RHEL 8/9 Setup
Prerequisites
To establish the necessary development tools and Python packages, ensure the installation of Python packages with versions 3.11 and above. Note that while this documentation employs Python 3.11, Apache Airflow is compatible with Python versions starting from 3.11 and higher.
sudo yum install python3.11-devel -ysudo yum -y groupinstall "Development Tools"Database Setup
For an optimal test drive experience of Airflow, choose a robust database backend such as PostgreSQL or MySQL. By default, Airflow uses SQLite, which is mainly intended for development.
Airflow supports only specific versions of database engines. Verify that your database version is compatible as older versions might not support certain SQL features:
- PostgreSQL: Versions 12, 13, 14, 15, 16
- MySQL: Version 8.0, Innovation
- MSSQL (experimental, support ending in version 2.9.0): 2017, 2019
- SQLite: Version 3.15.0 or later
MariaDB is not a supported backend. Despite similarities with MySQL, there are known incompatibilities (for example, index handling), and our migration scripts and application workflows are not tested against MariaDB.
Deployments using MariaDB have historically resulted in significant operational issues. As a result, its use is strongly discouraged, and no official support or compatibility guarantees should be expected.
For reference, see Choosing Database Backend for Airflow.
Before installing Apache Airflow, set up a compatible database. Choose PostgreSQL or MySQL based on your needs and ensure that your database version meets the following minimum requirements:
- MySQL: Version 8.0 or higher
- PostgreSQL: Version 12 or higher
Refer: Setup a Database Backend-Apache Airflow
Refer to the guidelines below for your selected database to prepare and configure it for Apache Airflow.
PostgreSQL Database Setup
To integrate PostgreSQL with Apache Airflow, complete the following steps to install and configure it:
Install the psycopg2-binary Python package:
pip3.11 install psycopg2-binaryInstall PostgreSQL:
- Install the repository RPM:
sudo dnf install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-8-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm- Disable the built-in PostgreSQL module:
sudo dnf -qy module disable postgresql- Install PostgreSQL:
sudo dnf install -y postgresql12-serverInitialize and start PostgreSQL:
- Access the PostgreSQL shell:
sudo -u postgres psql- Inside the PostgreSQL shell, execute the following commands:
- Create the Airflow database:
CREATE DATABASE airflow;- Create the Airflow user with a password:
CREATE USER airflow WITH PASSWORD 'airflow';- Set client encoding, default transaction isolation, and timezone for the Airflow user:
ALTER ROLE airflow SET client_encoding TO 'utf8';ALTER ROLE airflow SET default_transaction_isolation TO 'read committed';ALTER ROLE airflow SET timezone TO 'UTC';- Grant all privileges on the Airflow database to the Airflow user:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE airflow TO airflow;- Exit the PostgreSQL shell:
\qConfigure PostgreSQL settings for Airflow:
- Open the PostgreSQL configuration file:
vi /var/lib/pgsql/12/data/postgresql.conf- Inside the file, modify the following settings:
- Change and uncomment the listen_addresses to '*':
listen_addresses = '*'- Uncomment the following line (remove the '#' at the beginning):
port = 5432- Save and close the file.
- Open the pg_hba.conf file:
vi /var/lib/pgsql/12/data/pg_hba.conf- Add this line at the end of the file:
host airflow airflow {host_IP}/32 md5- Replace {host_IP} with the actual IP address of the machine running Apache Airflow.
- Save and close the file.
Restart PostgreSQL to apply changes:
sudo systemctl restart postgresql-12MySQL Database Setup for Airflow
To configure MySQL as the database backend for Apache Airflow, follow these steps:
Install MySQL Server:
sudo yum install mysql-serversudo yum install mysql-devel -y # or use sudo yum install mariadb-devel -y for MariaDBInstall the mysqlclient Python package:
pip3.11 install mysqlclientStart the MySQL service:
sudo systemctl start mysqldInstall MySQL Connector for Python:
pip3.11 install pymysqlSecure MySQL Installation (Optional but Recommended):
sudo mysql_secure_installationFollow the on-screen prompts to complete the security setup.
Create a database and user for Airflow:
- Access the MySQL shell:
sudo mysql -u root -pEnter the root password when prompted.
- Inside the MySQL shell, execute the following commands:
- Create the Airflow database:
CREATE DATABASE airflow CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;- Create a user for Airflow and set permissions:
CREATE USER 'airflow'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'airflow';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON airflow.* TO 'airflow'@'%';FLUSH PRIVILEGES;EXIT;Restart MySQL to apply changes:
sudo systemctl restart mysqldWith these steps, the MySQL database named 'airflow' and a user named 'airflow' are now set up with the necessary privileges. You can now proceed to configure Apache Airflow to use this MySQL database as its backend.
