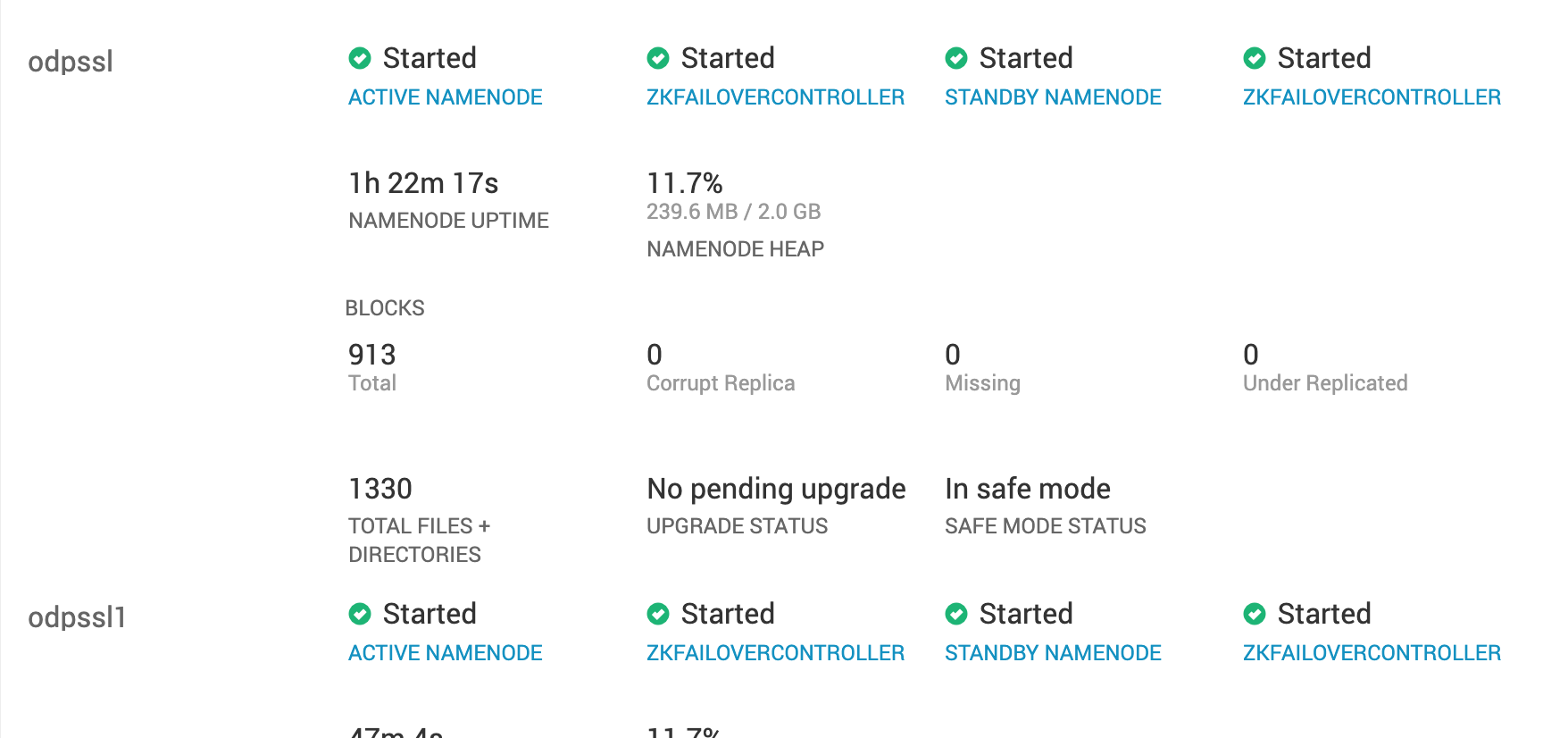
- Add the two Routers to the cluster on the nodes, which do not have NameNodes from action dropdown.
