Impala Installation
Impala integration with ODP is available as Ambari Mpack. You can download the impala-mpack tar on your ambari-server node and install mpack as mentioned in Guide for Management Packs.
Kerberos Configuration
The Impala service principal and keytab for service and spengo for UI can be configured with Ambari automation.
Confirm the Impala principal mapping in Hadoop core-site auth_to local property``, and enable the same in the Impala environment to map Kerberos credentials as per HDFS auth_to`_local` rules.
Ranger Configuration
Enable or disable the Ranger authorization from Ambari UI > Ranger > Configs > Hive Ranger Plugin.
Restart the Hive and Impala (both) services to implement changes.
Then, go to Ranger UI > edit the hive service def. Add impala user to download auth user properties, as shown in the below configurations.
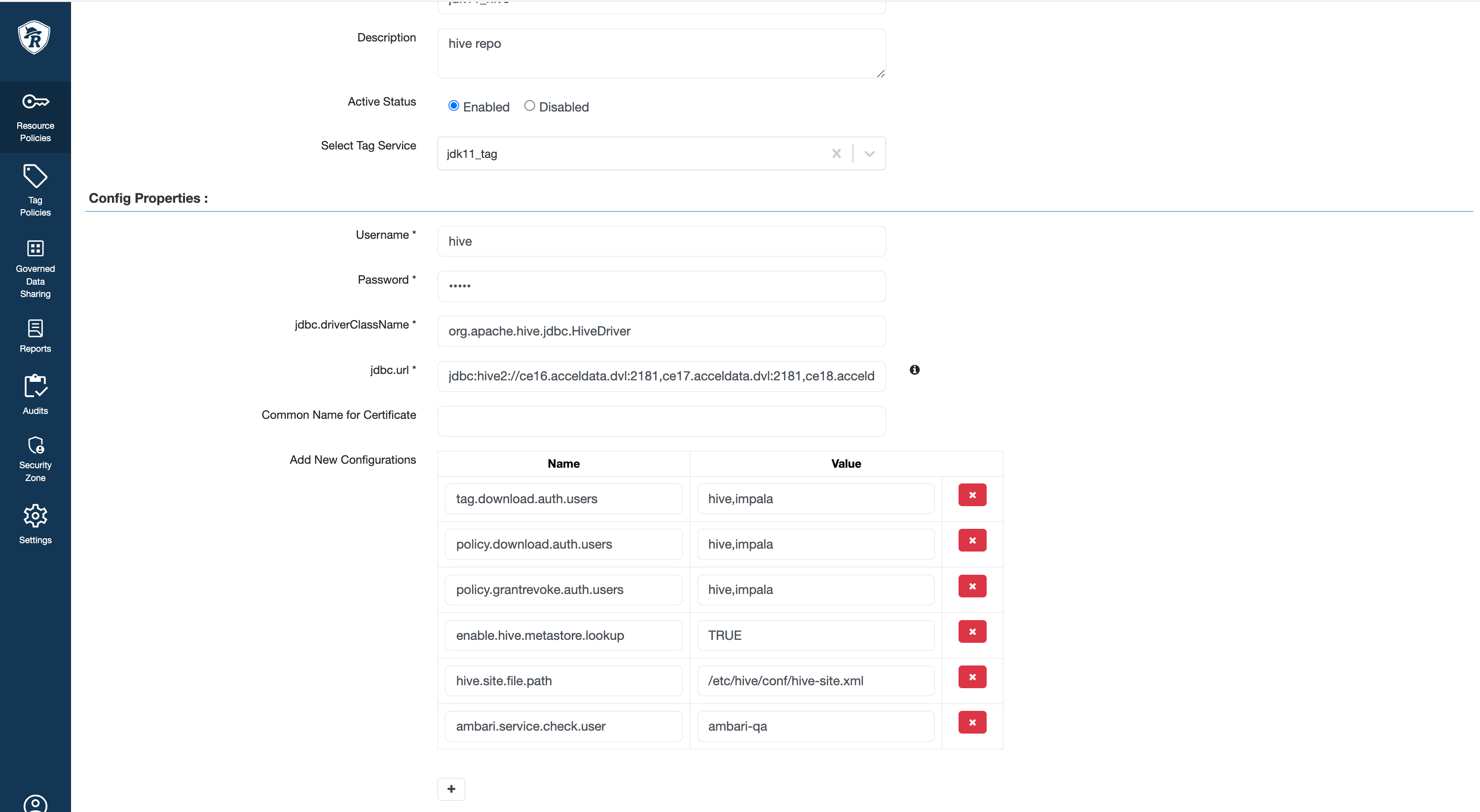
Include New Run Time Parameters for Impala Mpack
This feature aims to optimize the Impala mpack to add new parameters to the Impala component args directly from the Ambari UI configuration management.