Ubuntu 20/22 Setup
Prerequisites
Update the package list:
sudo apt updateAdd the Deadsnakes PPA repository to install newer Python versions:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppaInstall Python 3.11 and the Python virtual environment package:
sudo apt install python3.11 python3.11-venv -yVerify the installation of Python and pip:
- Check the Python version:
python3.11 --version- Check the pip version:
pip3.11 --versionDatabase Setup
Follow the respective instructions below to configure your chosen database system for use with Apache Airflow.
PostgreSQL Database Setup
Install the psycopg2-binary Python package:
pip3.11 install psycopg2-binaryInstall PostgreSQL:
sudo apt install postgresql-12 postgresql-client-12Create a PostgreSQL database and user for Airflow:
- Access the PostgreSQL shell:
sudo -u postgres psql- Inside the PostgreSQL shell, execute the following commands:
- Create the Airflow database:
CREATE DATABASE airflow;- Create the Airflow user with a password:
CREATE USER airflow WITH PASSWORD 'airflow';- Configure settings for the Airflow user:
ALTER ROLE airflow SET client_encoding TO 'utf8';ALTER ROLE airflow SET default_transaction_isolation TO 'read committed';ALTER ROLE airflow SET timezone TO 'UTC';- Grant all privileges on the Airflow database to the Airflow user:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE airflow TO airflow;- Exit the PostgreSQL shell:
\qConfigure PostgreSQL settings for Airflow:
- Open and edit the PostgreSQL configuration file:
vi /etc/postgresql/12/main/postgresql.conf- Change and uncomment the listen_addresses to allow all connections:
listen_addresses = '*'- Uncomment the port line to use the default port 5432:
port = 5432- Modify the pg_hba.conf file to allow specific connections:

vi /etc/postgresql/12/main/pg_hba.conf- Add this line to permit connections from the Airflow server:
host airflow airflow {host_IP}/32 md5- Replace {host_IP} with the actual IP address of the machine running Apache Airflow.
Restart PostgreSQL to apply changes:
sudo systemctl restart postgresql.serviceThese steps have prepared your PostgreSQL database named 'airflow' and a user named 'airflow' with the necessary settings and privileges. You can now proceed to integrate this setup into Apache Airflow's configuration.
MySQL Database Setup for Airflow
Install MySQL Server:
- Download and install the MySQL APT repository:
wget http://repo.mysql.com/mysql-apt-config_0.8.12-1_all.debsudo dpkg -i mysql-apt-config_0.8.12-1_all.debsudo dpkg-reconfigure mysql-apt-config- Update the package list and import the repository key:
sudo apt updatesudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys B7B3B788A8D3785Csudo apt update- Check the MySQL server version available and install it:
sudo apt-cache policy mysql-serversudo apt install -f mysql-client=5.7*sudo apt install -f mysql-community-server=5.7*sudo apt install -f mysql-server=5.7*- Install the MySQL Connector for Java:
wget https://downloads.mysql.com/archives/get/p/3/file/mysql-connector-j_8.0.32-1ubuntu20.04_all.debsudo dpkg -i mysql-connector-j_8.0.32-1ubuntu20.04_all.debchmod 644 /usr/share/java/mysql-connector-j-8.0.32.jarInstall the mysqlclient Python package:
pip3.11 install mysqlclientStart the MySQL service:
sudo systemctl start mysqldInstall MySQL Connector for Python:
pip3.11 install pymysqlSecure MySQL Installation (Optional but Recommended):
Run the command to secure your MySQL installation, including setting a root password:
sudo mysql_secure_installationFollow the on-screen prompts to complete the security setup.
Create a database and user for Airflow:
- Access the MySQL shell:
sudo mysql -u root -pEnter the root password when prompted.
- Inside the MySQL shell, execute the following commands:
- Create the Airflow database with UTF-8 encoding:
CREATE DATABASE airflow CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;- Create a user for Airflow and grant privileges:
CREATE USER 'airflow'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'airflow';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON airflow.* TO 'airflow'@'%';FLUSH PRIVILEGES;EXIT;Restart MySQL to apply changes:
sudo systemctl restart mysqldWith these steps completed, the MySQL database named 'airflow' and a user named 'airflow' are set up with the necessary privileges. You can now proceed to configure Apache Airflow to use this MySQL database as its backend.
