Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Configure Apache Hive with S3A (applies only to 3.3.6.1-101)
This document describes how Apache Hive supports secure, session-level access to Amazon S3 using S3A without requiring cluster-wide configuration or service restarts. It explains the limitations of traditional static credential management and introduces a JCEKS-based credential provider approach to safely enable DDL and DML operations.
The document outlines current constraints around multi-bucket access, Spark, Impala, and Hive Metastore integration. It also summarizes supported stack versions, known limitations, and recommended workarounds across the Hive ecosystem.
Open Source Pull Request Reference
- Apache Hive Pull Request: https://github.com/apache/hive/pull/5257
Problem Statements
Apache Hive integration with S3A presents the following challenges:
- Accessing a single S3 bucket at the session level
- Accessing multiple S3 buckets within a single session
- Providing fine-grained access control for a specific path within an S3 bucket
This document primarily addresses Problem Statement 1 and outlines the current limitations related to Problem Statement 2.
Existing Configuration Challenges
To access S3A storage, the following configurations must traditionally be defined in Ambari → HDFS → core-site.xml:
fs.s3a.endpointfs.s3a.access.keyfs.s3a.secret.key
Drawbacks of This Approach
- Only one S3 bucket can be configured for the entire cluster.
- All users gain access to the configured bucket.
- Any configuration change requires a service restart, which is unsuitable for production environments.
Session-Level Credential Limitations
If a user attempts to define S3A credentials at the session level, Data Definition Language (DDL) operations fail because the Hive Metastore (HMS) does not receive these credentials.
This occurs because HMS operates independently from the HiveServer2 (HS2) session and lacks access to runtime credentials.
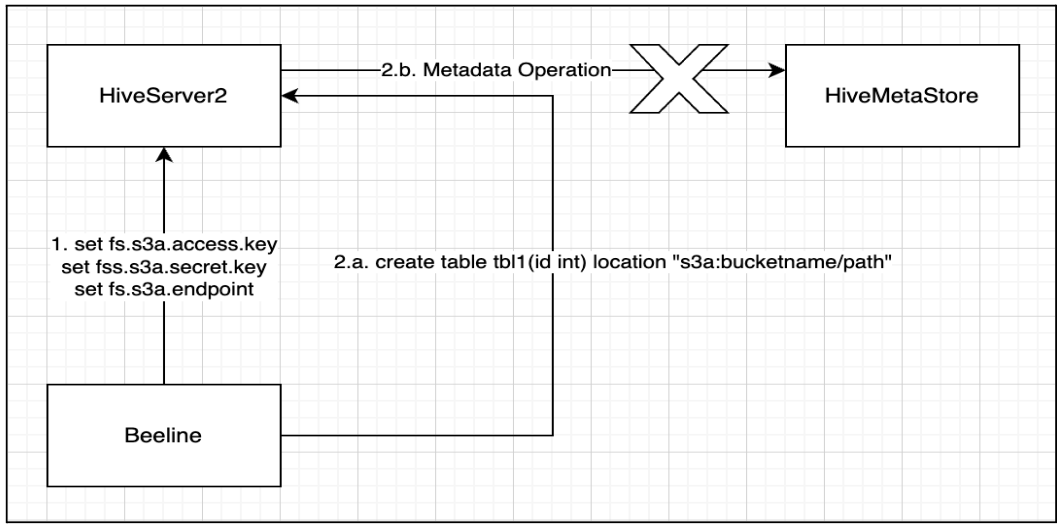
Introduced Improvements
To address this issue, the following Hive enhancements were introduced:
- HIVE-16913
- HIVE-28272
With the solution proposed in HIVE-28272, S3A-related configurations are exposed via metaconf. This enables users to define S3A credentials using Beeline, allowing successful execution of DDL operations.
