Apache Airflow LDAP Integration
To install required packages and configure Docker for LDAP Server and PHPLDAPADMIN, perform the following:
- Install and Configure Packages
- Install the OpenLDAP development package:
sudo yum install openldap-devel- Install Apache Airflow with LDAP support:
pip3.11 install apache-airflow[ldap]==2.8.1- Register the system and manage subscriptions:
sudo subscription-manager registersudo subscription-manager refreshsudo subscription-manager attach --auto- Set Up Docker for LDAP
- Add the Docker repository and install Docker CE with required configurations:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.reposudo dnf repolist -vsudo dnf install --allowerasing --nobest docker-cesudo dnf install https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/8/x86_64/stable/Packages/containerd.io-1.4.12-3.1.el8.x86_64.rpmsudo dnf install docker-ce- Start and verify Docker service:
sudo systemctl enable --now dockersystemctl is-active docker- Download and Configure Docker Compose
- Obtain Docker Compose and set permissions:
curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.23.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o docker-composesudo mv docker-compose /usr/local/bin && sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-composesudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/docker-compose /usr/bin/docker-compose- Prepare LDAP Directory Structure.
- Create directories and prepare the LDAP configuration in Airflow home directory:
mkdir -p airflow_ldap/ldapcd airflow_ldap/ldapvi bootstrap.ldif- Add the following content in the bootstrap.ldif file:
#In bootstrap.ldif file add below content# LDIF Export for dc=shihadeh,dc=intern# Server: openldap (openldap)# Search Scope: sub# Search Filter: (objectClass=*)# Total Entries: 9## Generated by phpLDAPadmin (http://phpldapadmin.sourceforge.net) on May 5, 2021 2:59 pm# Version: 1.2.5version: 1# Entry 1: dc=netflux,dc=comdn: dc=netflux,dc=comdc: netfluxo: netfluxobjectclass: topobjectclass: dcObjectobjectclass: organization# Entry 2: cn=bhead,dc=netflux,dc=comdn: cn=bhead,dc=netflux,dc=comcn: bheaddisplayname: Bob Headgivenname: bheadmail: bobhead@gmail.comobjectclass: inetOrgPersonobjectclass: topsn: BobHeaduserpassword: bob# Entry 3: cn=jwick,dc=netflux,dc=comdn: cn=jwick,dc=netflux,dc=comcn: jwickdisplayname: John Wickgivenname: jwickmail: johnwick@gmail.comobjectclass: inetOrgPersonobjectclass: topsn: JohnWickuserpassword: john# Entry 4: cn=mlamberti,dc=netflux,dc=comdn: cn=mlamberti,dc=netflux,dc=comcn: mlambertidisplayname: Marc Lambertigivenname: mlambertimail: marclamberti@gmail.comobjectclass: inetOrgPersonobjectclass: topsn: MarcLambertiuserpassword: marc# Entry 5: ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=comdn: ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=comobjectclass: organizationalUnitobjectclass: topou: Groups# Entry 6: cn=Admin,ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=comdn: cn=Admin,ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=comcn: Adminobjectclass: groupOfUniqueNamesobjectclass: topuniquemember: cn=mlamberti,dc=netflux,dc=com# Entry 7: cn=Data_science,ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=comdn: cn=Data_science,ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=comcn: Data_scienceobjectclass: groupOfUniqueNamesobjectclass: topuniquemember: cn=bhead,dc=netflux,dc=com# Entry 8: cn=Marketing,ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=comdn: cn=Marketing,ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=comcn: Marketingobjectclass: groupOfUniqueNamesobjectclass: topuniquemember: cn=jwick,dc=netflux,dc=com# Entry 9: ou=Users,dc=netflux,dc=comdn: ou=Users,dc=netflux,dc=comobjectclass: organizationalUnitobjectclass: topou: Users- Configure Docker Services for LDAP
- Create and configure docker-compose.yml in the airflow_ldap directory for LDAP and PHPLDAPADMIN:
vi airflow_ldap/docker-compose.ymlversion: '3'services: openldap: image: osixia/openldap:1.5.0 container_name: openldap hostname: openldap ports: - 389:389 - 636:636 volumes: - ./data/certificates:/container/service/slapd/assets/certs - ./data/slapd/database:/var/lib/ldap - ./data/slapd/config:/etc/ldap/slapd.d environment: - LDAP_ORGANISATION=netflux - LDAP_DOMAIN=netflux.com - LDAP_ADMIN_USERNAME=admin - LDAP_ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin - LDAP_CONFIG_PASSWORD=admin - "LDAP_BASE_DN=dc=netflux,dc=com" - LDAP_TLS_CRT_FILENAME=server.crt - LDAP_TLS_KEY_FILENAME=server.key - LDAP_TLS_CA_CRT_FILENAME=netflux.com.ca.crt phpldapadmin: image: osixia/phpldapadmin:0.9.0 container_name: phpldapadmin hostname: phpldapadmin ports: - 8888:80 environment: - PHPLDAPADMIN_LDAP_HOSTS=openldap - PHPLDAPADMIN_HTTPS=false depends_on: - openldapvolumes: postgres-db-volume:- Deploy services:
docker-compose up -d- Access PHPLDAPADMIN UI.