Before proceeding with the Apache Airflow installation from Ambari, ensure the Apache Airflow repository is set up correctly.
Apache Airflow Installation using Mpack on Ambari
Create symbolic links for Python to use Python 3.11:
sudo ln -sf /usr/bin/python3.11 /usr/bin/python3sudo ln -sf /usr/bin/pip3.11 /usr/bin/pip3This following provides the steps for installing and setting up Apache Airflow using Management Pack (Mpack) on an Ambari-managed cluster.
Install and Configure Mpack:
- Install Mpack:
ambari-server install-mpack --mpack=ambari-mpacks-airflow-2.8.1.tar.gz --verbose- Uninstall Previous Mpack (if needed):
ambari-server uninstall-mpack --mpack-name=airflow-ambari-mpack- Change Symlinks:
- Navigate to the services directory and update the Airflow symlink for each service version:
cd /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/stacks/ODP/3.0/servicesunlink AIRFLOWln -s /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/mpacks/airflow-ambari-mpack-2.8.1/common-services/AIRFLOW/2.8.1 AIRFLOWcd /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/stacks/ODP/3.1/servicesunlink AIRFLOWln -s /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/mpacks/airflow-ambari-mpack-2.8.1/common-services/AIRFLOW/2.8.1 AIRFLOWcd /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/stacks/ODP/3.2/servicesunlink AIRFLOWln -s /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/mpacks/airflow-ambari-mpack-2.8.1/common-services/AIRFLOW/2.8.1 AIRFLOWcd /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/stacks/ODP/3.3/servicesunlink AIRFLOWln -s /var/lib/ambari-server/resources/mpacks/airflow-ambari-mpack-2.8.1/common-services/AIRFLOW/2.8.1 AIRFLOW- Restart Ambari Server:
ambari-server restartYour Apache Airflow installation is now configured and ready for use on your Ambari-managed cluster.
Steps to install Apache Airflow from the Ambari UI
- Add the Airflow service from the Ambari UI.
- Specify the host details for the Airflow Scheduler and Airflow Webserver.
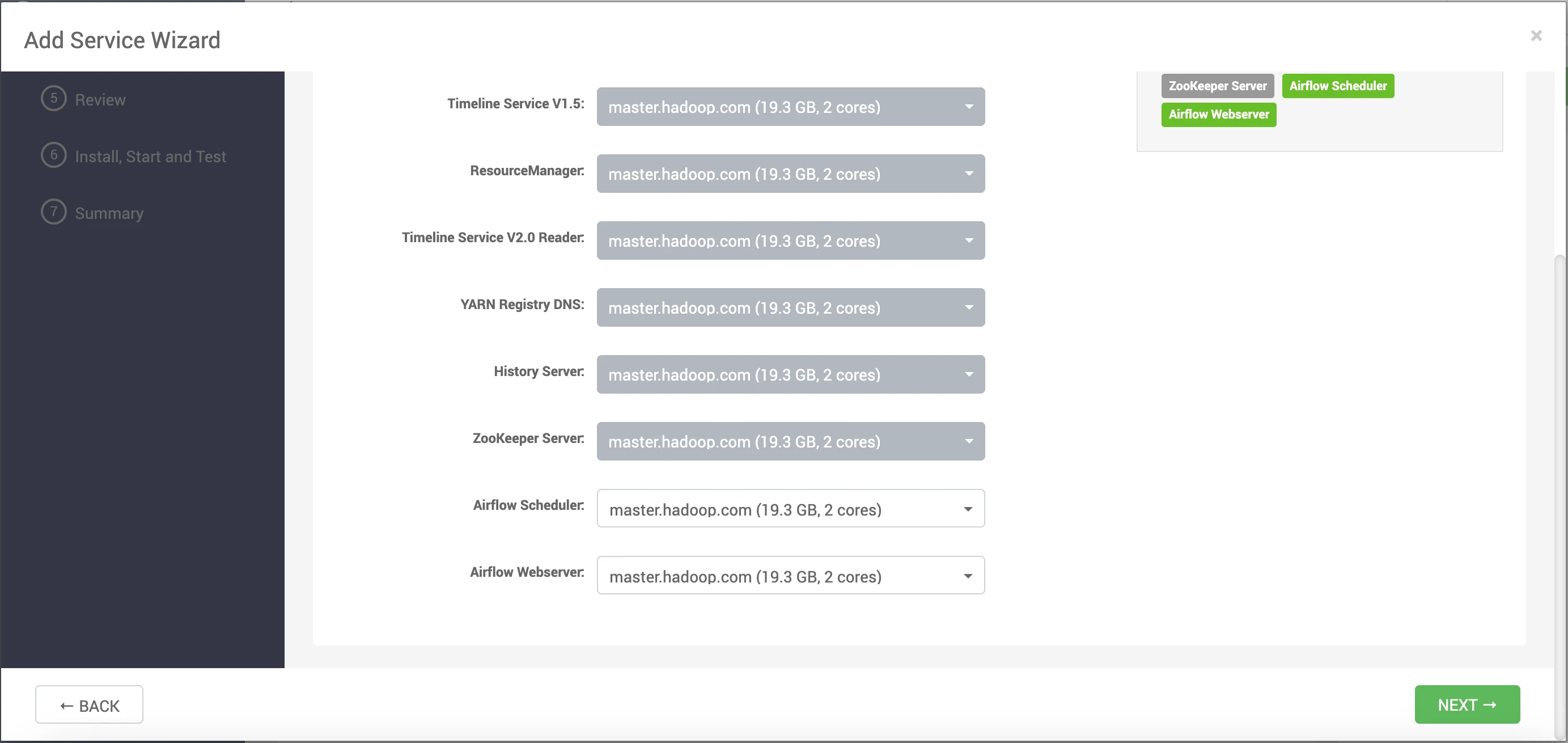
- Choose the slave client configuration.
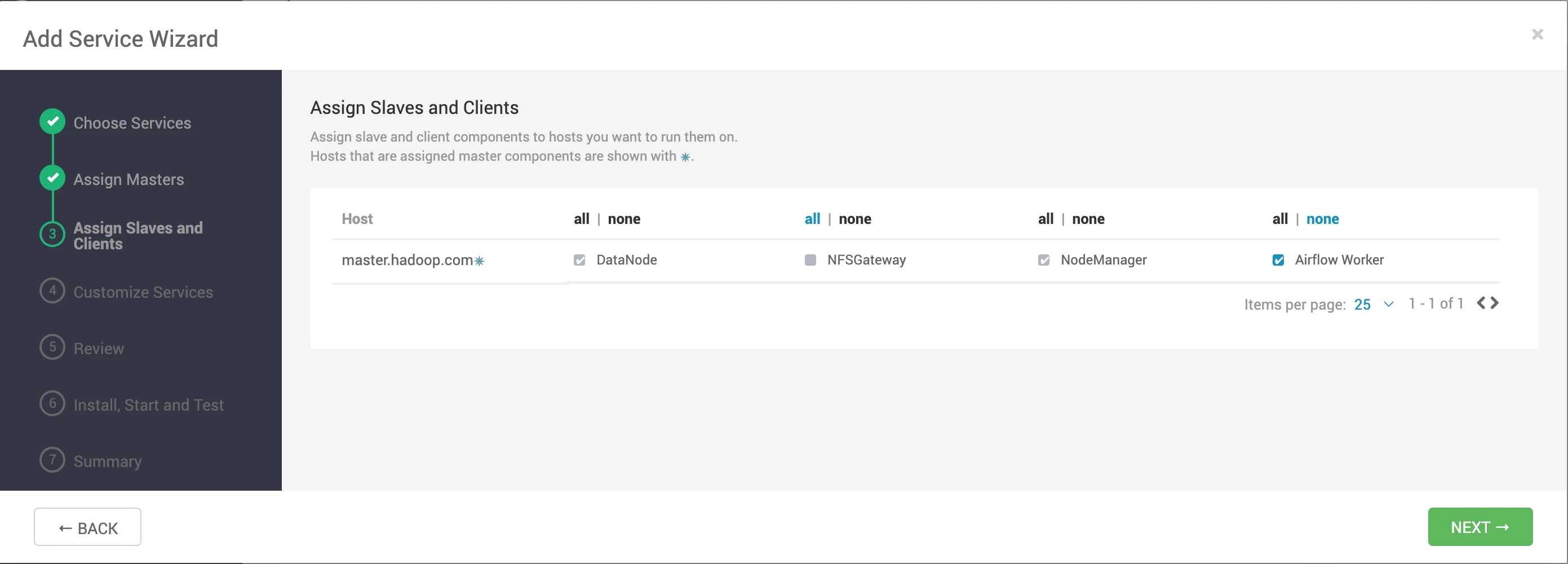
- Modify or customize the fields as needed.
