Documentation
ODP 3.3.6.3-1
Release Notes
What is ODP
Installation
Component User guide and Installation Instructions
Upgrade Instructions
Downgrade Instructions
Reference Guide
Security Guide
Troubleshooting Guide
Uninstall ODP
Title
Message
Create new category
What is the title of your new category?
Edit page index title
What is the title of the page index?
Edit category
What is the new title of your category?
Edit link
What is the new title and URL of your link?
Securing Hive with KNOX
Summarize Page
Copy Markdown
Open in ChatGPT
Open in Claude
Connect to Cursor
Connect to VS Code
KNOX with Hive Enablement
To secure the Hive beeline connection with Knox, you have to first change the transport mode of the connection.
- In General, edit the below parameter.
Bash
hive.server2.transport.mode=http- Add
hiveserver2to the KNOX topology.
hive.server2.thrift.http.path is the configuration in HIVE, which sets the URL endpoint while in HTTP mode, By default, its value is cliservice.
Bash
<service> <role>HIVE</role> <url>http://ce11.acceldata.dvl:10001/cliservice</url> </service>After adding these two configurations, you can access the hive beeline connection securely through KNOX.
Need the trust store password for KNOX and gateway.jks to access Beeline.
Bash
beeline -u 'jdbc:hive2://ce10.acceldata.dvl:8443/;sslTrustStore=/usr/odp/3.3.6.3-1/knox/data/security/keystores/gateway.jks;trustStorePassword=Acceldata@01;transportMode=http;httpPath=gateway/default/hive;ssl=true' -d org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver -n admin -p admin-passwordKNOX ODBC Connection
You can connect to Hive through Knox using either ODBC or JDBC jars.
You need to set up odbc.ini using ODBC jars, and the rest of the connection stays the same.
Bash
x
[root@ce12 ~]# cat /opt/SimbaHiveODBC-2.7.0.1002-Linux/setup/odbc.ini[ODBC]# Specify any global ODBC configuration here such as ODBC tracing.[ODBC Data Sources]Simba Hive 32-bit=Simba Hive ODBC Driver 32-bitSimba Hive 64-bit=Simba Hive ODBC Driver 64-bit[ODPKNOX]# Description: DSN Description.# This key is not necessary and is only to give a description of the data source.Description=Simba Hive ODBC Driver (64-bit) DSN# Driver: The location where the ODBC driver is installed to.Driver=/opt/SimbaHiveODBC-2.7.0.1002-Linux/SimbaHiveODBC64-2.7.0.1002/lib/libhiveodbc_sb64.so# When using No Service Discovery, specify the IP address or host name of the Hive server.# When using ZooKeeper as the Service Discovery Mode, specify a comma-separated list of ZooKeeper# servers in the following format:# <zk_host1:zk_port1>,<zk_host2:zk_port2>,...HOST=ce10.acceldata.dvl# The TCP port Hive server is listening. This is not required when using ZooKeeper as the service# discovery mode as the port is specified in the HOST connection attribute.PORT=8443HttpPath=gateway/default/hive# The name of the database schema to use when a schema is not explicitly specified in a query.Schema=default# Set to 0 to when connecting directory to Hive Server 2 (No Service Discovery).# Set to 1 to do Hive Server 2 service discovery using ZooKeeper.# Note service discovery is not support when using Hive Server 1.ServiceDiscoveryMode=0# The namespace on ZooKeeper under which Hive Server 2 znodes are added. Required only when doing# HS2 service discovery with ZooKeeper (ServiceDiscoveryMode=1).ZKNamespace=# Set to 1 if you are connecting to Hive Server 1. Set to 2 if you are connecting to Hive Server 2.HiveServerType=2# The authentication mechanism to use for the connection.# Set to 0 for No Authentication# Set to 1 for Kerberos# Set to 2 for User Name# Set to 3 for User Name and Password# Note only No Authentication is supported when connecting to Hive Server 1.AuthMech=3# The Thrift transport to use for the connection.# Set to 0 for Binary# Set to 1 for SASL# Set to 2 for HTTP# Note for Hive Server 1 only Binary can be used.ThriftTransport=2# When this option is enabled (1), the driver does not transform the queries emitted by an# application, so the native query is used.# When this option is disabled (0), the driver transforms the queries emitted by an application and# converts them into an equivalent from in HiveQL.UseNativeQuery=0# Set the UID with the user name to use to access Hive when using AuthMech 2 to 8.UID=# The following is settings used when using Kerberos authentication (AuthMech 1 and 10)# The fully qualified host name part of the of the Hive Server 2 Kerberos service principal.# For example if the service principal name of you Hive Server 2 is:# hive/myhs2.mydomain.com@EXAMPLE.COM# Then set KrbHostFQDN to myhs2.mydomain.comKrbHostFQDN=ce10.acceldata.dvl# The service name part of the of the Hive Server 2 Kerberos service principal.# For example if the service principal name of you Hive Server 2 is:# hive/myhs2.mydomain.com@EXAMPLE.COM# Then set KrbServiceName to hiveKrbServiceName=hive# The realm part of the of the Hive Server 2 Kerberos service principal.# For example if the service principal name of you Hive Server 2 is:# hive/myhs2.mydomain.com@EXAMPLE.COM# Then set KrbRealm to EXAMPLE.COMKrbRealm=ADSRE.COM# Set to 1 to enable SSL. Set to 0 to disable.SSL=1# Set to 1 to enable two-way SSL. Set to 0 to disable. You must enable SSL in order to# use two-way SSL.TwoWaySSL=0AllowSelfSignedServerCert=1# The file containing the client certificate in PEM format. This is required when using two-way SSL.ClientCert=/root/gateway.jkstrustStorePassword=Acceldata@01# The client private key. This is used for two-way SSL authentication.ClientPrivateKey=# The password for the client private key. Password is only required for password protected# client private key.ClientPrivateKeyPassword=The Connection String is as follows.
