Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Zookeeper to Kraft Migration
Benefits
The following are the benefits of Kafka New Quorum Controller:
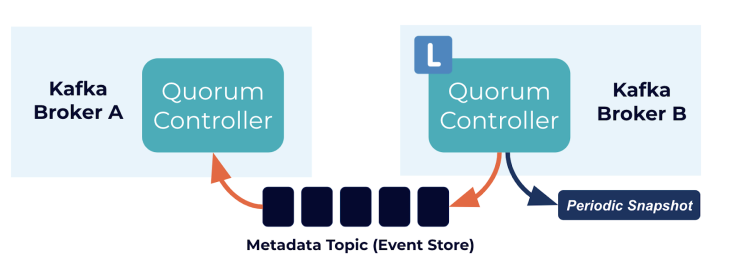
- Quorum controllers use the KRaft protocol to ensure accurate metadata replication across the quorum.
- Event-sourced storage model: The quorum controller stores its state in an event log, allowing internal state machines to be recreated accurately.
- Metadata topic: The event log, also called the metadata topic, is periodically abridged by snapshots to prevent indefinite growth.
- Follower controllers: Other controllers in the quorum follow the active controller by responding to events stored in the log.
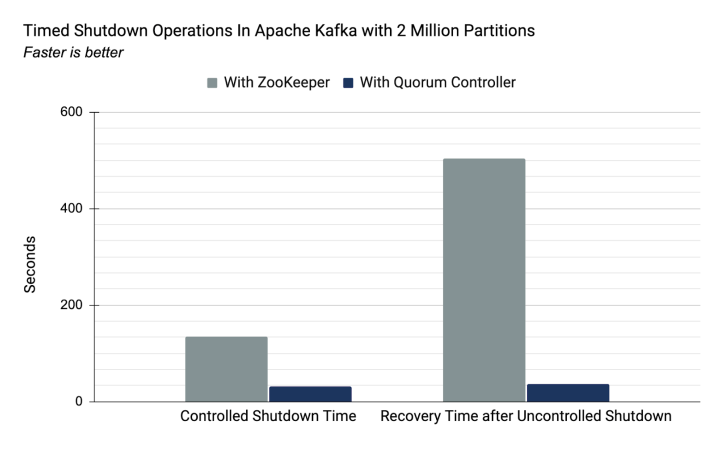
- Fast recovery: If a controller node pauses due to an event such as network partitioning, it can quickly catch up by reading missed events from the log, reducing unavailability and improving worst-case recovery time.
- No dependency on ZooKeeper: Unlike the ZooKeeper-based controller, the quorum controller doesn’t need to load state from ZooKeeper before becoming active.
- Committed metadata records in memory: Upon leadership change, a new active controller already has all committed metadata records loaded in memory.
- Event-driven metadata tracking: The same event-driven mechanism is used across the cluster to track metadata, replacing the need for RPCs (Remote Procedure Calls) with a more efficient log-based communication system.
- Manages and stores Kafka metadata (topics and partitions).
- Handles leader election for brokers and partitions.
- Synchronizes the broker and cluster configurations.
- Monitors the broker and partition health.
- Provides distributed consensus using the Zab (Zookeeper Atomic Broadcast) protocol.
Role of Kraft in Kafka:
- Uses Raft-based consensus for internal metadata management.
- Manages metadata with a quorum of controller nodes.
- Simplifies Kafka’s architecture by removing Zookeeper.
- Integrates controller and broker roles within Kafka itself.
- Improves scalability with efficient metadata replication.
Reasons to shift from Zookeeper to KRaft:
- Eliminates the need for an external Zookeeper dependency.
- Enhances scalability for larger clusters and more topics.
- Simplifies operational management and maintenance.
- Provides stronger fault tolerance with Raft consensus.
- Unifies metadata management directly within Kafka brokers.
Terminology
- The brokers that are in the ZK mode store their metadata in Apache ZooKeeper. This is the old mode of handling metadata.
