Documentation
ODP 3.3.6.3-1
Release Notes
What is ODP
Installation
Component User guide and Installation Instructions
Upgrade Instructions
Downgrade Instructions
Reference Guide
Security Guide
Troubleshooting Guide
Uninstall ODP
Title
Message
Create new category
What is the title of your new category?
Edit page index title
What is the title of the page index?
Edit category
What is the new title of your category?
Edit link
What is the new title and URL of your link?
Important Considerations for Master Removal and Recovery
Summarize Page
Copy Markdown
Open in ChatGPT
Open in Claude
Connect to Cursor
Connect to VS Code
This page describes key security, availability, and backup considerations when removing or recovering a Kudu Master in a multi-master deployment.
Security and Permissions
- Run all command-line operations as the Kudu UNIX user (typically
kudu). - If your cluster is secure, authenticate as the Kudu service user before running commands.
High Availability Impact
- After removal, the cluster now operates with two masters instead of three, resulting in reduced fault tolerance.
- With two masters, the cluster can tolerate the loss of only one additional master.
- If high availability is critical, plan to add a replacement master to restore redundancy.
Backup Recommendations
- Ensure you have recent backups before making configuration changes.
- Consider taking a snapshot of the current cluster state before proceeding.
Recover from a Dead Kudu Master in a Multi-Master Deployment
If a Kudu Master is determined to be dead:
Prevent the dead master from running again
- Ensure the affected master is not running and cannot be restarted at any point during the replacement process.
- Accidentally starting the dead master can lead to corruption.
- Allocate at least one hour to complete this process.
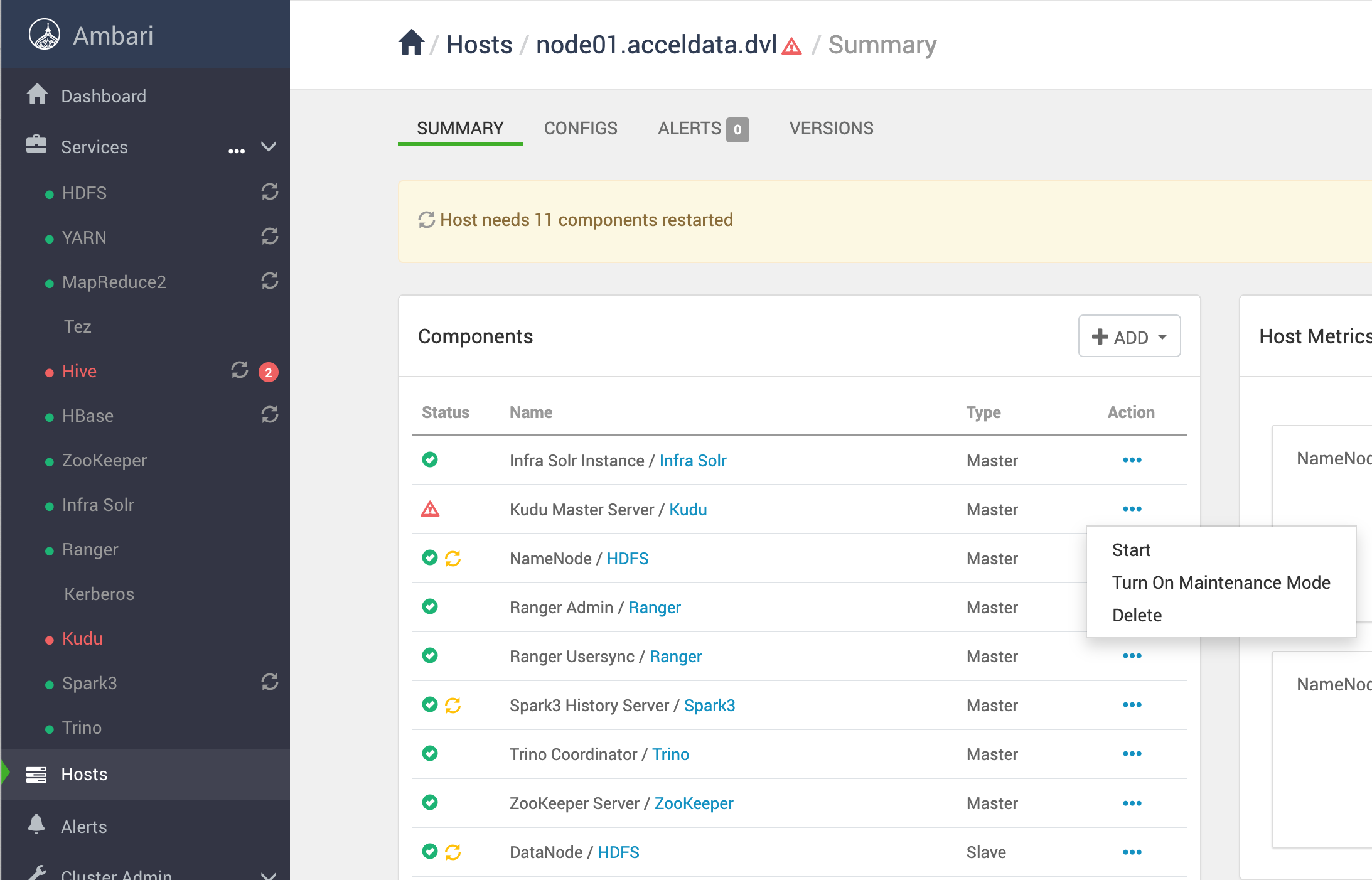
Delete the affected master in Ambari
- In the Ambari UI, delete the Kudu Master component on the affected host.