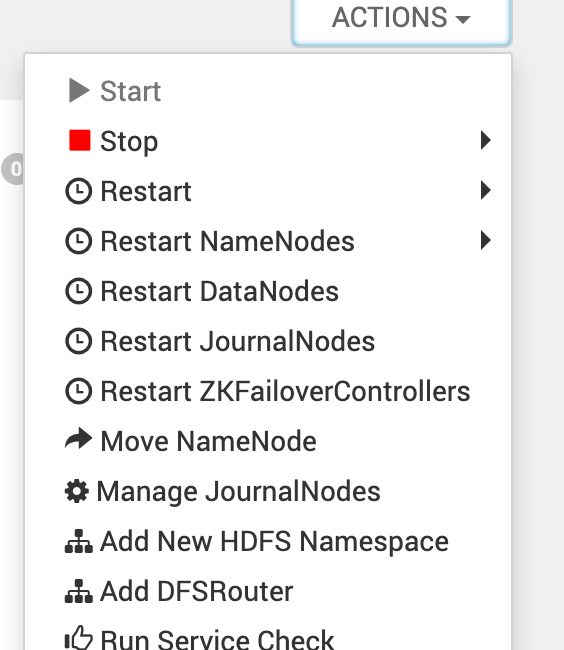
- Select the Router Hosts.
- Once the Installation is completed, restart the Router Services from the Host components list. Currently the HDFS summary Page does allow an option to restart HDFS routers.