In Ambari UI > Impala > Configs > Advanced impala-env: The template content is decided into the following properties :
- impala_defaults: To define environmental variables with definite values to be taken up by catalog/state-store/daemon args.
- impala_catalog_content: To include or exclude runtime arguments for the catalog process.
- impala_state_store_args: To include or exclude runtime arguments for the Impala state store process.
- impala_server_args: To include or exclude runtime arguments for the Impala server or daemon process.
To include or exclude runtime parameters from any impala component:
- Go to the respective property (as mentioned above).
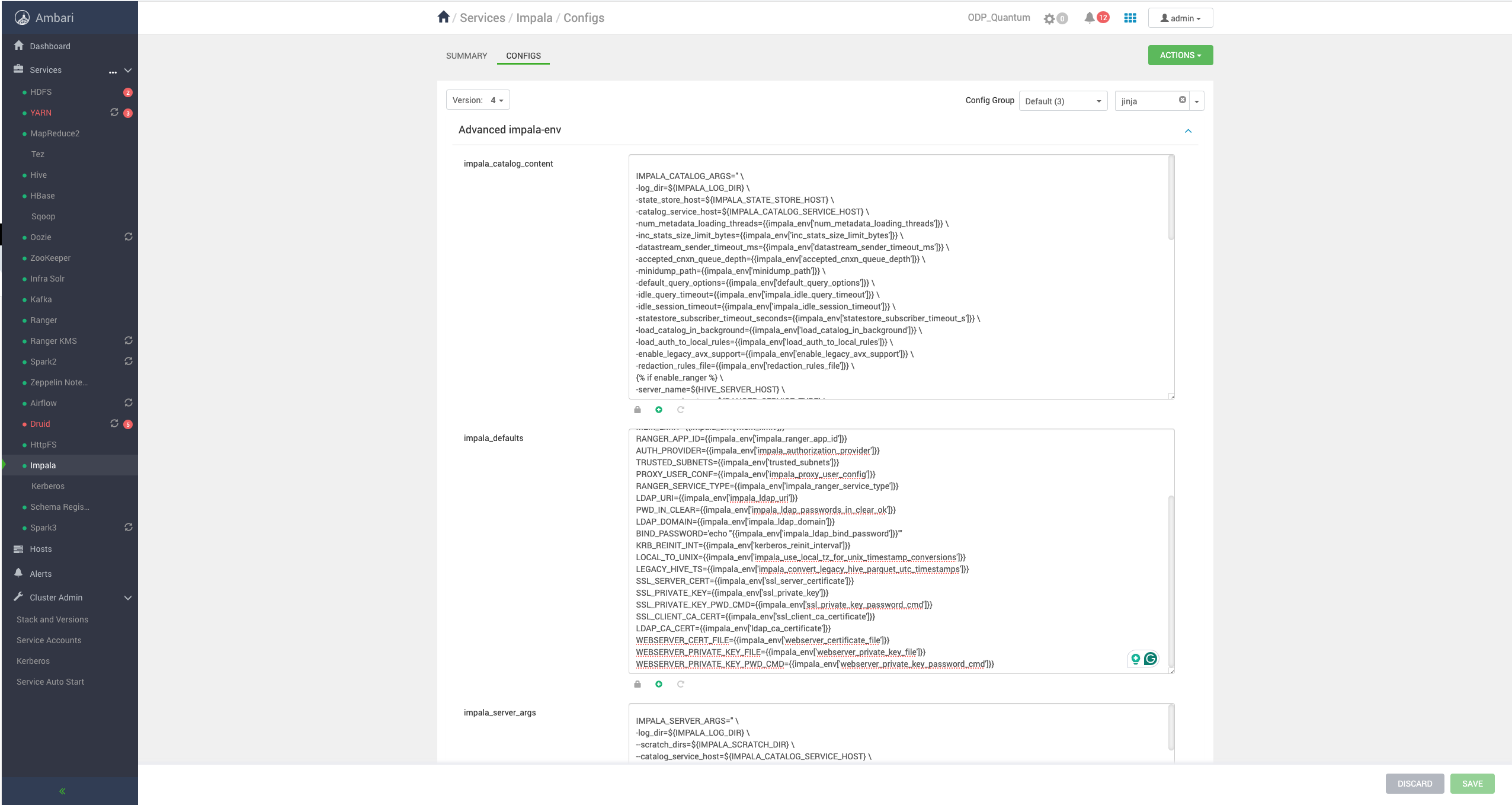