- Example:
Remove master configuration and WAL data from the affected host
Bash
rm -f /etc/kudu/conf/master.confrm -rf /var/lib/kudu/wal/These steps ensure the affected master cannot accidentally be restarted.
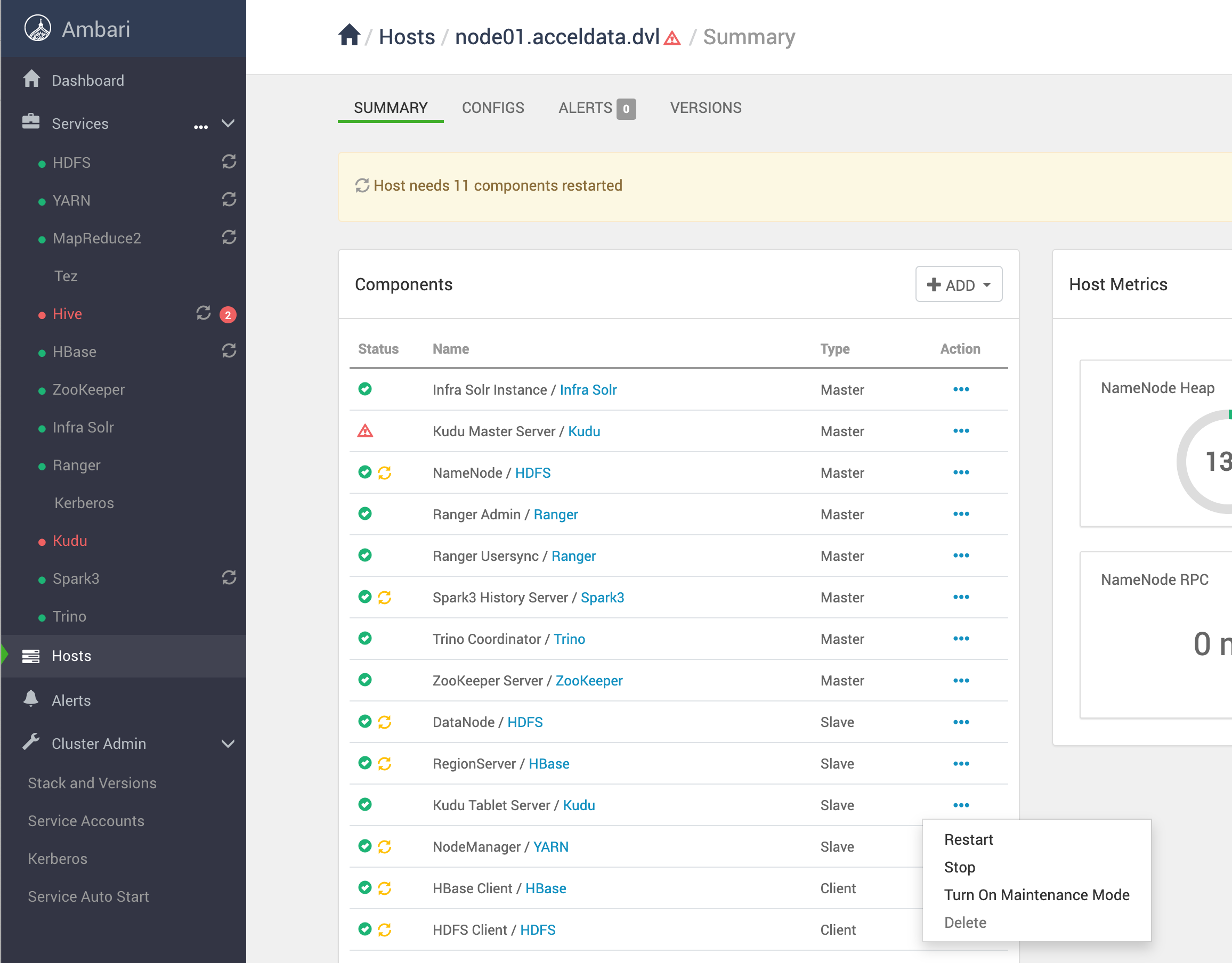
Stop all tablet servers in the cluster
- Use the Ambari UI to stop tablets individually for each host that has a tablet.
- Example:
For more details, see Apache Documentation.
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Last updated on Sep 18, 2025
Was this page helpful?
Next to read:
Known Limitations in Apache KuduDiscard Changes
Do you want to discard your current changes and overwrite with the template?
Archive Synced Block
Message
Create new Template
What is this template's title?
Delete Template
Message
On This Page
Important Considerations for Master Removal and RecoverySecurity and PermissionsHigh Availability ImpactBackup RecommendationsRecover from a Dead Kudu Master in a Multi-Master DeploymentPrevent the dead master from running againDelete the affected master in AmbariRemove master configuration and WAL data from the affected hostStop all tablet servers in the cluster