Documentation
ODP 3.3.6.3-1
Release Notes
What is ODP
Installation
Component User guide and Installation Instructions
Upgrade Instructions
Downgrade Instructions
Reference Guide
Security Guide
Troubleshooting Guide
Uninstall ODP
Title
Message
Create new category
What is the title of your new category?
Edit page index title
What is the title of the page index?
Edit category
What is the new title of your category?
Edit link
What is the new title and URL of your link?
What is SSL?
Summarize Page
Copy Markdown
Open in ChatGPT
Open in Claude
Connect to Cursor
Connect to VS Code
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a security protocol for establishing encrypted communication between two systems. It ensures confidentiality and integrity by encrypting data exchanged over networks.
Although SSL is often referred to, it has evolved into TLS (Transport Layer Security). However, the term SSL is still widely used.
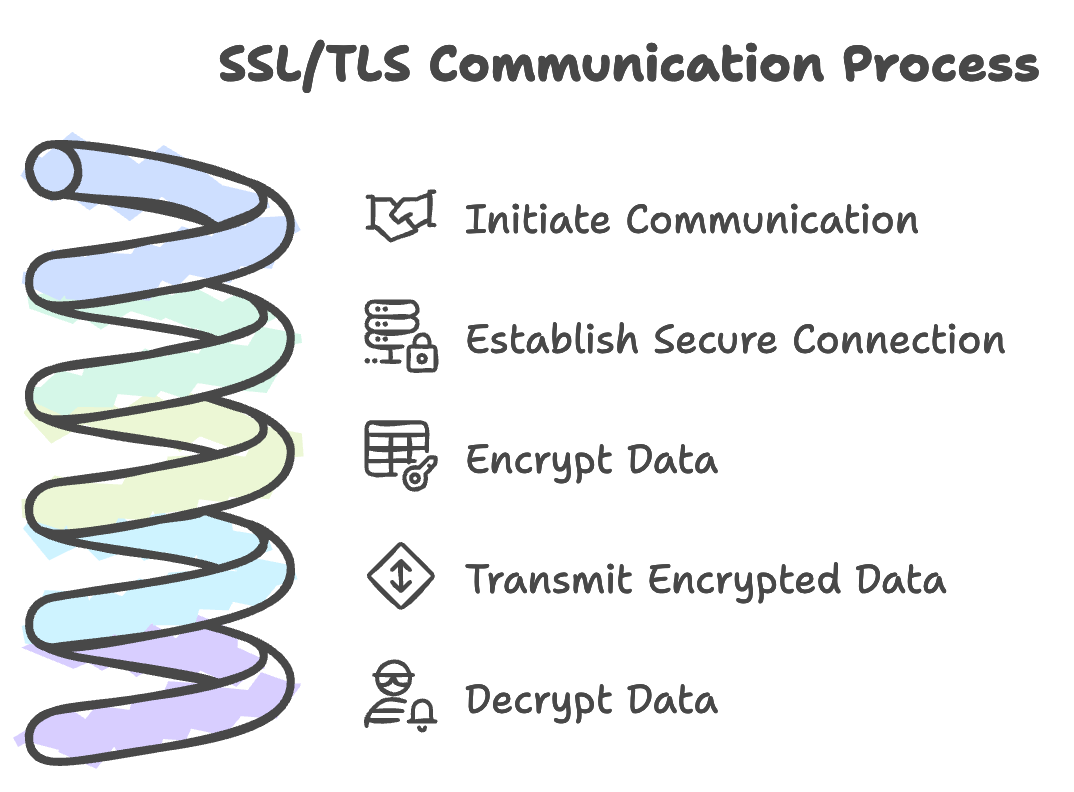
Why is SSL Important?
SSL prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data, such as passwords, personal information, and financial transactions. It's commonly used in websites, APIs, and distributed systems (like Hadoop) to secure communication between services.