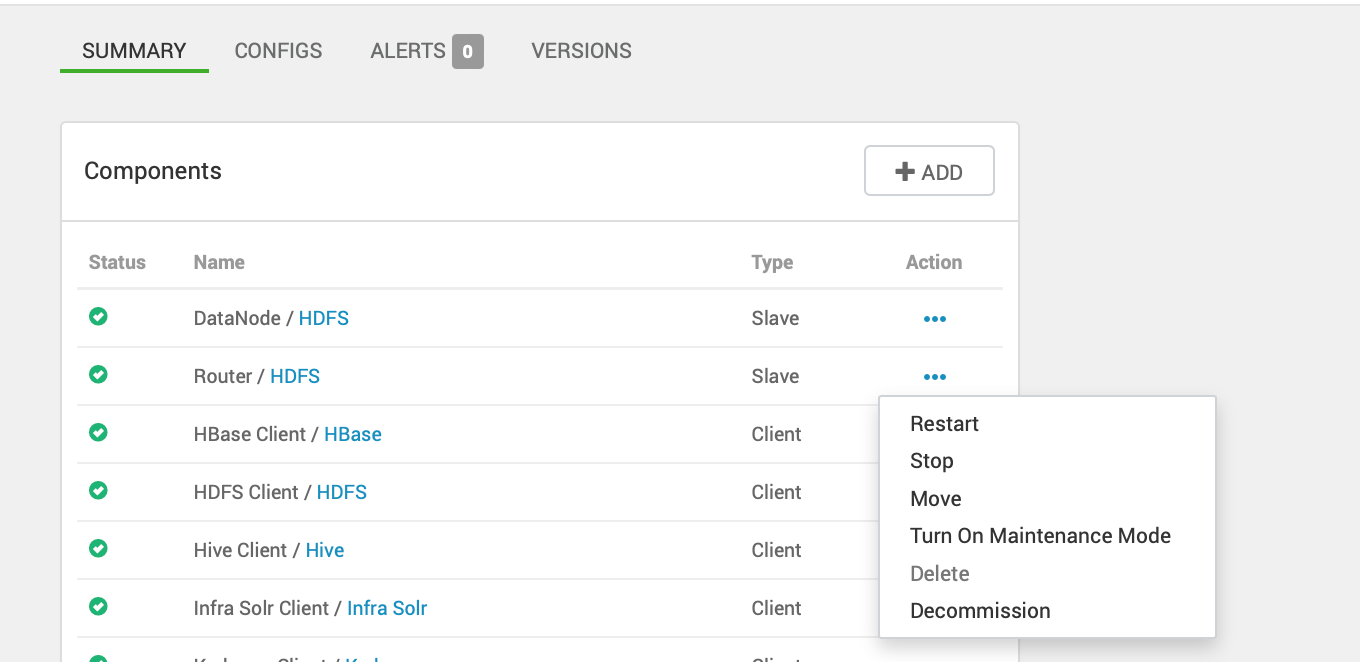
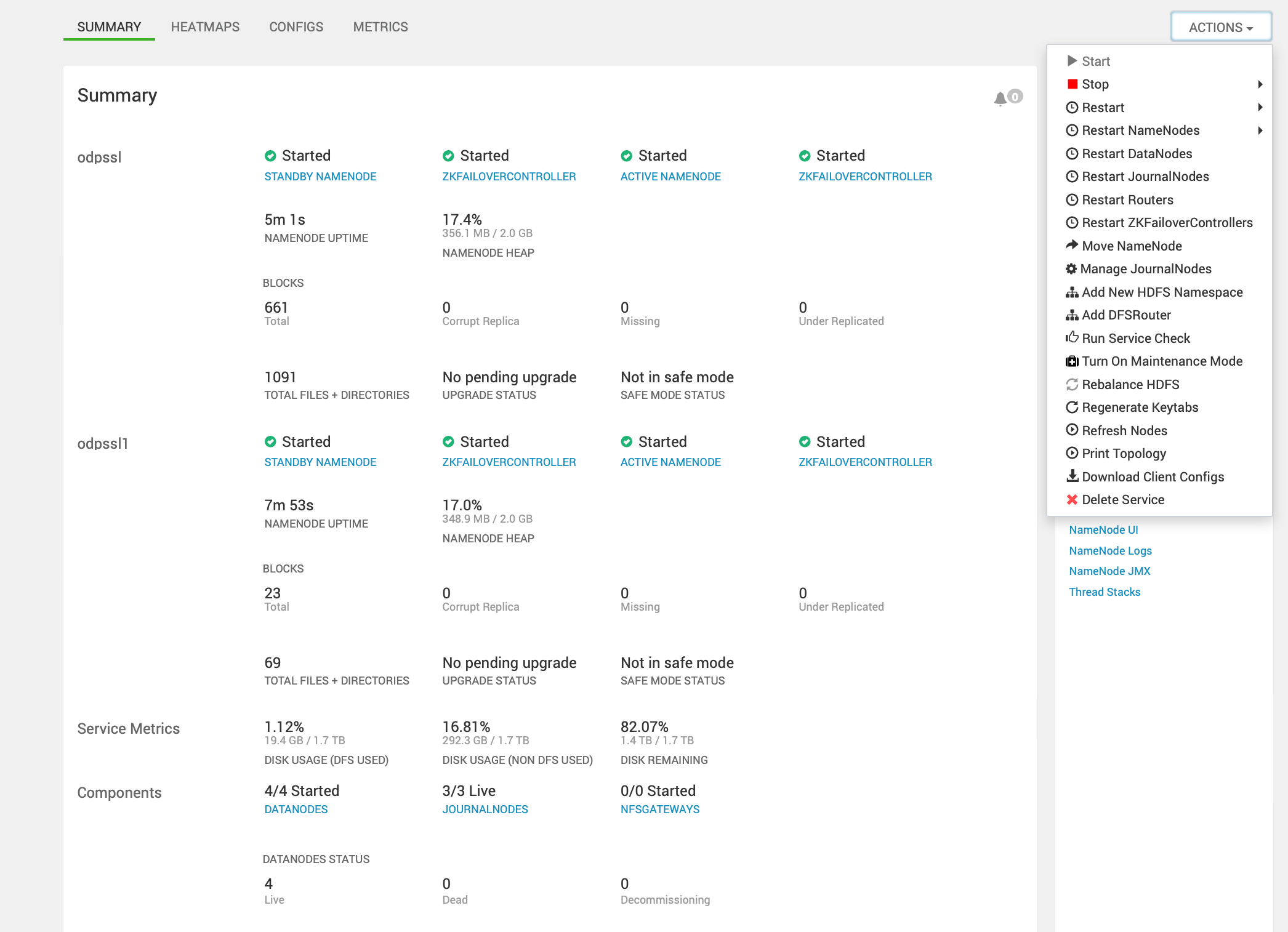
- Set and tune the following properties with respect to HDFS router federation under, Advanced hdfs-rbf-site.