- Add the property name starting with '-' and ending with ' /' (
-{{property name and value}} /)to maintain the template format. Example: Addingcatalog_service_portas 26000 in catalog args.
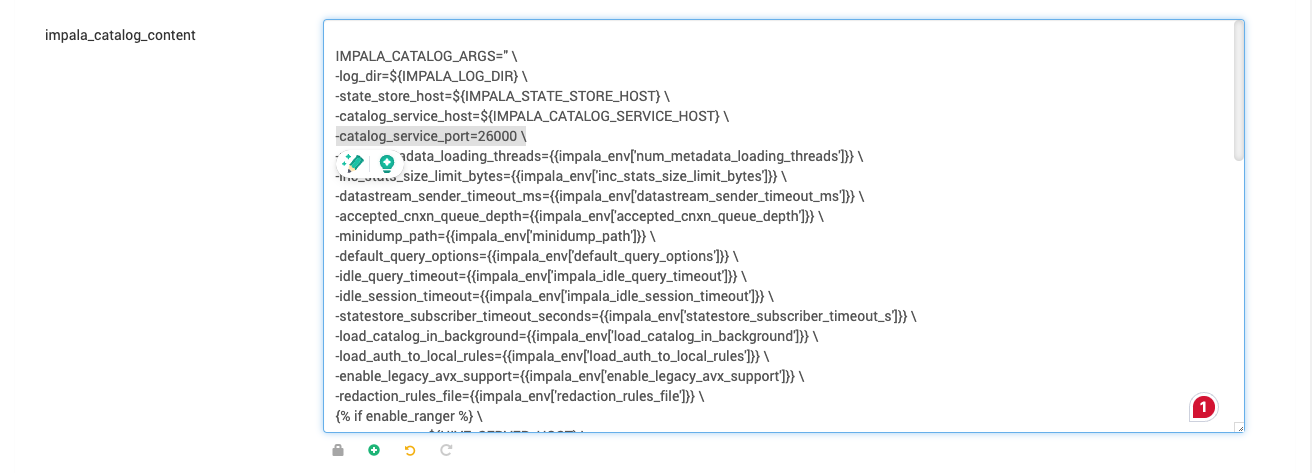
- Save changes and restart the Impala service.
Changes are implemented and can be confirmed in
/etc/default/impala.
[root@harshith1 ~]# cat /etc/default/impala | grep catalog-catalog_service_host=${IMPALA_CATALOG_SERVICE_HOST} \‑catalog_service_port=26000 \-load_catalog_in_background=False \An alternate method to add runtime parameters from the Ambari UI is also provided under this optimization. Custom environment configurations can be added, automatically segregated, and added to the respective Jinja templates.