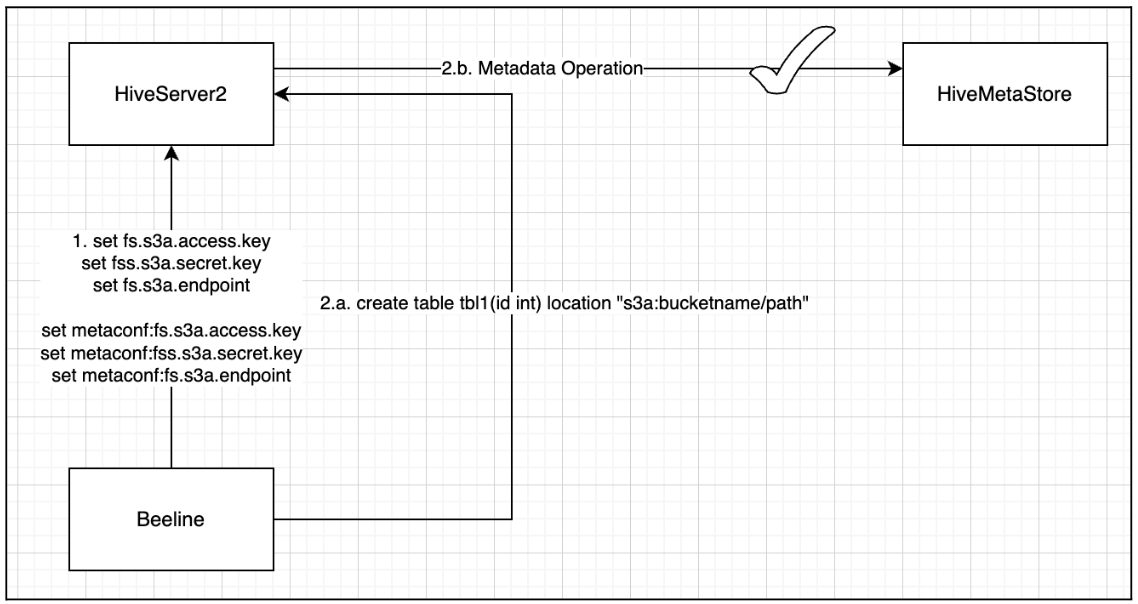
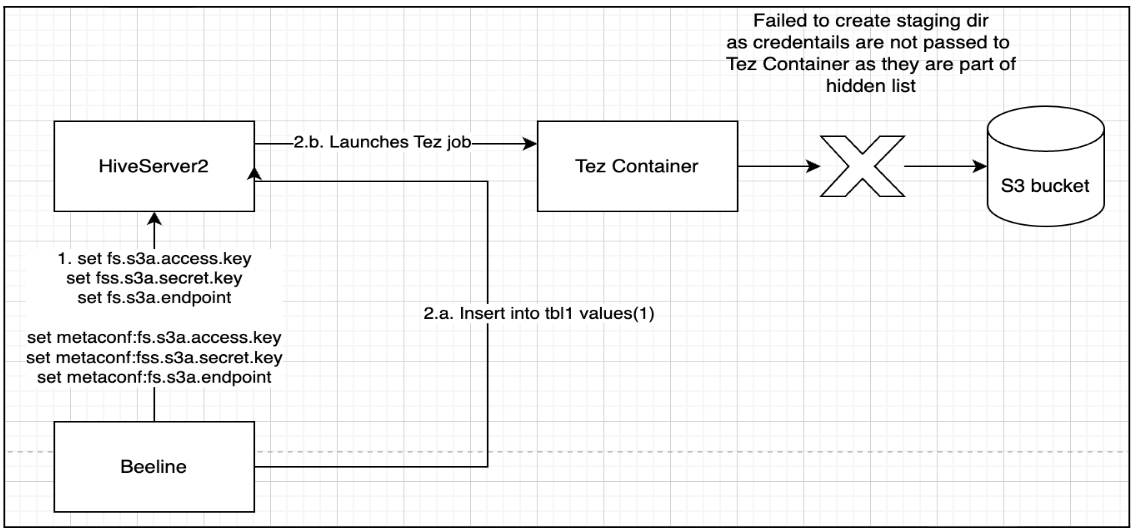
Remaining Issue with DML Operations
During INSERT (DML) operations, queries fail because:
- Tez containers cannot create staging directories in S3A table locations.