- Use the URL
http://{hostname/IP}:8888/to configure Apache Airflow LDAP authentication.
- Once the User Interface is accessible, modify Airflow Configuration
- Adjust
webserver_config.pyfor LDAP integration:
## Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one# or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file# distributed with this work for additional information# regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file# to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the# "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance# with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at## http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0## Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,# software distributed under the License is distributed on an# "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY# KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the# specific language governing permissions and limitations# under the License."""Default configuration for the Airflow webserver"""import osfrom flask_appbuilder.security.manager import AUTH_LDAPAUTH_TYPE = AUTH_LDAPAUTH_LDAP_SERVER = "ldap://10.90.9.78:389"AUTH_LDAP_USE_TLS = False# searchesAUTH_LDAP_SEARCH = "dc=netflux,dc=com" # the LDAP search baseAUTH_LDAP_UID_FIELD = "cn" # the username field# For a typical OpenLDAP setup (where LDAP searches require a special account):AUTH_LDAP_BIND_USER = "cn=admin,dc=netflux,dc=com" # the special bind username for searchAUTH_LDAP_BIND_PASSWORD = "admin" # the special bind password for search# registration configsAUTH_USER_REGISTRATION = True # allow users who are not already in the FAB DBAUTH_USER_REGISTRATION_ROLE = "Public" # this role will be given in addition to any AUTH_ROLES_MAPPINGAUTH_LDAP_FIRSTNAME_FIELD = "givenName"AUTH_LDAP_LASTNAME_FIELD = "sn"AUTH_LDAP_EMAIL_FIELD = "mail" # if null in LDAP, email is set to: "{username}@email.notfound"# a mapping from LDAP DN to a list of FAB rolesAUTH_ROLES_MAPPING = { "cn=Marketing,ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=com": ["Op"], "cn=Data_science,ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=com": ["Viewer"], "cn=Admin,ou=Groups,dc=netflux,dc=com": ["Admin"],}# the LDAP user attribute which has their role DNsAUTH_LDAP_GROUP_FIELD = "memberOf"# if we should replace ALL the user's roles each login, or only on registrationAUTH_ROLES_SYNC_AT_LOGIN = True# force users to re-auth after 30min of inactivity (to keep roles in sync)PERMANENT_SESSION_LIFETIME = 1800- Update Airflow through Ambari UI
- Navigate to the Ambari UI and update LDAP settings as specified:
[ldap]bind_user = cn=admin,dc=netflux,dc=comsearch_scope = LEVELbasedn = dc=netflux,dc=comuri = ldap://10.90.9.78:389group_member_attr = memberOfdata_profiler_filter =bind_password = admincacert =user_filter = objectClass=*user_name_attr = cnsuperuser_filter =[api]auth_backend = airflow.api.auth.backend.session[webserver]rbac = Trueauthenticate = TrueAdvanced airflow-ldap-site:

Advanced airflow-api-site:
Advanced airflow-webserver-site:

- Restart Airflow Components
- Restart to apply the new configurations and access the Airflow webserver UI using LDAP credentials.
It is advised to set up your own LDAP server with custom user configurations for security and management purposes.