This /etc/default/impala contains combined data from templates of default parameters, catalog args, state store args, and server args, with custom configurations.
To utilize this alternative method, navigate to Ambari UI > Impala > Configs > Custom impala-env, and add a new runtime parameter with the following prefix rule:
- The catalog args should start with icatalog_(param)
- The state store args should start with isstore_(param) [Eg: key: isstore_new-conf , property: “new conf”]
- The Impala server args should start with iserver_(param) [Eg: key: iserver_new-conf , property: “new conf”]
Adding the same configuration catalog_service_port using the alternate method:
- Navigate to the Ambari UI >
Impala>Configs>Custom impala-env: Add your new parameter with the respective prefix.
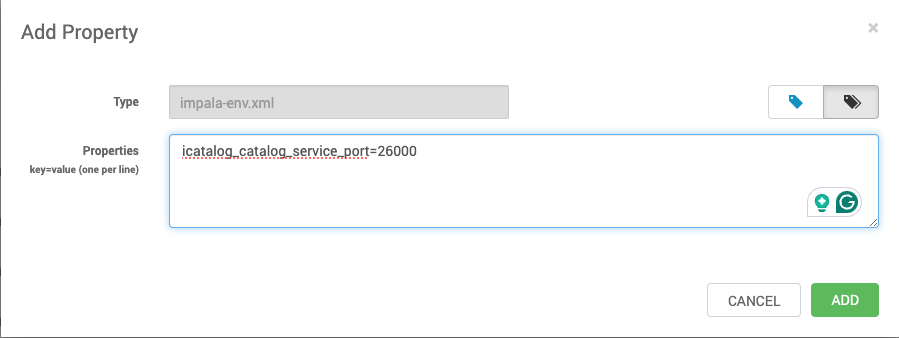
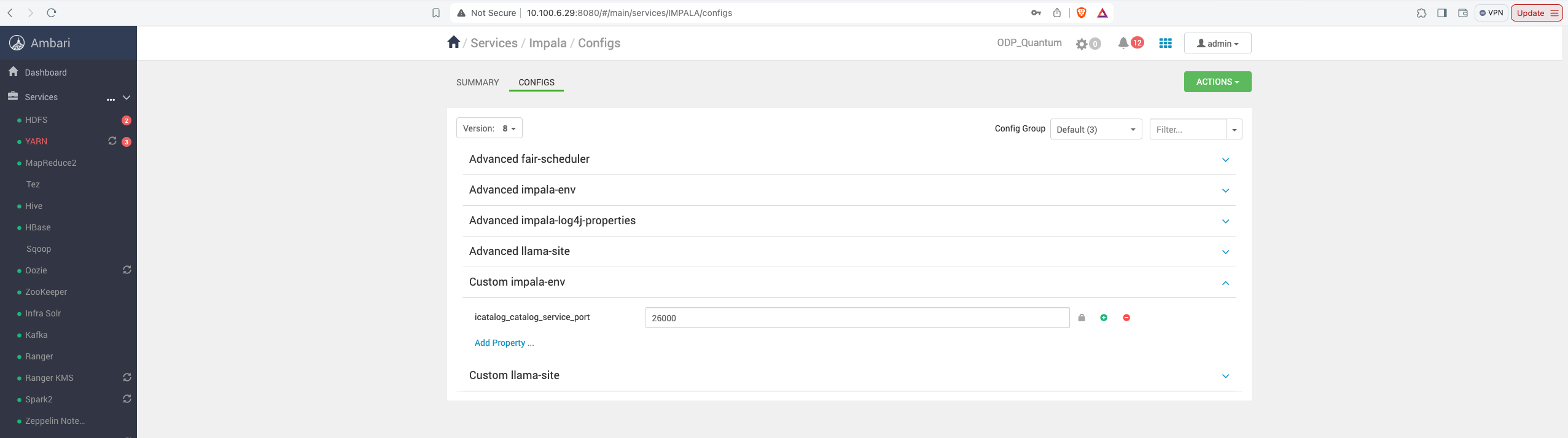
- Save the property and restart Impala. The changes are implemented and can be confirmed in
/etc/default/impala.