Bash
isql ODPKNOX admin admin-password -vvvKNOX JDBC Connection
You can use this JDBC url format for the Knox JDBC connection.
Bash
jdbc:hive2://ce10.acceldata.dvl:8443/;sslTrustStore=/Users/sehajpalsinghsandhu/commit/delete/tr/43/gateway.jks;trustStorePassword=Acceldata@01;transportMode=http;httpPath=gateway/default/hive;auth=KERBEROS;ssl=true;user=admin;password=admin-password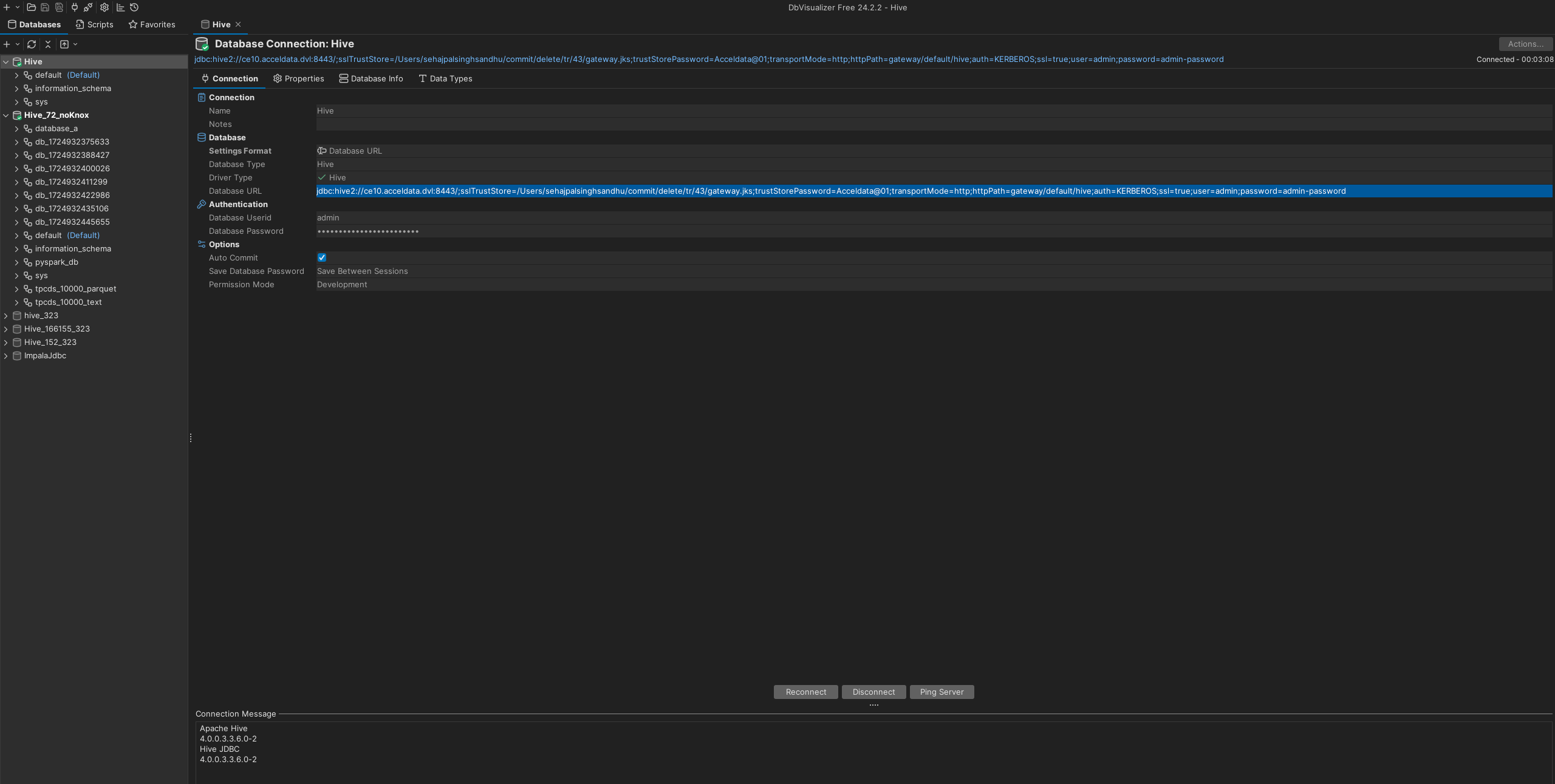
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Last updated on Jan 13, 2026
Was this page helpful?
Next to read:
Set up HAProxy Load Balancer for HiveServer2Discard Changes
Do you want to discard your current changes and overwrite with the template?
Archive Synced Block
Message
Create new Template
What is this template's title?
Delete Template
Message