Below the LDAP admin user has been configured:- Username: mlamberti- Password: marc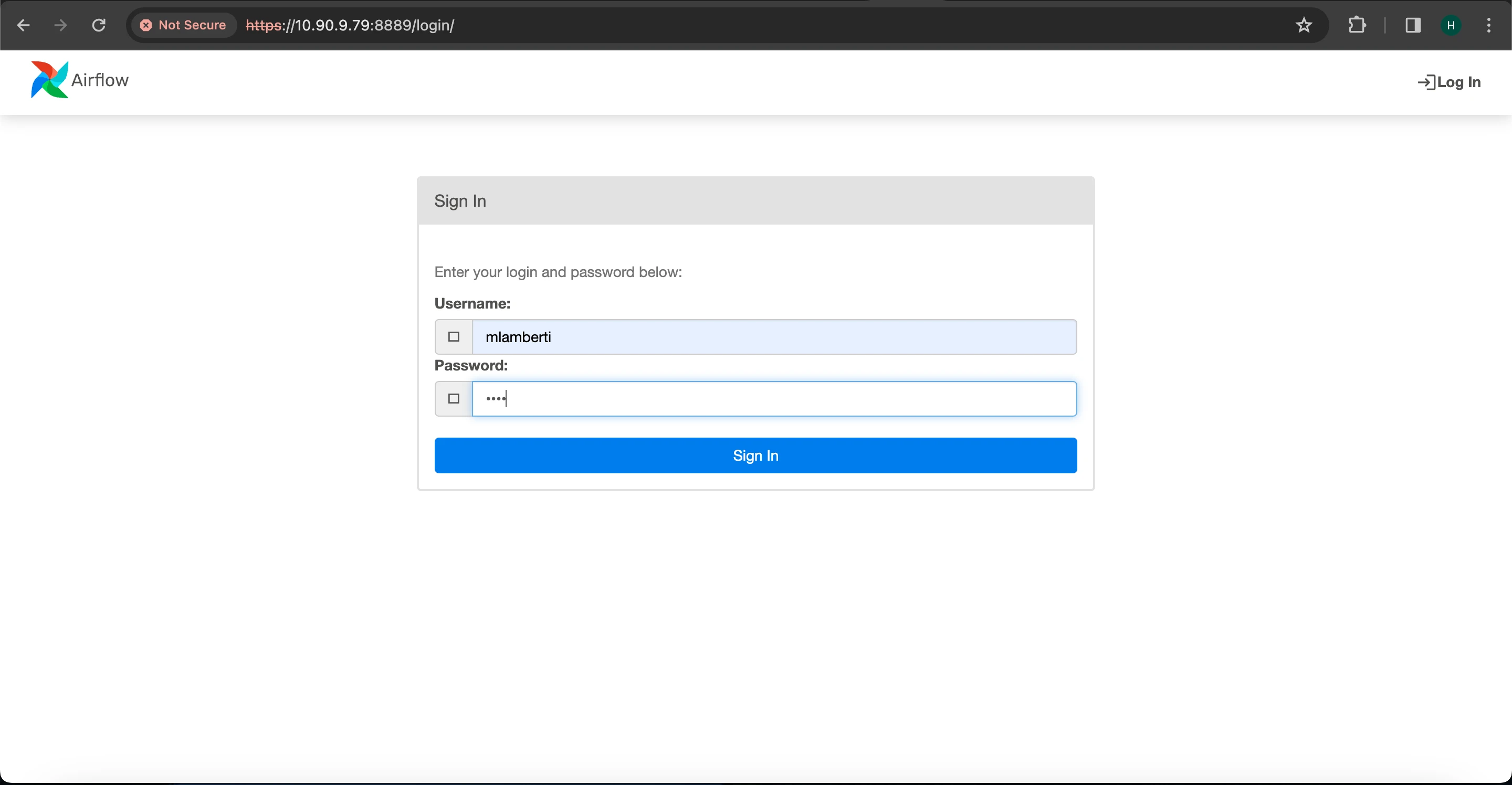
Apache Airflow SSL and Kerberos Integration
This section provides step by step instructions for setting up SSL within the Airflow environment. Beginning with generating SSL certificates and keys using OpenSSL, the process continues with configuring Airflow's web server settings via the Ambari UI. Following these steps ensures a robust SSL setup, enabling users to access the Airflow web server securely. Additionally, this guide touches on Kerberos integration, clarifying automated setup within Airflow and offering instructions for disabling Kerberos if needed.
SSL Setup
To set up SSL, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the Airflow home directory.
- Generate a new SSL certificate and key by running the following OpenSSL command:
openssl req \ -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout domain.key \ -x509 -days 365 -out airflow.crtAfter generating the SSL certificate and key, update the Airflow webserver configurations from the Ambari UI with the following settings:
- Set SSL Enable to True.
- Specify the web server host IP address.