[root@harshith1 ~]# cat /etc/default/impala | grep catalog-catalog_service_host=${IMPALA_CATALOG_SERVICE_HOST} \-load_catalog_in_background=False \-catalog_service_port=26000 \LDAP Configuration
The LDAP authentication in Impala ensures that only authorized users can access the server.
When LDAP is enabled, user credentials are verified when connecting via various interfaces such as impala-shell, Hue, Business Intelligence tools, JDBC, or ODBC applications. However, regardless of the authentication method used, all HDFS directories and data files created through Impala are owned by the same user (typically impala).
For the user-level access control to databases, tables, and other resources, Impala integrates with Ranger for authorization. You can also use Kerberos for secure authentication as an alternative to LDAP.
Note:
- The LDAP authentication applies to client-to-Impala connections only.
- You need to enable the correct flags and options to configure the LDAP authentication for your Impala deployment.
To enable the LDAP-based authentication, the following configurations must be set:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
enable_ldap_auth | Enables the LDAP authentication between the client and Impala. |
ldap_uri | Specifies the URI of the LDAP server. Use ldap:// for standard connections or ldaps:// for secure connections. The default ports are 389 for LDAP and 636 for secure LDAP. Example: ldap://ldap.example.com:389 or ldaps://ldap.example.com:636. |
ldap_search_bind_authentication | Switches between search bind and simple bind for user lookup methods. Default: false (simple bind). |
impala_ldap passwords_in_clear_ok | (optional) Allows clear text password to make LDAP connection. Set true when ldap_tls is not enabled. |
Bind User Credentials
To search for users and groups in LDAP, Impala requires bind user credentials, which can be configured as follows.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
ldap_allow_anonymous_binds | If set to true, allows anonymous binding to the LDAP server (no password required). Default: false. |
ldap_bind_dn | Specifies the distinguished name (DN) of the user for binding during searches. Applicable when ldap_allow_anonymous_binds is false. |
impala_ldap_bind_password | Specifies a command whose output provides the password for --ldap_bind_dn. The output will be truncated to 1024 bytes and any trailing whitespace will be removed. |
Simple Bind User Authentication
In simple bind mode, Impala connects to the LDAP server and authenticates users using their credentials. However, the LDAP servers often require more complex usernames, so Impala provides options to transform the short username (e.g., 'henry') into a full LDAP distinguished name.
Key Options for Simple Bind Authentication
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
ldap_domain | Transforms the username into username@ldap_domain. |
ldap_baseDN | Transforms the username into a distinguished name (DN) like uid=username,ldap_baseDN. |
ldap_bind_pattern | Replaces #UID with the username in a custom bind pattern. Example: user=#UID,OU=foo,CN=bar would bind the user henry as user=henry,OU=foo,CN=bar. |
ldap_user_filter | A comma-separated list of usernames allowed for authentication. |
ldap_group_filter | Specifies groups the user must belong to for authentication. |
ldap_group_dn_pattern | A colon-separated list of DN patterns for searching groups. Patterns may contain %s, which is replaced with each group name. |
NOTE: The options --ldap_domain, --ldap_baseDN, and --ldap_bind_pattern are mutually exclusive. Impala does not start if more than one is specified.
Example: LDAP Simple Bind User Authentication
Here is an example setup to implement LDAP with simple bind user authentication. Set up the following configurations in Ambari UI > Impala configs > Impala Environment.
enable_ldap_auth = trueimpala_ldap_uri = <ldap_uri>ldap_allow_anonymous_binds = falseimpala_ldap_passwords_in_clear_ok = trueimpala_ldap_bind_password = <ldap_bind_password>ldap_bind_dn = cn=#UID,dc=netflux,dc=comldap_search_bind_authentication = false #To implemet simple bind user authldap_bind_pattern = cn=#UID,dc=netflux,dc=comThe ldap_allow_anonymous_binds option is set to false by default to use password-based connection.