Database Options:
Choose between MySQL or PostgreSQL as the backend database:
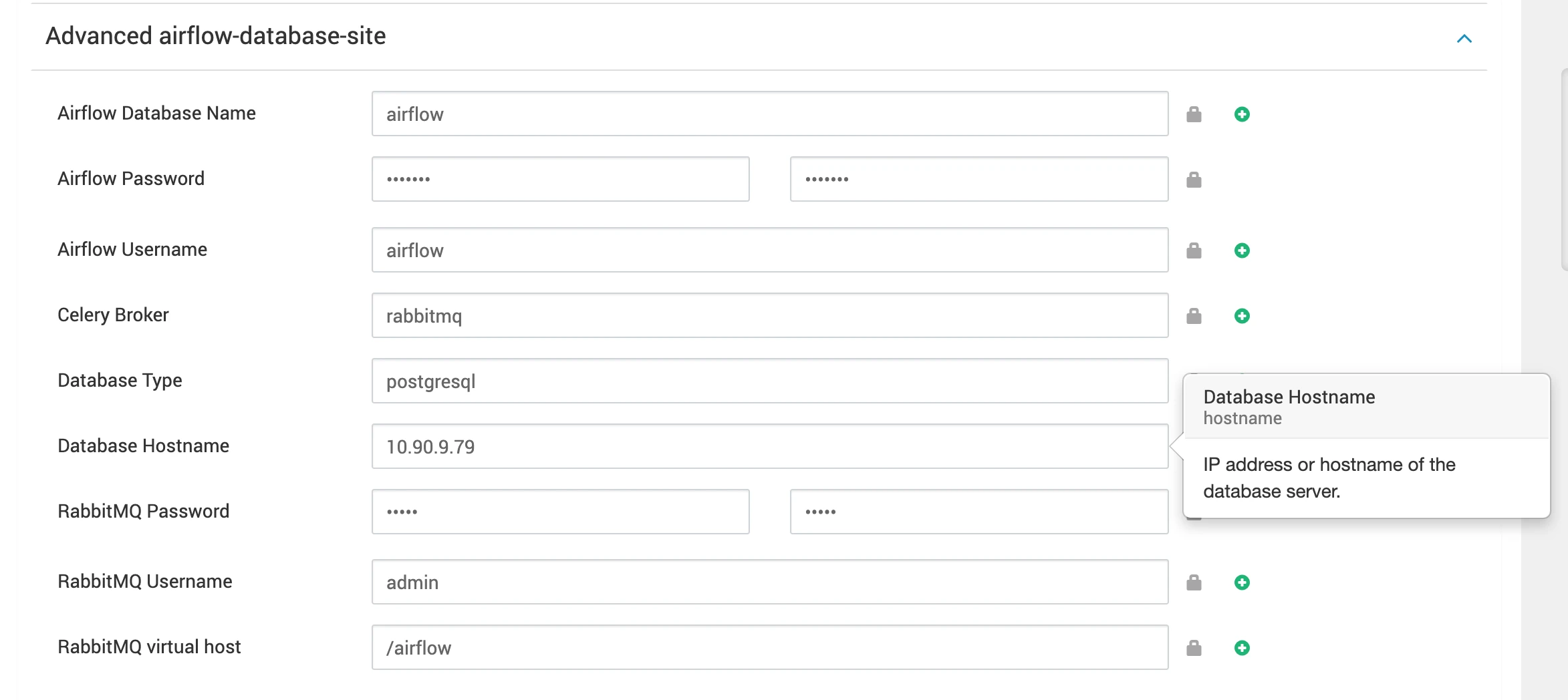
Configuring the Airflow backend database connection string and Celery settings. Users will be prompted to input specific information, including the database name, password, username, database type (choose between MySQL or PostgreSQL), and host IP. The provided script will then automatically generate the necessary configuration details for the database connection string and Celery settings.
Enter Database Information in ambari UI.
- Database Name
- Password
- Username
- Database Type: Choose between mysql or postgresql.
- Host IP
If you are using RabbitMQ then you have to setup and add RabbitMQ configurations.
- RabbitMQ Username
- RabbitMQ Password
- RabbitMQ virtual host
- Celery Broker
Once you have provided all the necessary details, click on the Next button.
- Deploy the Airflow service.