Additionally, in the Ambari UI for the web server configuration, update the following parameters:
- Web server SSL certificate: /usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/airflow/airflow.crt
- Web server SSL key: /usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/airflow/domain.key
Specify the file path for the certificate and key files in the Ambari UI. __
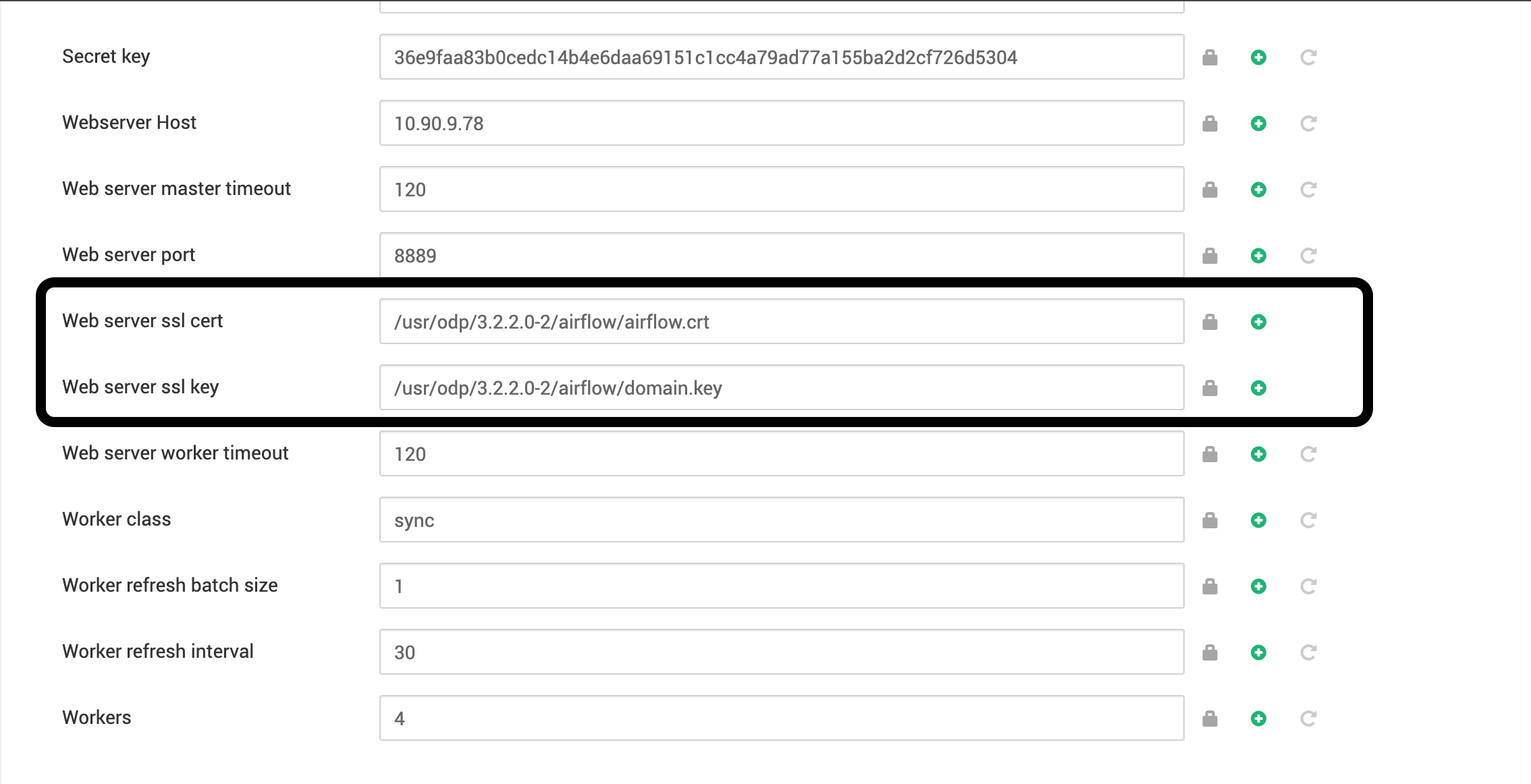
- Adjust the ownership and permissions of the SSL certificate and key files using the following commands:
chown airflow:airflow /usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/airflow/airflow.crt chmod 644 /usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/airflow/airflow.crt chown airflow:airflow /usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/airflow/domain.key chmod 600 /usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/airflow/domain.keyEnsure that the Certificate and Key files have the correct permissions assigned to them for both the airflow user and group.
- Restart the Airflow components and then access the Airflow webserver UI using the HTTPS protocol and the specified host IP and port (8889).
- Check if the HTTPS URL is functioning properly.
Kerberos Setup
Kerberos integration in Apache Airflow is automated when the cluster has Kerberos enabled. You need not manually configure Kerberos for Airflow. To disable or stop Kerberos after it's been enabled, simply toggle the Disable Kerberos checkbox. Kerberos will then be deactivated for the Apache Airflow service.
The checkbox to disable Kerberos can be found in the Advanced Kerberos Site section. Navigate to this section, locate the checkbox labeled Disable Kerberos, and select it to deactivate Kerberos for the Apache Airflow service.