After setting the above configurations, restart impala.
Access impala shell using ldap user impala-shell -l -u <ldap_user> --auth_creds_ok_in_clear.
# impala-shell --ldap --auth_creds_ok_in_clear -u'mlamber'/usr/bin/impala-shell: line 37: warning: setlocale: LC_CTYPE: cannot change locale (UTF-8): No such file or directory/usr/bin/impala-shell: line 37: warning: setlocale: LC_CTYPE: cannot change locale (UTF-8): No such file or directoryStarting Impala Shell with LDAP-based authentication using Python 3.11.9LDAP password for mlamber:Error connecting: TTransportException, TSocket read 0 bytesKerberos ticket found in the credentials cache, retrying the connection with a secure transport.Opened TCP connection to ce.acceldata.dvl:21050Connected to ce16.acceldata.dvl:21050Server version: impalad version 4.4.1.3.3.6.2.1 RELEASE (build cd66363c1f4d992b7ea7b131b150c40b5bf3e691)***********************************************************************************Welcome to the Impala shell.(Impala Shell v4.4.1.3.3.6.2.1 (cd66363) built on Fri Sep 20 11:58:06 CEST 2024)To see how Impala will plan to run your query without actually executing it, usethe EXPLAIN command. You can change the level of detail in the EXPLAIN output bysetting the EXPLAIN_LEVEL query option.***********************************************************************************LDAP authentication is enabled, but the connection to Impala is not secured by TLS.ALL PASSWORDS WILL BE SENT IN THE CLEAR TO IMPALA.[ce16.acceldata.dvl:21050] default> select * from t10;Query: select * from t10Query submitted at: 2024-09-27 20:47:43 (Coordinator: http://ce16.acceldata.dvl:25000)Query state can be monitored at: http://ce.acceldata.dvl:25000/query_plan?query_id=134f0a6505b37d4a:9394e85c00000000+----+| id |+----+| 10 |+----+Fetched 1 row(s) in 0.61s[ce16.acceldata.dvl:21050] default> insert into t10 values(20);Query: insert into t10 values(20)Query submitted at: 2024-09-27 20:56:48 (Coordinator: http://ce16.acceldata.dvl:25000)Query state can be monitored at: http://ce.acceldata.dvl:25000/query_plan?query_id=384dcb3ff5ad78b3:4855958800000000Modified 1 row(s) in 0.35s[ce16.acceldata.dvl:21050] default> select * from t10;Query: select * from t10Query submitted at: 2024-09-27 20:56:52 (Coordinator: http://ce16.acceldata.dvl:25000)Query state can be monitored at: http://ce.acceldata.dvl:25000/query_plan?query_id=b94fd6f1e6aad382:02a1f6ec00000000+----+| id |+----+| 10 || 20 |+----+Fetched 2 row(s) in 0.12sSearch Bind User Authentication
In search bind mode, Impala binds to the LDAP server by using a configured bind user, searches for the connecting user in LDAP, and, if successful, retrieves the user’s DN to perform another bind for authentication.