- S3A credentials are not propagated from HS2 to Tez.
- Credentials such as access key and secret key are part of the hidden configuration list.
DAGUtilsclears these sensitive configurations before passing them to the job configuration.
Insecure Workaround (Not Recommended)
Removing S3A credentials from the hidden configuration list allows both DDL and DML operations to succeed. However, this approach introduces a critical security risk, as credentials become visible in:
- Tez View
- Tez DAGs
- Hive protocol logging
This approach is strongly discouraged.
Proposed Solution
Based on the Hadoop AWS module documentation, the recommended and secure approach is to use Hadoop Credential Providers (JCEKS) to store and propagate S3A credentials.
Create Hadoop Credential File
Execute the following commands to create credentials securely:
hadoop credential create fs.s3a.access.key \ -value <access_key> \ -provider jceks://hdfs@<ActiveNameNode>:<port>/user/backup/s3.jcekshadoop credential create fs.s3a.secret.key \ -value <secret_key> \ -provider jceks://hdfs@<ActiveNameNode>:<port>/user/backup/s3.jceks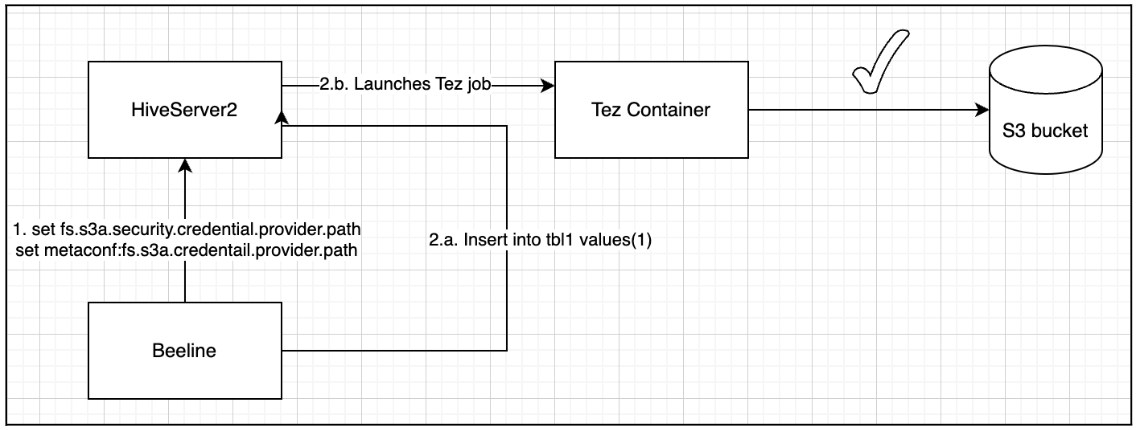
Credential files can be stored on any Hadoop-supported filesystem. File permissions are automatically restricted to the creator. However, directory permissions must be manually verified to ensure restricted access.
Configure Session-Level Access in Beeline
set fs.s3a.security.credential.provider.path=jceks://hdfs@<ActiveNameNode>:<port>/user/backup/s3.jceks;set metaconf:fs.s3a.security.credential.provider.path=jceks://hdfs@<ActiveNameNode>:<port>/user/backup/s3.jceks;The property hadoop.security.credential.provider.path is global to all filesystems and secrets. There is another property, fs.s3a.security.credential.provider.path which only lists credential providers for S3A filesystems. The two properties are combined into one, with the list of providers in the fs.s3a. property takes precedence over that of the hadoop.security list (i.e. they are prepended to the common list).
This approach ensures:
- Credentials are never exposed in plaintext.
- No service restart is required.
- Access is limited to authorized users.
Validated Steps and Example
ODP Hive Configuration Requirements
S3 access key, secret key, and endpoint configurations must not be defined statically in Hive or HDFS configuration files.