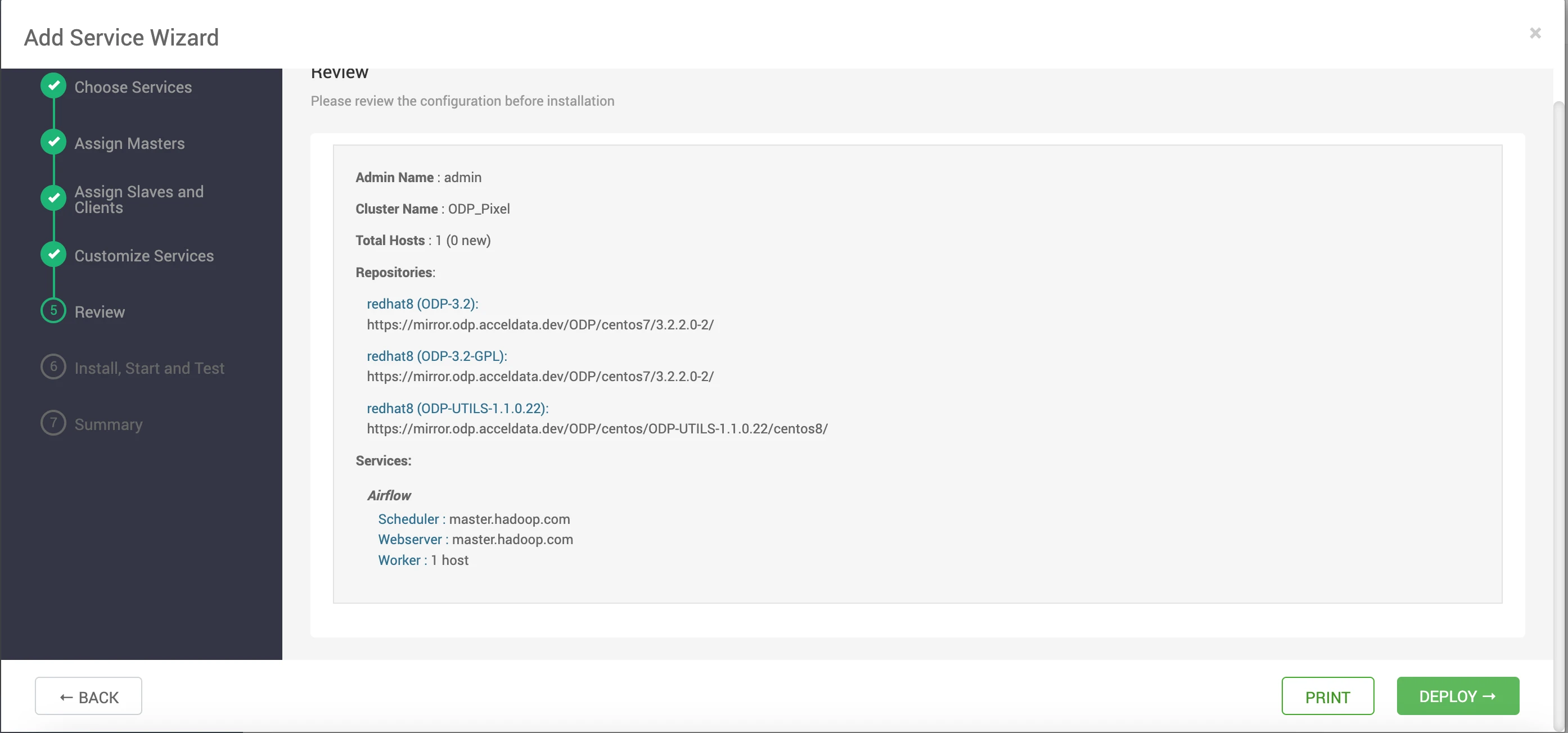
- This step will install all the necessary components and initiate the service.