Key Options for Search Bind Authentication:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
ldap_user_search_basedn | The DN used to search for the authenticating user. Required for search bind. |
ldap_group_search_basedn | The DN used to search for the authenticating group. If left empty, no group checks are performed. |
ldap_user_filter | An LDAP filter used during user search. Example for AD: (&(objectClass=user)(sAMAccountName={0})). |
ldap_group_filter | An LDAP filter used during group search. Example: (&(objectClass=group)(member={0})). |
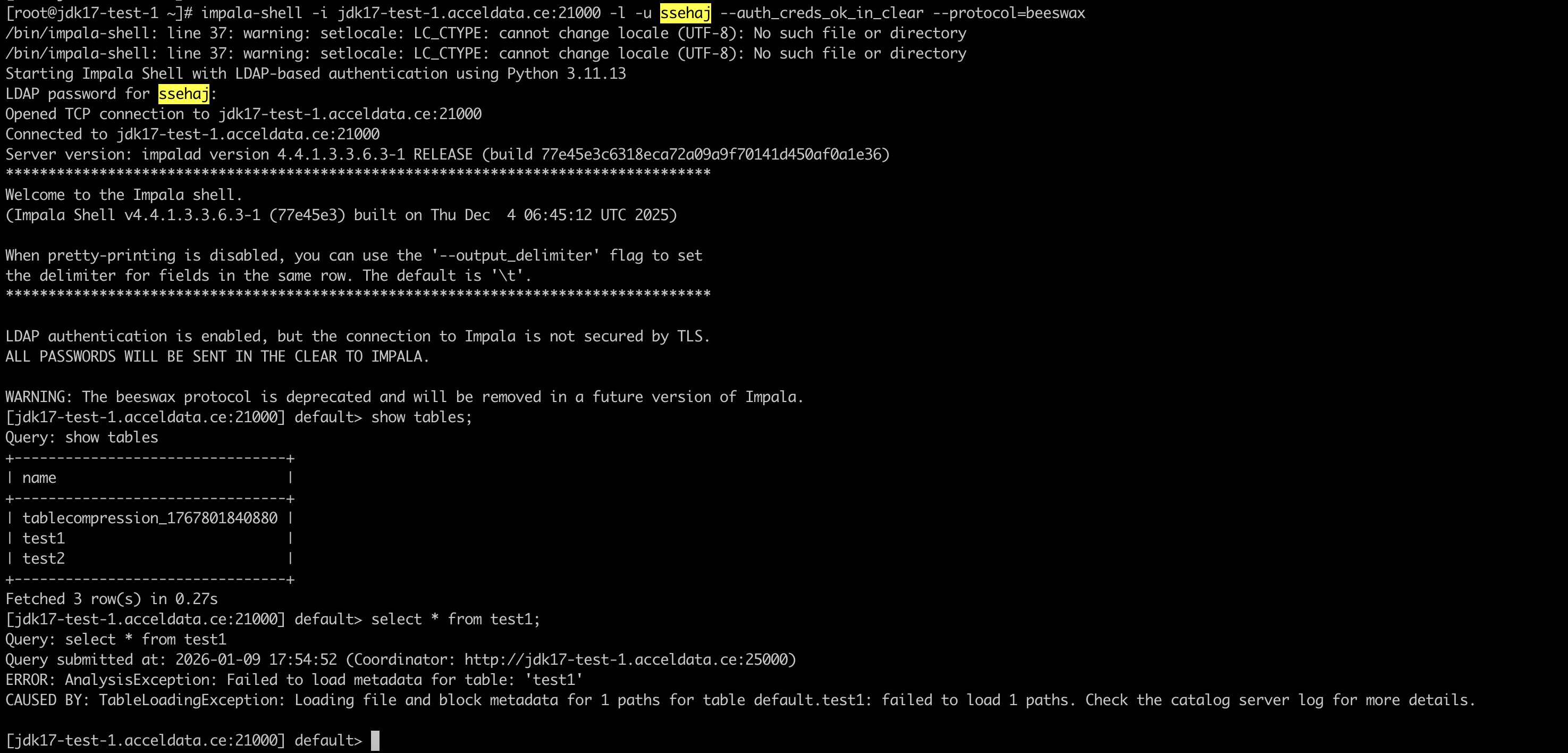
Example: LDAP Search Bind User Authentication
Here is an example setup to implement LDAP with search bind user authentication. Set up the following configurations in Ambari UI > Impala configs > Advanced Impala Env:
enable_ldap_auth = trueimpala_ldap_uri = <ldap_uri>ldap_allow_anonymous_binds = falseimpala_ldap_passwords_in_clear_ok = trueimpala_ldap_bind_password = <ldap_bind_password>ldap_bind_dn = <ldap_bind_dn>ldap_search_bind_authentication = True #To implement search bind user authldap_user_search_basedn = <user_search_basedn>ldap_group_search_basedn = <greoup_search_basedn>ldap_user_filter = (&(objectClass=user)(sAMAccountName={0}))ldap_group_filter = (&(objectClass=group)(member={1}))ldap_allow_anonymous_binds is set to false by default to use a password-based connection.