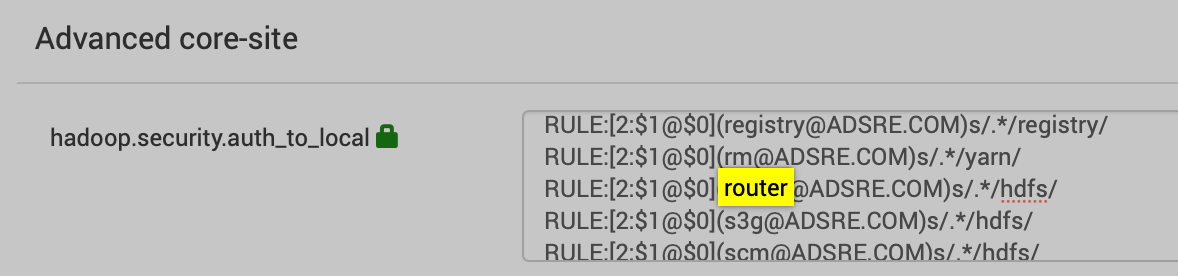
dfs.federation.router.admin-address=0.0.0.0:8111dfs.federation.router.admin-bind-host=0.0.0.0dfs.federation.router.admin.enable=truedfs.federation.router.admin.handler.count=1dfs.federation.router.cache.ttl=60000dfs.federation.router.connection.clean.ms=10000dfs.federation.router.connection.pool-size=1dfs.federation.router.connection.pool.clean.ms=60000dfs.federation.router.handler.count=10dfs.federation.router.heartbeat.interval=5000dfs.federation.router.http-address=0.0.0.0:50071dfs.federation.router.http-bind-host=0.0.0.0dfs.federation.router.http.enable=truedfs.federation.router.https-address=0.0.0.0:50072dfs.federation.router.https-bind-host=0.0.0.0dfs.federation.router.monitor.localnamenode.enable=truedfs.federation.router.mount-table.cache.update=falsedfs.federation.router.mount-table.cache.update.client.max.time=5mdfs.federation.router.mount-table.cache.update.timeout=1mdfs.federation.router.namenode.heartbeat.enable=true=dfs.federation.router.reader.queue.size=100dfs.federation.router.rpc-address=0.0.0.0:8888dfs.federation.router.rpc-bind-host=0.0.0.0dfs.federation.router.rpc.enable=truedfs.federation.router.secret.manager.class=org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.federation.router.security.token.ZKDelegationTokenSecretManagerImpldfs.federation.router.store.connection.test=60000dfs.federation.router.store.driver.class=org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.federation.store.driver.impl.StateStoreZooKeeperImpldfs.federation.router.store.enable=truedfs.federation.router.store.membership.expiration=300000dfs.federation.router.store.serializer=org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.federation.store.driver.impl.StateStoreSerializerPBImpl- For a kerberized cluster, the router entry will be added into
auth_to_local of hdfs-core-siteas per the below screenshot.
- Modify the `dfs.federation.router.kerberos.principal=`
nn/_HOST@${realm}under Kerberos → Advanced → Edit. - Once all the affected services of HDFS are restarted, you can access the router UI link to fetch the details and confirm the setup.