To allow runtime configuration changes, include the following property in hive-site.xml:
hive.security.authorization.sqlstd.confwhitelist.append=fs\\.s3a\\.path\\.style\\.access|fs\\.s3a\\.security\\.credential\\.provider\\.path|fs\\.s3a\\.bucket\\..*\\.security\\.credential\\.provider\\.pathWhen creating and storing Hadoop credentials on HDFS or a Unix file system, permissions are automatically set to restrict file access to the reader. However, as directory permissions are not inherently modified, users must verify that the containing directory's permissions limit readability exclusively to the current user.
Credential Creation Example
hadoop credential create fs.s3a.access.key \ -value <access_key> \ -provider jceks://hdfs@<nn_ip_or_nameservice>:8020/user/hive/s3.jcekshadoop credential create fs.s3a.secret.key \ -value <secret_key> \ -provider jceks://hdfs@<nn_ip_or_nameservice>:8020/user/hive/s3.jceksVerify path ownership and permissions based on user requirements.
Example Beeline Session
The available S3 bucket for this example is odp-ranger-test here, and the subsequent commands are executed via beeline. The Hive user was utilized to initiate the session, as it possesses the requisite access to the local JCEKS file within the Hive configuration located at /etc/hive/conf. Upon initialization, the initial session configuration will persist and will not be overridden, as the warehouse configuration is loaded only once.
#Set endpoint configurationset fs.s3a.endpoint=s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com;set metaconf:fs.s3a.endpoint=s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com;#Set credential provider configurationsset fs.s3a.security.credential.provider.path=jceks://hdfs@<nn_ip or nameservice>:8020/user/hive/s3.jceks;set metaconf:fs.s3a.security.credential.provider.path=jceks://hdfs@<nn_ip or nameservice>:8020/user/hive/s3.jceks;CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS sample_table_S16 ( id INT, name STRING ) STORED AS PARQUET LOCATION 's3a://odp-ranger-test/test-bucket';Current Limitation – Accessing Multiple Buckets in a Session
Hadoop AWS supports per-bucket credential providers, for example:
set fs.s3a.bucket.bucket1.security.credential.provider.path=/path/to/s3.jceks;set metaconf:fs.s3a.bucket.bucket1.security.credential.provider.path=/path/to/s3.jceks;However, Hive does not currently allow dynamic creation of metaconf keys unless they are explicitly defined in MetastoreConf.java.
As a result:
- Per-bucket configuration keys cannot be set dynamically.
- Accessing multiple buckets within a single session is not supported.
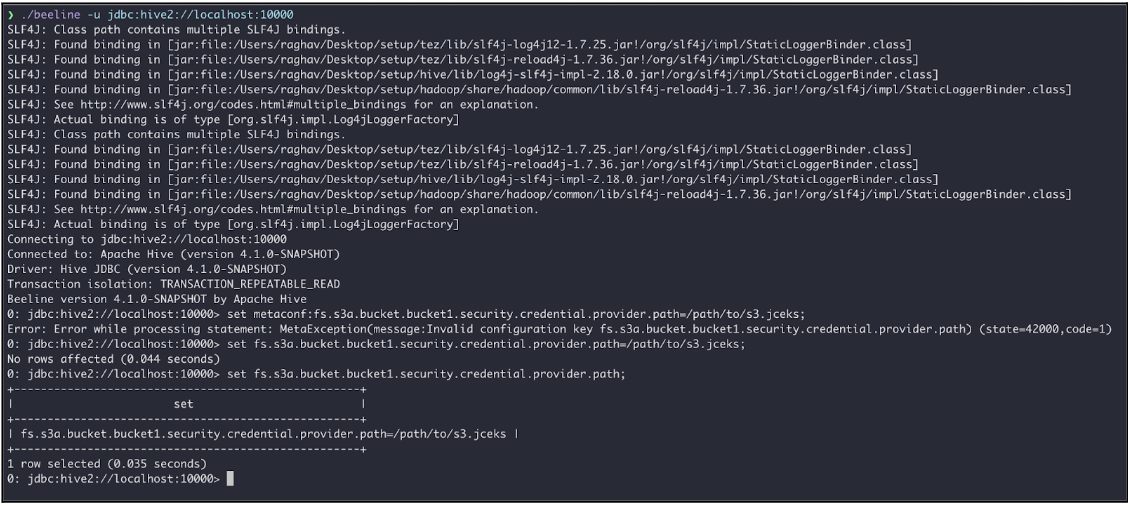
To make this work, you need to allow metaconf to create the configuration that starts with prefix fs.s3a.bucket at runtime. Otherwise, the user cannot access multiple buckets simultaneously in a session. This will be additional work in order to support accessing multiple buckets in a session and being tracked here.