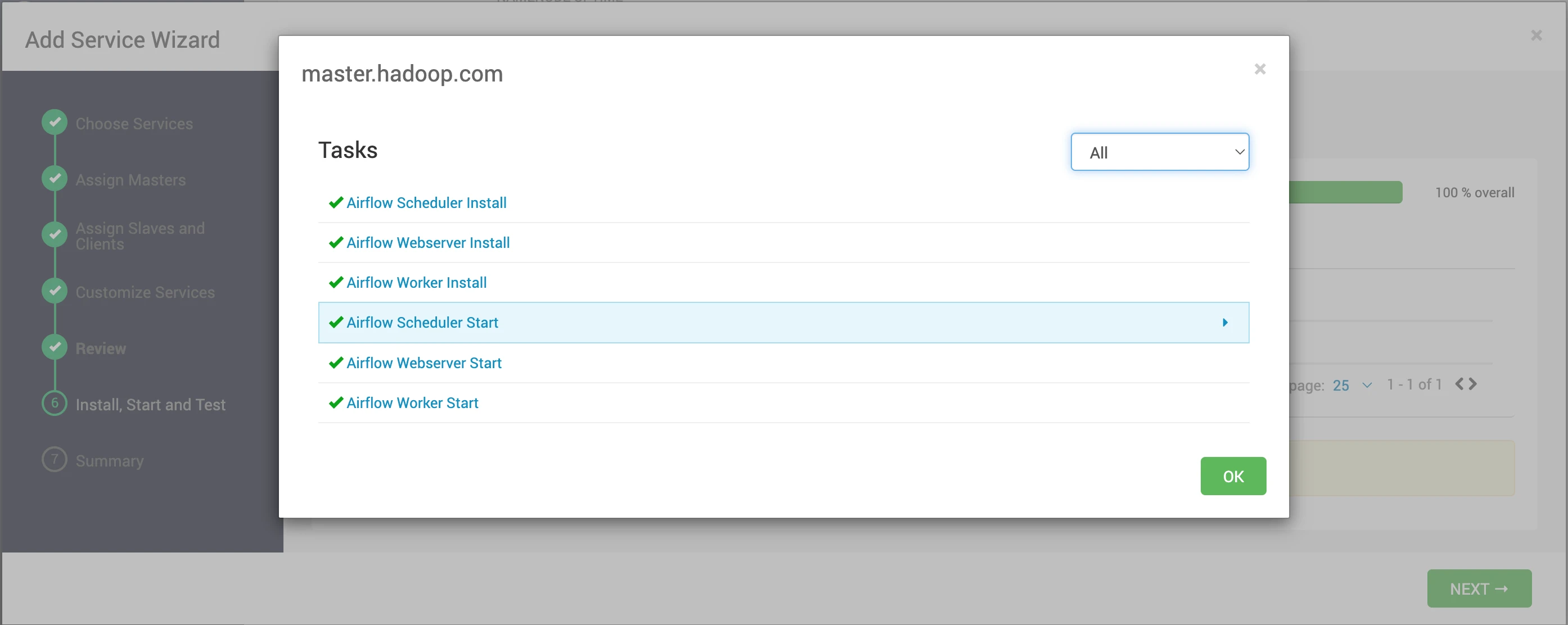
- The Airflow webserver is up and running. To access the UI, you need to create a username and password. To create the admin user, you must run the
initdbcommand from the Ambari UI.
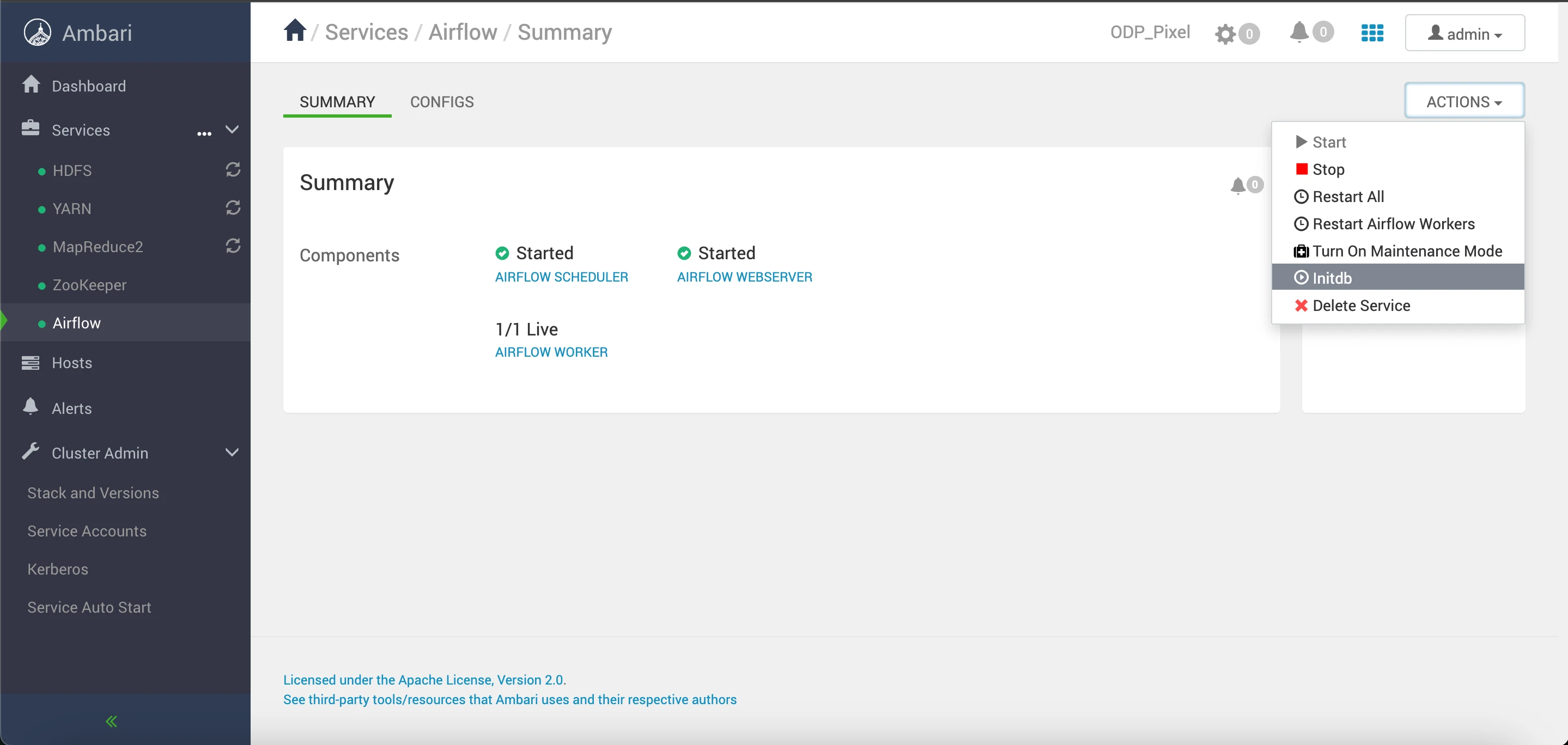
This command will generate an admin user named "airflow" with the password "airflow."