After setting the above configurations, restart Impala.
Access Impala shell using LDAP user impala-shell -l -u <ldap_user> --auth_creds_ok_in_clear
Secure LDAP Authentication Support (SSL/TLS)
Impala also supports the LDAP authentication over secure connections such as SSL and TLS. Secure connections prevent the transmission of credentials in clear text. This is particularly useful when integrating with systems like Active Directory or OpenLDAP that rely on LDAP protocols.
Configure the following properties, alongside above LDAP properties, to implement secure LDAP. In Ambari UI > Impala Configs > Impala environment.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
ldap_tls | true |
ldap_ca_certificate | LDAP ca certificate (Location on disk to the certificate, in .pem format) |
Metadata Management
This section describes configuring impala to control how Impala manages its metadata in order to improve performance and scalability.
On-demand Metadata
Enabling this feature enables the coordinators to pull metadata as needed from catalogd and cache it locally. The cached metadata gets evicted automatically under memory pressure. This feature is disabled by default.
To enable on-demand metadata mode for all coordinators, make the following changes in cluster.
In Ambari UI > Impala > Advanced configs > Impala-environment:
- Set
is_coordinator=trueto enable all impala daemons to run in coordinator mode. - Set the following on
catalogd.
--catalog_topic_mode=minimal- Set the following on all
impaladcoordinators.
--use_local_catalog=trueTo enable metadata mixed mode, only some coordinators are enabled to use the metadata on-demand, make the following changes in cluster :
- Set the following on
catalogd.
--catalog_topic_mode=mixed- Set the following on
impaladcoordinators with metdadata on-demand.
--use_local_catalog=trueImpala Admission Control
Impala includes features that balance and maximize resources in your Apache Hadoop cluster. This topic describes how you can improve efficiency of your a Apache Hadoop cluster using those features.
The configuration options for admission control range from the simple (a single resource pool with a single set of options) to the complex (multiple resource pools with different options, each pool handling queries for a different set of users and groups).
Configure the following properties as per your use cases from the Ambari UI.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| enable_admission_control | Set to trueto enable the admission control |
| fair_scheduler.xml | Template for fair scheduler XML |
| llama-site.xml | Template for fair scheduler XML |
| mem_limit | Modify the “-mem_limit” to required memory values like 180gb /150gb. |
Accessing Impala Web UI Consoles
Each of the Impala daemons (impalad, statestored, and catalogd) includes a built-in web server that displays diagnostic and status information.
Catalogd WebUI Console
The catalogd Web UI includes information about the databases, tables, and other objects managed by Impala, in addition to the resource usage and configuration settings of the catalogd. Because there is only a single instance of the catalogd within any Impala cluster, you access the Web UI only on the particular host that serves as the Impala Catalog Server.
http://<catalog-host-name>:25020Statesoted WebUI Console
The statestored Web UI includes information about memory usage, configuration settings, and ongoing health checks performed by statestored. Because there is only a single instance of the statestored within any Impala cluster, you can access the Web UI only on a particular host that serves as the Impala StateStore.
http://<Statestore-host-name>:25010Impald WebUI Console
The impalad Web UI includes information about configuration settings, running and completed queries, and associated performance and resource usage for queries. In particular, the Details link for each query displays alternative views of the query including a graphical representation of the plan, and the output of the EXPLAIN, SUMMARY, and PROFILE statements from impala-shell. Each host that runs the impalad daemon has its own instance of the Web UI, with details about those queries for which that host served as the coordinator. The impalad Web UI is primarily used for diagnosing query problems that can be traced to a particular node.
http://<Impalad-host-name>:25000For more information about accessing the Impala Web interface, see Impala Web User Interface for Debugging.