SSL Handshake Process Overview
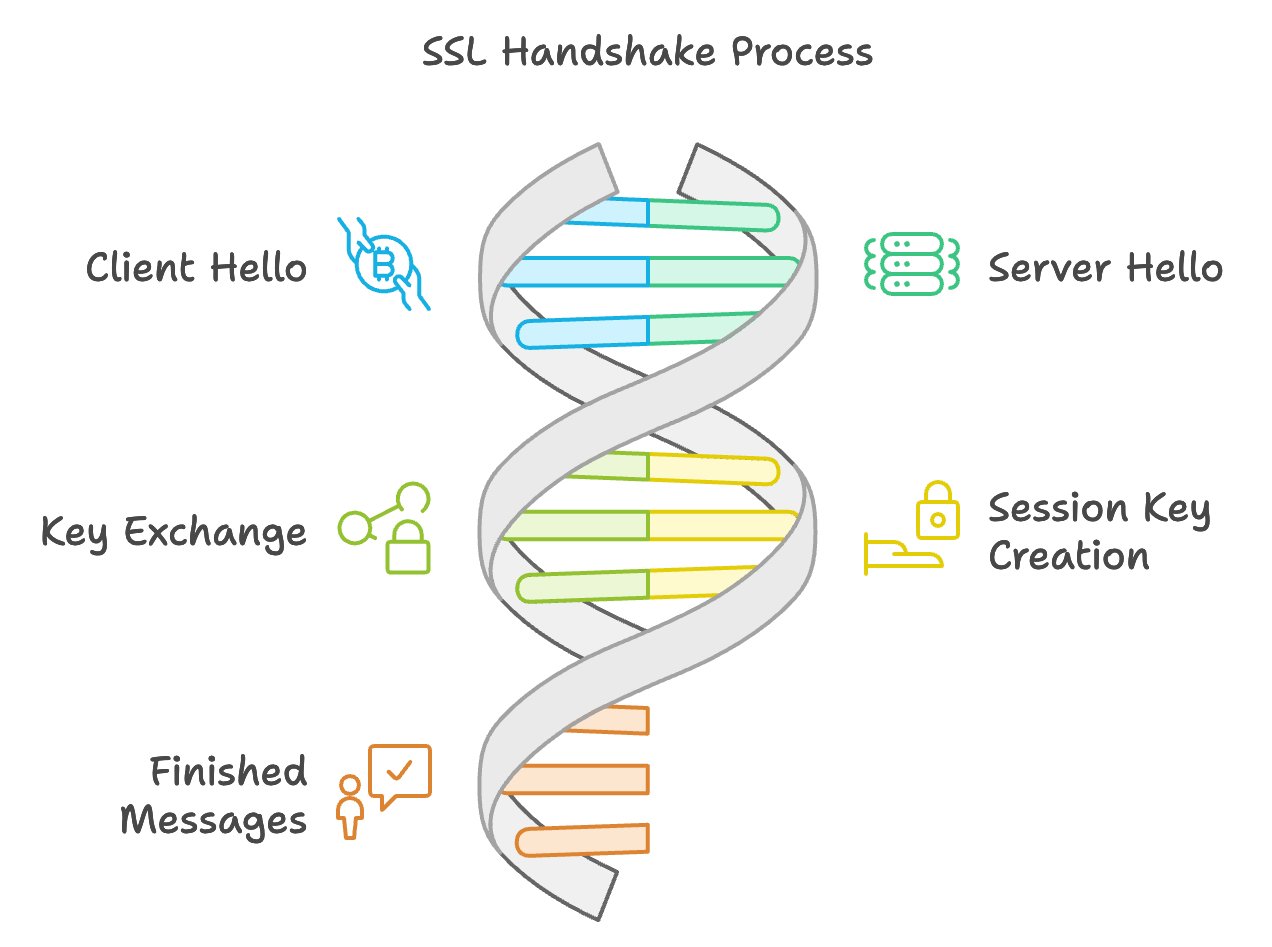
The SSL handshake is the process used to establish a secure connection between a client and a server.
- Client Hello: The client sends its SSL version, cipher suites, and a random number to the server.
- Server Hello: The server responds with its SSL version, chosen cipher suite, a random number, and its certificate.
- Key Exchange: The client sends a pre-master secret, encrypted with the server's public key.
- Session Key Creation: Both client and server create a session key from the pre-master secret.
- Finish Messages: Both parties exchange encrypted "Finished" messages.
- Secure Communication: Data is encrypted and exchanged using the session key.
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Last updated on Nov 18, 2024
Was this page helpful?
Next to read:
Key Concepts: Keystore and TruststoreDiscard Changes
Do you want to discard your current changes and overwrite with the template?
Archive Synced Block
Message
Create new Template
What is this template's title?
Delete Template
Message