You can utilize these credentials (username: "airflow", password: "airflow") to log in and access the Airflow webserver UI.
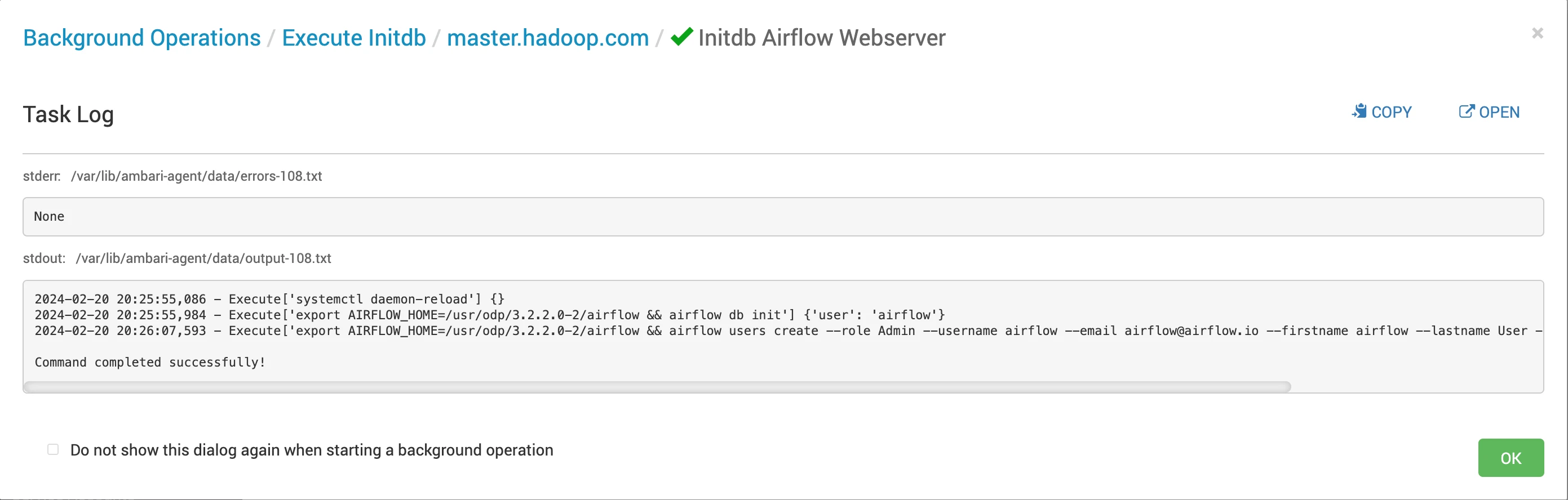
On completion of the database initialization, you can access the Airflow Webserver UI. Enter the provided credentials ("airflow" as the username and "airflow" as the password) to log in and access the Airflow webserver UI.