Apache Airflow RabbitMQ Setup
RabbitMQ, an implementation of the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP), serves as a queueing service. It stands as a fast and reliable open-source message server, accommodating diverse scenarios such as reliable integration, content-based routing, global data dissemination, and robust monitoring alongside high-capacity data ingestion.
To configure RabbitMQ, perform the following:
- Install the EPEL repository and the curl utility:
dnf install epel-release curl -y- Add RabbitMQ repositories and proceed to install Erlang:
curl -s "https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/script.rpm.sh" | bashcurl -s "https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/rabbitmq/erlang/script.rpm.sh" | bashdnf install erlang -y- Install the RabbitMQ server:
dnf install rabbitmq-server -y- Initiate and enable the RabbitMQ server:
systemctl start rabbitmq-serversystemctl enable rabbitmq-server- Create an administrator user:
rabbitmqctl add_user admin- Configure tags for the administrator user:
rabbitmqctl set_user_tags admin administrator- View the list of users:
rabbitmqctl list_users- Establish a virtual host specifically for Airflow:
rabbitmqctl add_vhost airflow- Review the list of virtual hosts:
rabbitmqctl list_vhosts- Define permissions for the administrator user on the Airflow virtual host:
rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p airflow admin ".*" ".*" ".*"- Enable the RabbitMQ management plugin:
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management- Restart the RabbitMQ server:
systemctl restart rabbitmq-server- Install the pyamqp package for Python 3:
pip3.11 install pyamqp- Verify the current status:
rabbitmqctl statusss -antpl | grep 15672Update RabbitMQ Configuration via Ambari UI
For updating RabbitMQ configuration via the Ambari UI, perform the following:
- Log in to the Ambari UI.
- Navigate to the RabbitMQ service within the database configuration section.
- Locate the configuration section for the RabbitMQ service.
- Adjust relevant parameters in the RabbitMQ configuration, including host, port, credentials, and virtual host.
- Save the changes made.
- Restart the Airflow service, if necessary, to implement the modifications.
By utilizing the Ambari UI to update RabbitMQ configuration, ensure that the RabbitMQ service aligns with your specific needs.

Initiate the Airflow database initialization process through the Ambari UI.
Restart the Airflow services.
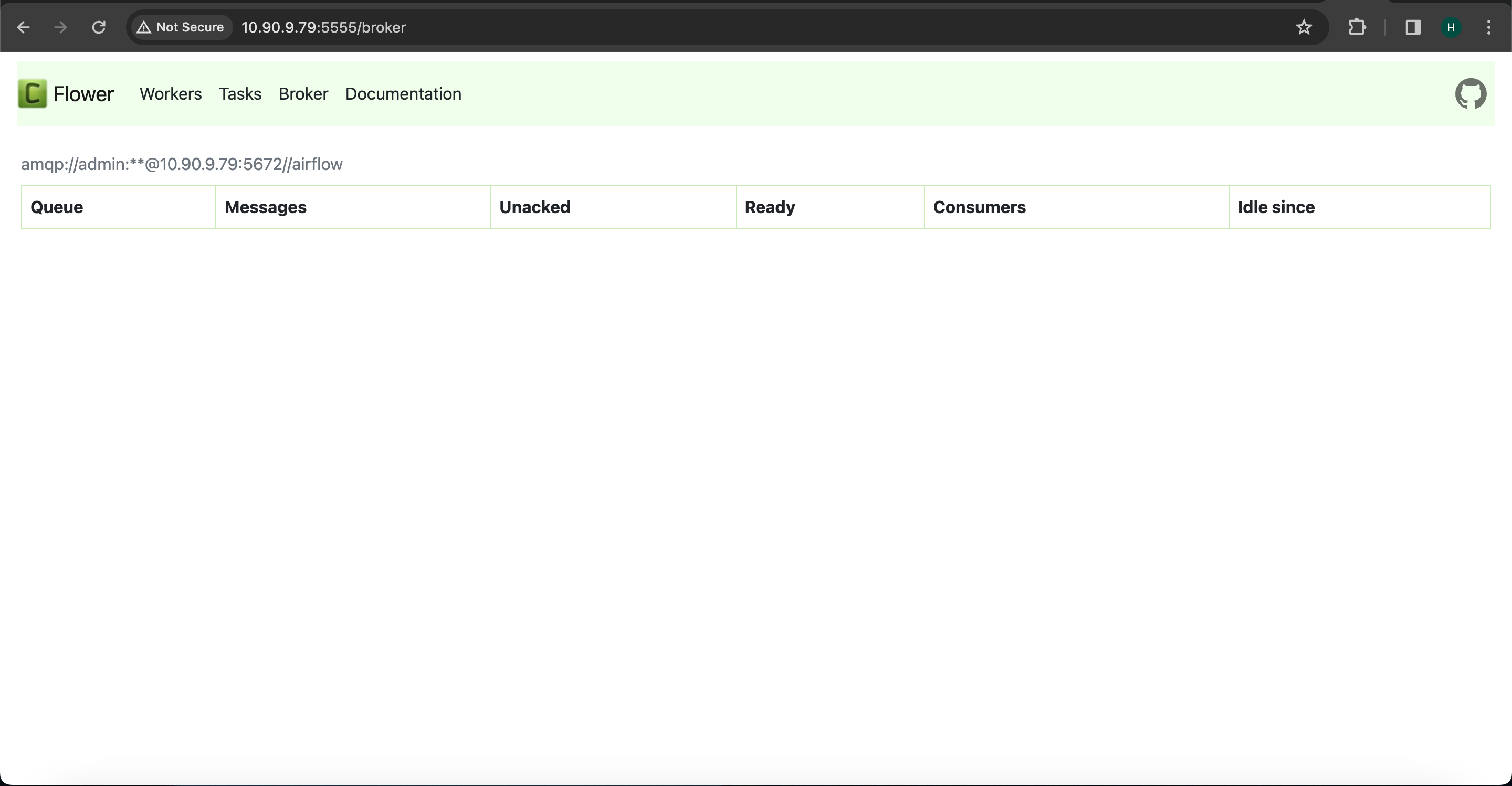
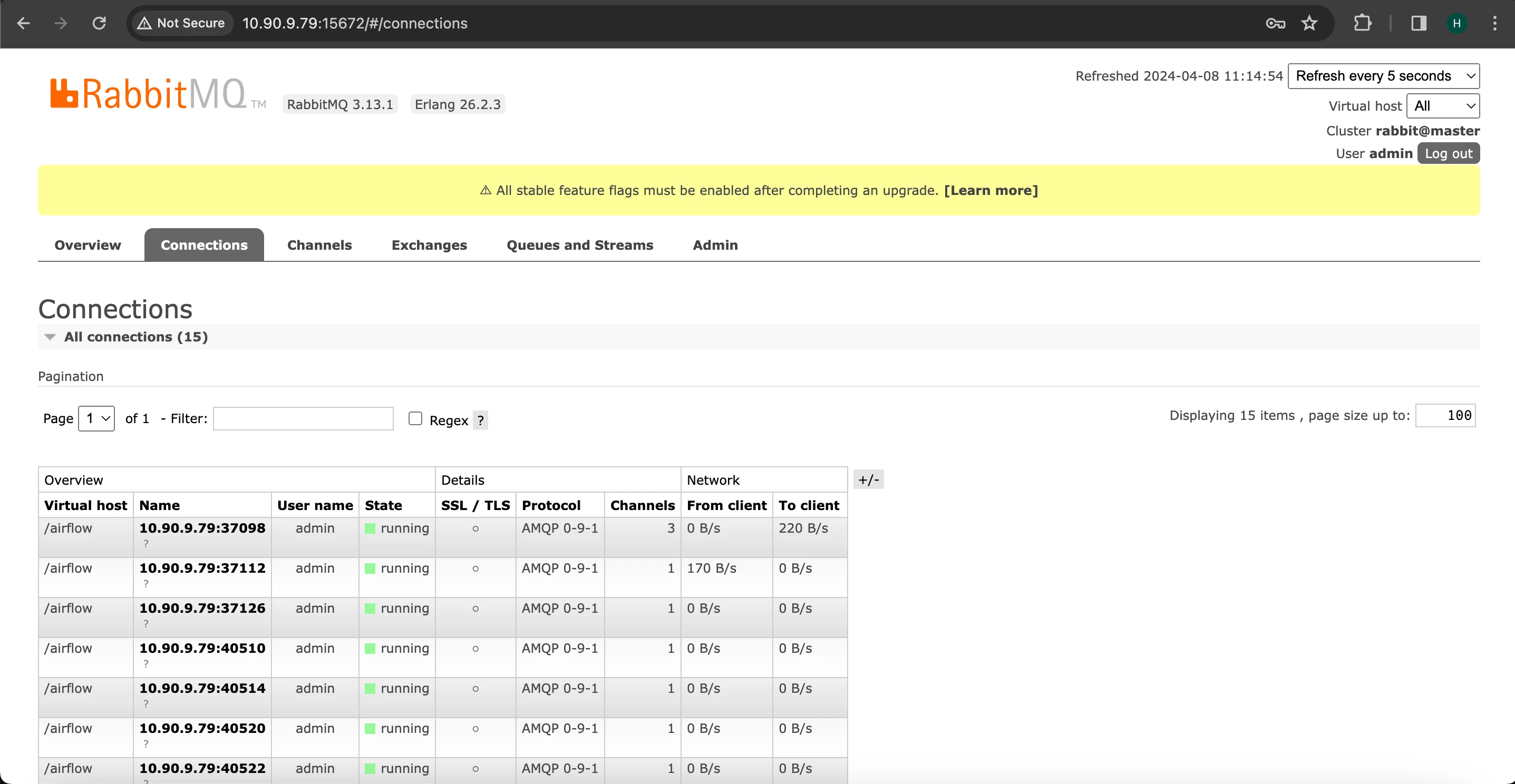
Check within the RabbitMQ UI to confirm the successful establishment of the connection.