HDFS Support
Starting with Hadoop 3.3, delegation token support (HDFS-14556) allows S3A properties to be defined at runtime without requiring service restarts
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="<AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID>"export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="<AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY>"export S3_ENDPOINT_URL="https://s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com"hdfs dfs -Dfs.s3a.security.credential.provider.path="jceks://hdfs@rocky8tpl:8020/user/hive/s3.jceks" -Dfs.s3a.endpoint="s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com" -ls s3a://hadoops3testbucket/dynamic\_demo/sample\_table\_spark/25/12/19 10:22:58 INFO impl.MetricsConfig: Loaded properties from hadoop-metrics2.properties25/12/19 10:22:58 INFO impl.MetricsSystemImpl: Scheduled Metric snapshot period at 10 second(s).25/12/19 10:22:58 INFO impl.MetricsSystemImpl: s3a-file-system metrics system startedFound 3 items-rw-rw-rw- 1 hive hive 0 2025-12-19 09:26 s3a://hadoops3testbucket/dynamic_demo/sample_table_spark/_SUCCESS-rw-rw-rw- 1 hive hive 723 2025-12-19 09:26 s3a://hadoops3testbucket/dynamic_demo/sample_table_spark/part-00000-77d63d45-1de0-428a-977c-c7d210c2e28b-c000.snappy.parquet-rw-rw-rw- 1 hive hive 708 2025-12-19 09:26 s3a://hadoops3testbucket/dynamic_demo/sample_table_spark/part-00001-77d63d45-1de0-428a-977c-c7d210c2e28b-c000.snappy.parquet25/12/19 10:23:00 INFO impl.MetricsSystemImpl: Stopping s3a-file-system metrics system...25/12/19 10:23:00 INFO impl.MetricsSystemImpl: s3a-file-system metrics system stopped.25/12/19 10:23:00 INFO impl.MetricsSystemImpl: s3a-file-system metrics system shutdown complete.Spark S3 Support
Spark 3 does not support propagating Hive Metastore (metaconf) properties from the session to HMS.
As a result:
- Session-level S3A configuration updates are ineffective for HMS-backed operations.
- File-level reads and writes work.
- DDL and DML operations requiring HMS interaction fail after data is written.
Impala Support
Session-level credential updates are not supported in Impala.
Reference: https://impala.apache.org/docs/build/html/topics/impala_s3.html
Ranger S3 Support
Addressing Problem Statement 3 (fine-grained access control at the path level) requires S3 governance solutions such as Apache Ranger.
This capability is currently under internal evaluation.
Matrix Support
To implement static configurations, please refer to the standard documentation and incorporate the following configuration into the Ambari Hive configuration:
hive.conf.hidden.list = javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword,hive.server2.keystore.password,fs.s3a.proxy.password,dfs.adls.oauth2.credential,fs.adl.oauth2.credentialCaution: This configuration modification is insecure, as it permits configurations containing sensitive information (secrets) to be displayed in plain text.