router http UI - <router-hostname>:50071
router jmx - <router-hostname>:50071/jmx
Example:
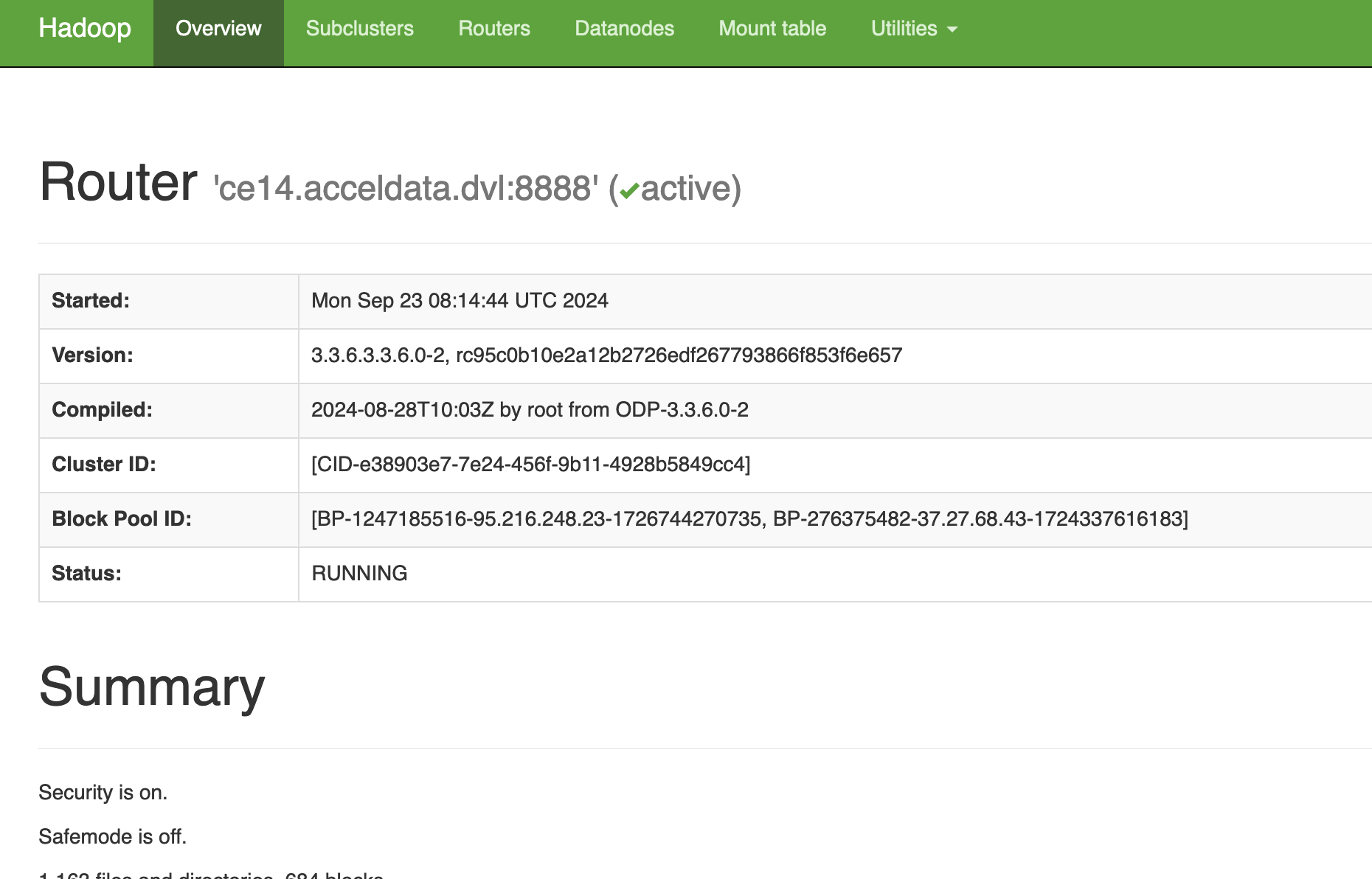
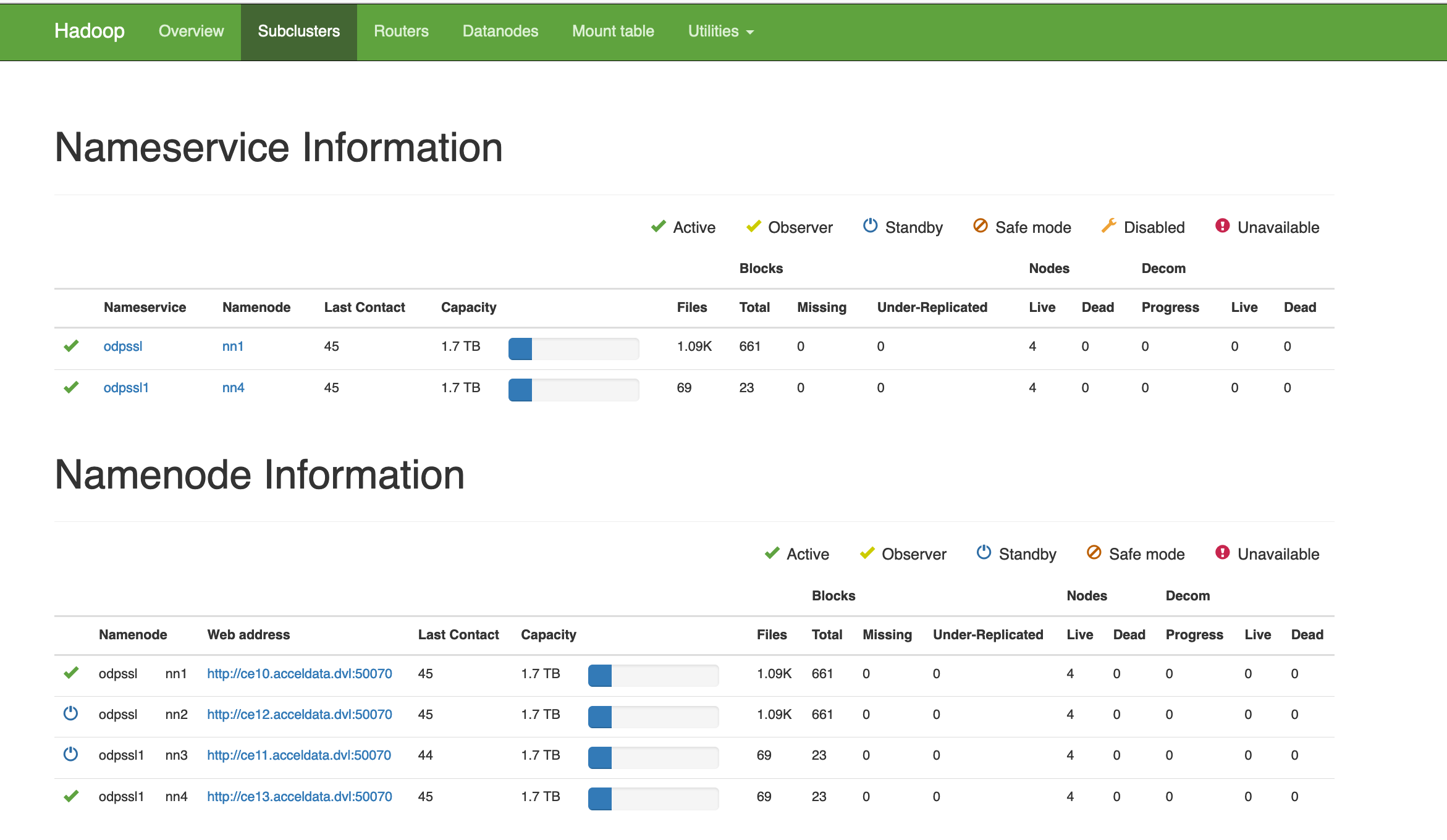
The sub clusters are monitored by router. For example, odpssl and ospssl1.
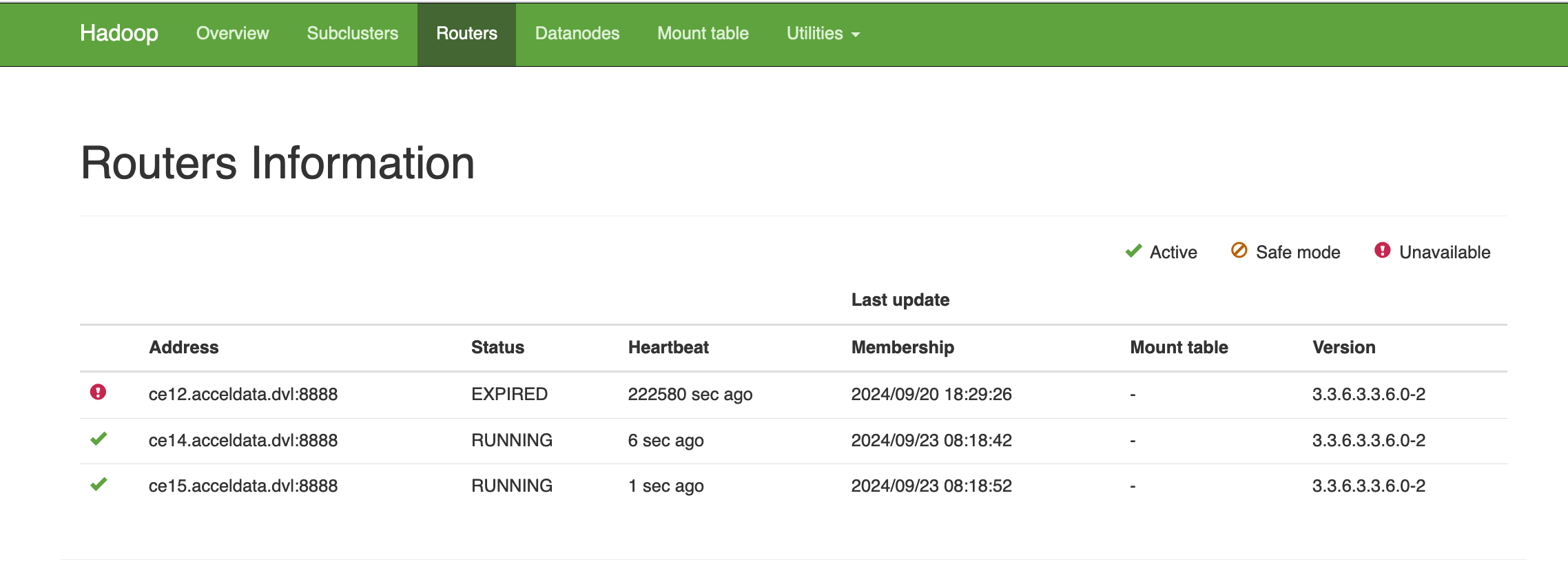
The routers Information of the cluster.
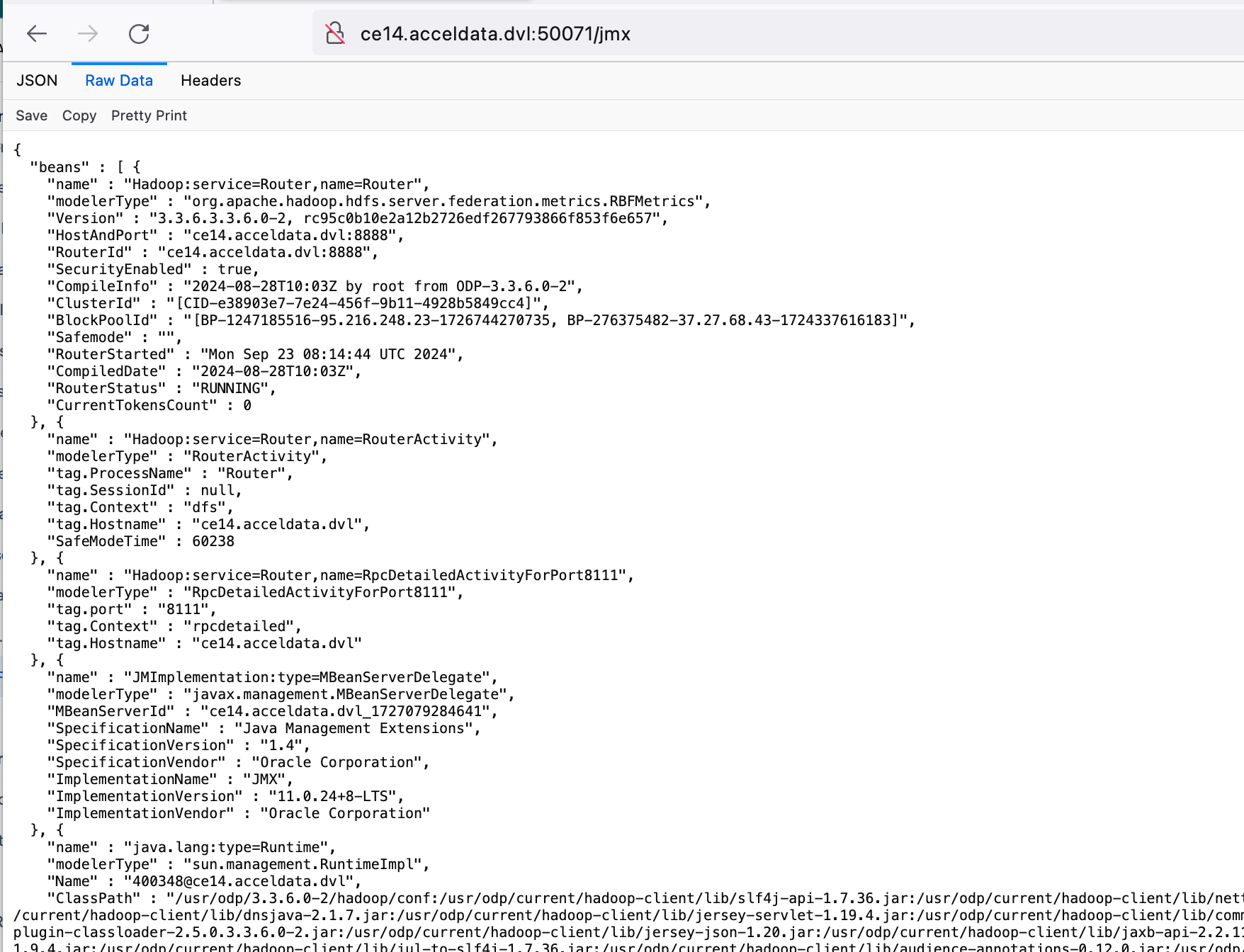
Router JMX
dfsrouter Operations
Mount table management
The federation admin tool supports managing the mount table. For example, to create three mount points and list them:
hdfs dfsrouteradmin -add /app2 odpssl /app2hdfs dfsrouteradmin -add /user/app1 odpssl1 /user/app1hdfs dfsrouteradmin -add /tmp odpssl /tmp[root@ce14 ~]# hdfs dfsrouteradmin -lsMount Table Entries:Source Destinations Owner Group Mode Quota/Usage/ranger odpssl->/ranger,odpssl1->/ranger