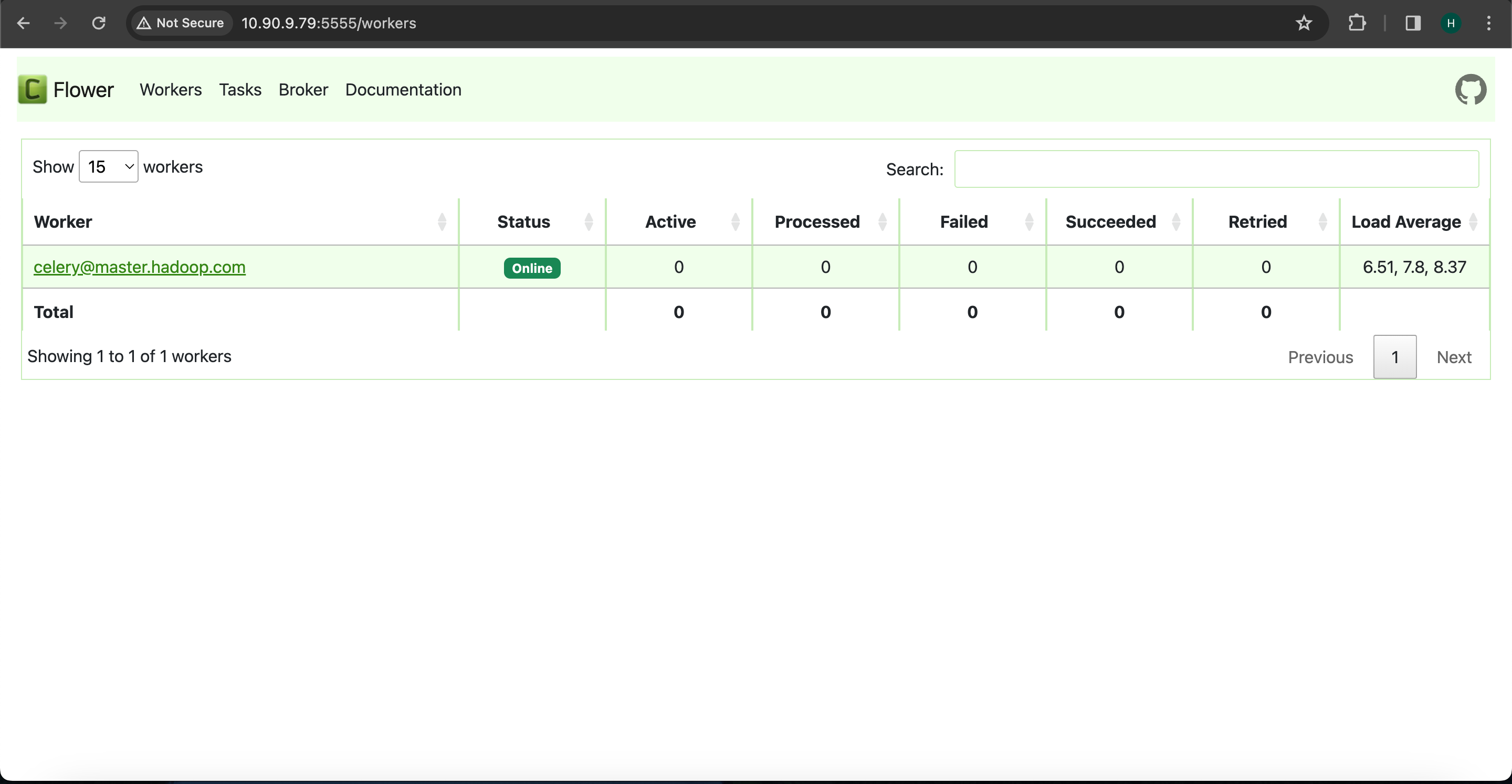
Monitor Celery Workers Using Flower UI
To monitor Celery workers, utilize the Flower UI.