Mandatory Configurations to be Incorporated within the requisite XML configurations for HDFS, Hive, Impala, Tez, and Spark3
<property> <name>fs.s3a.access.key</name> <value>YOUR_ACCESS_KEY</value></property><property> <name>fs.s3a.secret.key</name> <value>YOUR_SECRET_KEY</value></property><property> <name>fs.s3a.endpoint</name> <value>YOUR_VAST_S3_ENDPOINT</value></property><property> <name>fs.s3a.connection.ssl.enabled</name> <value>false</value> <description>This setting should be configured as 'true' if the specified endpoint utilizes the HTTPS protocol.</description></property><property> <name>fs.s3a.path.style.access</name> <value>true</value> <description>This configuration is mandatory for the majority of S3 implementations that do not reside within the Amazon Web Services environment.</description></property><property> <name>fs.s3a.impl</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.fs.s3a.S3AFileSystem</value></property><property> <name>fs.s3a.aws.credentials.provider</name><value>org.apache.hadoop.fs.s3a.SimpleAWSCredentialsProvider</value> <description>For production deployments, the utilization of a more robust security provider, such as JceksspCredentialProvider, is highly recommended.</description></property>The primary distinction between session and static configuration lies in their usability during Spark operations on non-ACID tables, given that Hive metastore configurations cannot be propagated within a Spark session, as detailed in the Spark support section mentioned previously.
The S3 session level credential operational support and the matrix below is valid for stack support on ODP-3.2 (v3.2.3.5-2 onwards) and ODP-3.3 (v3.3.6.3-101 onwards).
| Operation(s) | Hive(JDBC/Beeline) | Spark(Direct) without HWC | Spark with HWC * | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Create Table (Partitioned & Unpartitioned) | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Create a table using Hive as it's a metastore operation |
Insert into/overwrite (Partitioned & Unpartitioned) static or dynamic | ✅ | ❗ | ✅ | Create the table using Beeline, but insert data using Spark DataFrame operations instead of INSERT SQL statements. Run msck repair on Beeline to view new or updated partition results. |
| show partitions | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| msck repair | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Metastore operation |
| Alter table | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Metastore operation |
| Drop table | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Metastore operation |
| Alter partition | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Metastore operation |
| Drop partition | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Metastore operation |
| Update ACID table (Partitioned & Unpartitioned) | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ACID operation |
| Delete ACID table (Partitioned & Unpartitioned) | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ACID operation |
Spark + Hive Integration (Write) - Known Limitation
INSERT via Spark SQL: Failure
S3 credential propagation to the Hive Metastore Server (HMS) is unsuccessful.
Issue Description: When an INSERT operation is submitted via Spark, the Hive Metastore Server (HMS) attempts to validate the S3A location. However, the HMS lacks the necessary S3A credentials that are present in the Spark session. This represents a known limitation when employing session-level S3A configurations.
Recommended Workaround: Utilize the DataFrame API in lieu of SQL INSERT statements.
df.write.mode("append").insertInto("table_name")Please utilize the following Spark configuration for establishing a connection with the Hive Warehouse Connector (HWC) using prepared jceks file:
import com.acceldata.hwc.HiveWarehouseSessionimport com.acceldata.hwc.HiveWarehouseSession._val hive = HiveWarehouseSession.session(spark).build()hive.execute("set fs.s3a.endpoint=s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com")hive.execute("set metaconf:fs.s3a.endpoint=s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com")hive.execute("set fs.s3a.security.credential.provider.path=jceks://hdfs@rocky8tpl:8020/user/hive/s3.jceks")hive.execute("set metaconf:fs.s3a.security.credential.provider.path=jceks://hdfs@rocky8tpl:8020/user/hive/s3.jceks")hive.executeQuery("""UPDATE hive_partition_tbl_full_hwc SET name = 'Aaron_Updated' WHERE id = 1 AND dt = '2026-01-13'""")Minimum Beeline configurations required to utilize the aforementioned operations:
set fs.s3a.endpoint=s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com;set metaconf:fs.s3a.endpoint=s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com;set fs.s3a.security.credential.provider.path=jceks://hdfs@rocky8tpl:8020/user/hive/s3.jceks;set metaconf:fs.s3a.security.credential.provider.path=jceks://hdfs@rocky8tpl:8020/user/hive/s3.jceks;