hdfs hadoop rwxr-xr-x [NsQuota: 100/0, SsQuota: 1 KB/0 B]/tmp odpssl->/tmp hdfs hadoop rwxr-xr-x [NsQuota: -/-, SsQuota: -/-]/user/app1 odpssl1->/user/app1 hdfs hadoop rwxr-xr-x [NsQuota: -/-, SsQuota: -/-]/user/app2 odpssl->/user/app2 hdfs hadoop rwxr-xr-x [NsQuota: -/-, SsQuota: -/-]Quotas
The router-based federation supports global quota at mount table level. The mount table entries may spread multiple sub clusters and the global quota will be accounted across these sub clusters.
The federation admin tool supports setting quotas for specified mount table entries:
hdfs dfsrouteradmin -setQuota /ranger -nsQuota 100 -ssQuota 1024The above command means that we allow the path to have a maximum of 100 file/directories and use at most 1024 bytes storage space. The parameter for ssQuota supports multiple size-unit suffix (e.g. 1k is 1KB, 5m is 5MB). If no suffix is specified then bytes is assumed.
quota operation:
- Set storage type quota for specified mount table entry
- Remove quota for specified mount table entry
- Remove storage type quota for specified mount table entry
- Mount table cache refresh by manual command
Multiple subclusters
A mount point also supports mapping multiple sub clusters. For example, to create a mount point that stores files in sub clusters odpssl and ospssl1.
[root@ce14 ~]# hdfs dfsrouteradmin -ls /Source Destinations Owner Group Mode Quota/Usage/ranger odpssl->/ranger,odpssl1->/ranger hdfs hadoop rwxr-xr-x [NsQuota: -/-, SsQuota: -/-]Disabling name services
To prevent accessing a name service (sub cluster), it can be disabled from the federation. For example, one can disable ns1, list it, and enable it again:
hdfs dfsrouteradmin -nameservice disable odpsslhdfs dfsrouteradmin -getDisabledNameserviceshdfs dfsrouteradmin -nameservice enable odpsslRouter state dump
To diagnose the current state of the routers, you can use the dumpState command. It generates a text dump of the records in the State Store. Since it uses the configuration to find and read the state store, it is often the easiest to use the machine where the routers run. The command runs locally, so the routers do not have to be up to use this command.
hdfs dfsrouteradmin -dumpStateMetrics
The Router and State Store statistics are exposed in metrics/JMX. These info will be very useful for monitoring. More metrics information can see be seen here, RBF Metrics, Router RPC Metrics, and State Store Metrics.