Flower is a web-based tool designed for monitoring and managing Celery clusters. It features a user interface that provides comprehensive insights into all Celery workers. The interface offers clear statistics regarding active tasks and processed tasks, indicating their success or failure status, along with the load average of the tasks. Additionally, Flower maintains detailed information such as task names, arguments, results, and task completion times.
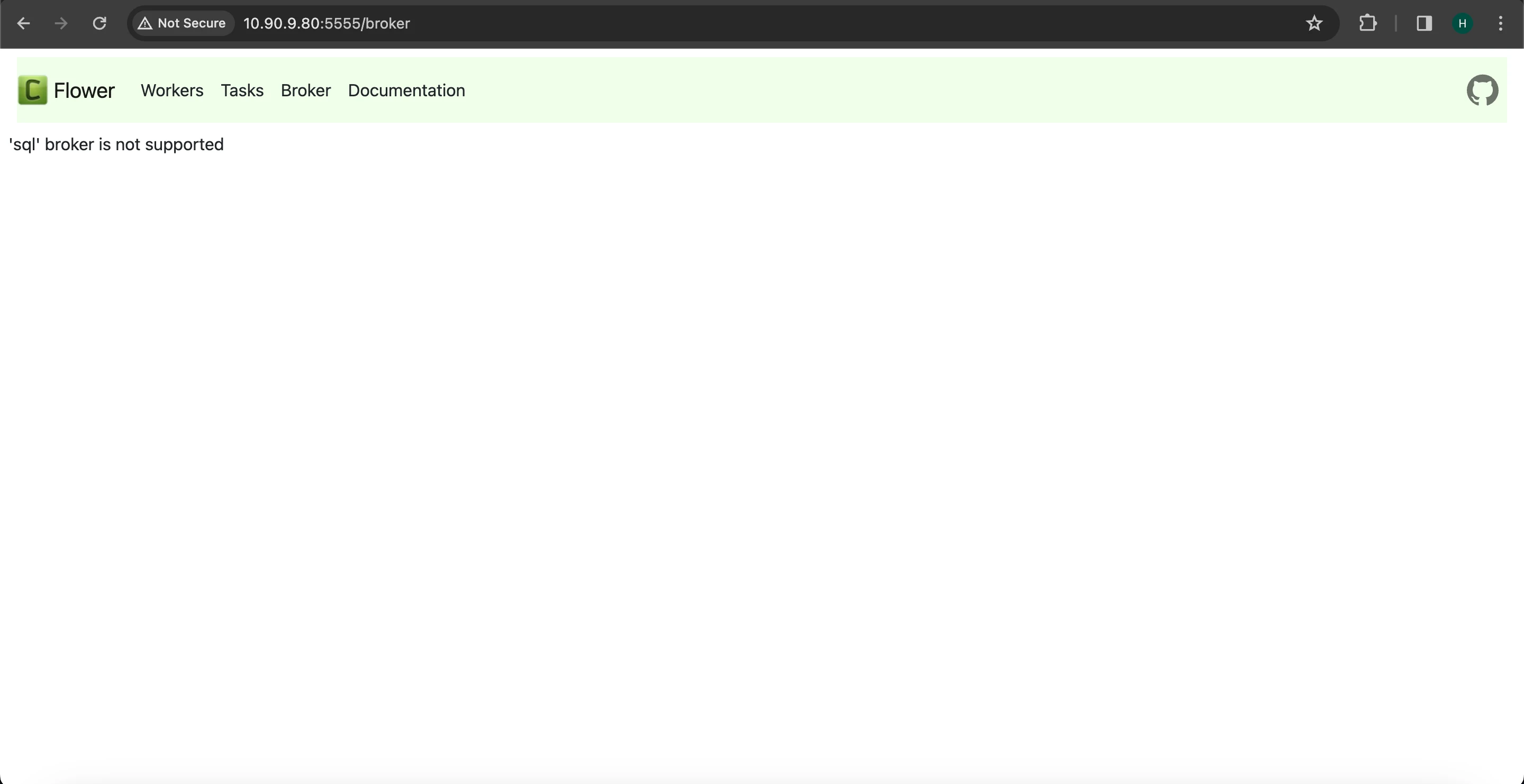
The Flower UI for Celery Worker is currently operational on port 5555. However, it is incompatible with SQL brokers. To enable monitoring with the Flower UI for Celery workers, it is necessary to configure RabbitMQ as the message queuing broker.
Once RabbitMQ is configured and the connection is established as visible in the RabbitMQ UI, attempt to access the Flower UI. This should allow you to observe the Celery workers running within the Flower UI.