Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Explore the Architecture
ClickHouse is architected with a layered design for high performance and flexibility.
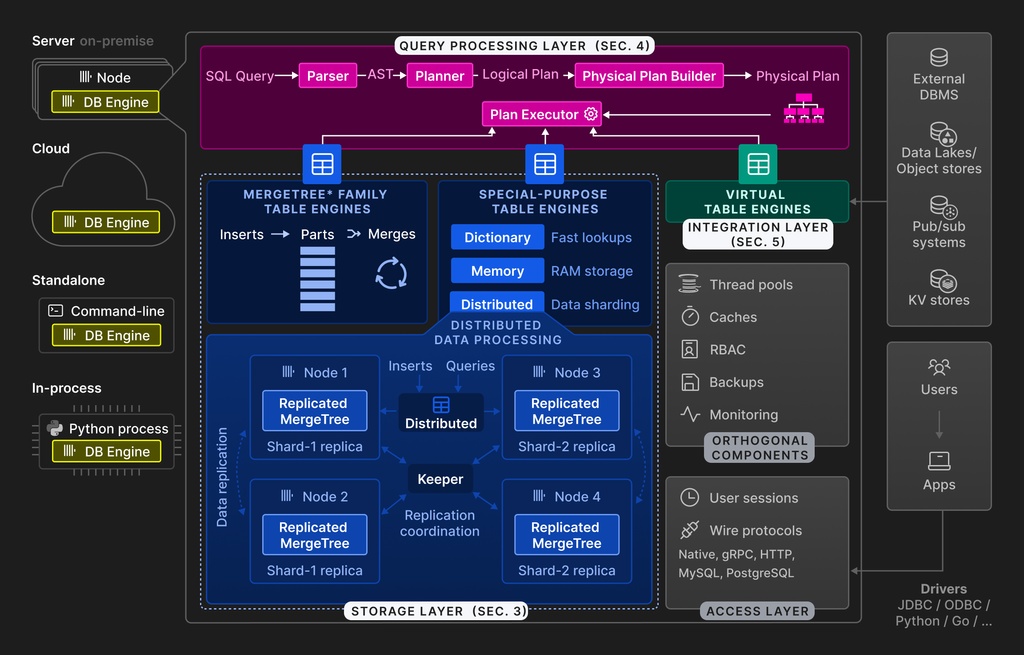
Core Layers
Query Processing Layer: This layer handles parsing, logical/physical plan building, and execution using a vectorized engine, similar to MonetDB/X100. It supports SQL, PRQL, and Kusto-like KQL. Runtime optimizations such as opportunistic compilation make it extremely efficient across diverse query types and data patterns.
Storage Layer: The storage backend is pluggable with multiple table engines:
- MergeTree engines (e.g. ReplacingMergeTree, AggregatingMergeTree) form the core persistent format. Based on LSM-tree principles, they maintain sorted parts and continuously merge them in the background.
- Special-purpose engines like Dictionaries support fast in-memory key-value lookups (even from external sources), and Distributed engines allow transparent sharding across nodes.
- Virtual engines integrate with external systems like MySQL, Kafka, S3, Iceberg, and Redis for both read and write, enabling data federation and hybrid architectures.
Integration Layer: Facilitates connections to external systems via protocols (MySQL, PostgreSQL, HTTP), or direct engine bindings. It also includes observability, role-based access control, and backup hooks.
Access Layer: Manages sessions, authentication, and protocol-level communication with clients.
Performance Engineering
ClickHouse emphasizes low-level optimizations:
- It chooses from 30+ hash table implementations dynamically at runtime.
- Uses data-aware algorithms for sorting, filtering, and join operations.
- Employs column-level compression codecs (like ZSTD, Gorilla, Delta, AES) for high-speed storage and efficient I/O.
Sharding and Replication
- Sharding enables massive scalability by partitioning data horizontally across nodes.
- Replication is handled via ReplicatedMergeTree engines using a Raft-based coordination mechanism called Keeper (a C++ Zookeeper replacement).
- The Distributed engine provides a global view across shards.
Deployment Modes
- On-prem: Classic ClickHouse cluster or single-node server.
- Cloud: Fully-managed ClickHouse Cloud (autoscaling DBaaS).
- Standalone: CLI tool for local analytics, replacing tools like awk, grep.
- Embedded (chDB): In-process OLAP database, ideal for Jupyter/Pandas workflows. No IPC or serialization overhead.
For detailed information, see ClickHouse Architecture.
ACID-compliant
| ACID Property | ClickHouse Support | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Atomicity | ❌ Not guaranteed | Inserts are not forced to disk (fsync is skipped by default), so power loss can lead to data loss. |
| Consistency | ⚠️ Partially | No constraints or transactional checks across tables; assumes clean input. |
| Isolation | ✅ Snapshot Isolation | Queries see a consistent snapshot via MVCC-like versioned parts. |
| Durability | ❌ Optional | No fsync by default, meaning durability isn’t guaranteed unless explicitly configured. |