- The brokers that are in the KRaft mode store their metadata in KRaft quorum. This is a new and improved mode of handling metadata.
- Migration is a process of moving cluster metadata from ZooKeeper into KRaft quorum.
Limitations
- While a cluster is being migrated from ZooKeeper to KRaft mode, we do not support changing the metadata version (also known as the inter.broker.protocol.version). Please do not attempt to do this during a migration, or you may break the cluster.
- After the migration is finalized, it is not possible to revert back to the ZooKeeper mode.
- During the migration, if a Zookeeper broker is running with multiple log directories, any directory failure causes the broker to shut down. Brokers with broken log directories can only be able to migrate to KRaft once the directories are repaired.
Prerequisites and planning for migration
Before migration:
- You need to perform the following prerequisites before starting Zookeeper to KRaft migration:
In Step 4: Migrating brokers to KRaft, the configuration
kraft-broker-list, which is basically a string list of comma-separated values,broker.id@hostnameneeds to be provided. This can be found before the start of the migration using the steps.
[root@odp01 bin] source /usr/odp/current/kafka3-broker/config/kafka3-env.sh ; /usr/odp/current/kafka3-broker/bin/broker-list.shEnter the bootstrap server (e.g., hostname:6669): odp01.acceldata.dvl:6669,odp02.acceldata.dvl:6669,odp03.acceldata.dvl:6669Is the cluster Kerberized? (yes/no): yesIs the cluster using SSL? (yes/no): noEnter the path to the client configuration file (e.g., /root/tpo/client-kerb.prop): /root/tpo/client-kerb.prop[2024-09-17 01:22:34,609] WARN [Principal=null]: TGT renewal thread has been interrupted and will exit. (org.apache.kafka.common.security.kerberos.KerberosLogin)kraft-broker-list: 1004@odp02.acceldata.dvl,1005@odp01.acceldata.dvl,1006@odp03.acceldata.dvl List, Create, Produce and Consume data:######LIST######./kafka-topics.sh --list --bootstrap-server odp01.acceldata.dvl:6669,odp02.acceldata.dvl:6669,odp03.acceldata.dvl:6669 --command-config /root/tpo/client-kerb.prop######CREATE######./kafka-topics.sh --create --topic dilraj --partitions 3 --replication-factor 3 --bootstrap-server odp01.acceldata.dvl:6669,odp02.acceldata.dvl:6669,odp03.acceldata.dvl:6669 --command-config /root/tpo/client-kerb.prop######PRODUCE######echo "Hello team, If you are able to consume this message in kraft mode after migration, then the migration is successful. Eureka....." | ./kafka-console-producer.sh --topic dilraj --bootstrap-server odp01.acceldata.dvl:6669 --producer.config /root/tpo/client-kerb.prop######CONSUME######./kafka-console-consumer.sh --topic dilraj --bootstrap-server odp01.acceldata.dvl:6669 --consumer.config /root/tpo/client-kerb.prop --from-beginningNote: The client configuration file must be provided for Kerberos or SSL authentication, and is typically in the form of:
Kerberos is enabled:
cat client-kerb.prop
security.protocol=SASL_PLAINTEXTSSL is enabled:
cat client-ssl.prop
security.protocol = SSLssl.truststore.location = /opt/security/pki/truststore.jksssl.truststore.password = WelcomeBoth Kerberos and SSL are enabled:
cat client-kerb-ssl.prop
security.protocol = SASL_SSLssl.truststore.location = /opt/security/pki/truststore.jksssl.truststore.password = Welcome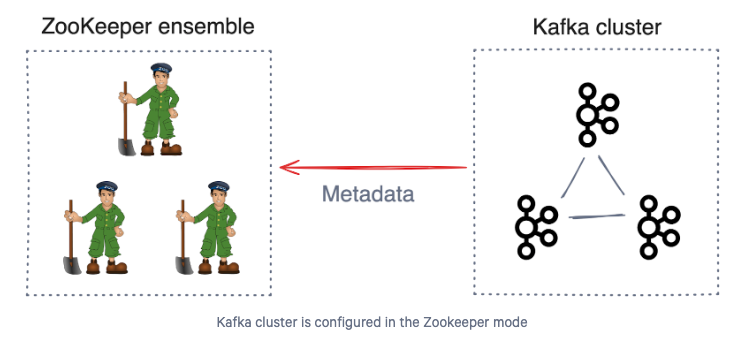
Migration steps
You can follow the below steps to perform Zookeeper to Kraft Migration:
Preparing for Migration
- Add the following property under
Custom kafka3-broker:
inter.broker.protocol.version=3.7.1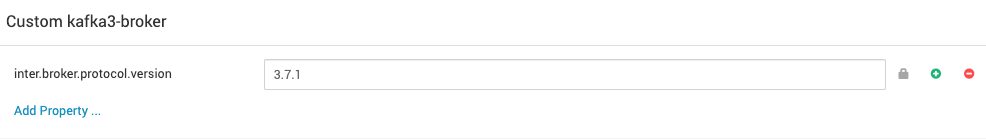
Custom kafka3-broker
- Add the following property under
Advanced kafka3-log4j:
log4j.logger.org.apache.kafka.metadata.migration=TRACE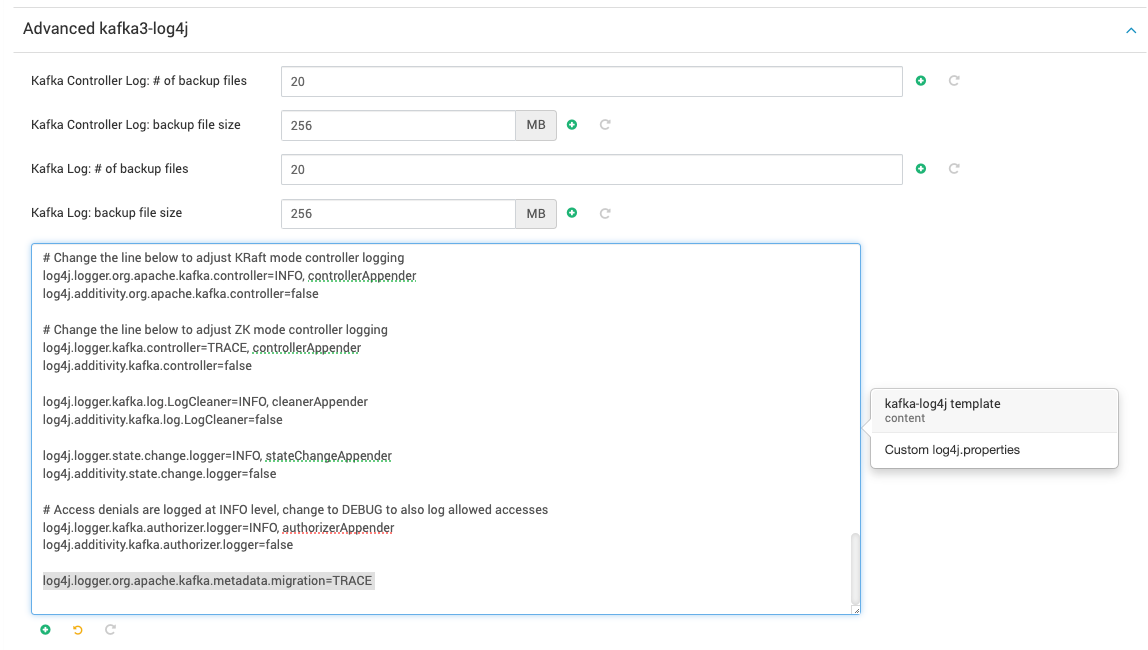
Advanced kafka3-log4j
- After making the above configuration changes through Ambari, Restart all kafka brokers.
Provisioning the KRaft controller quorum
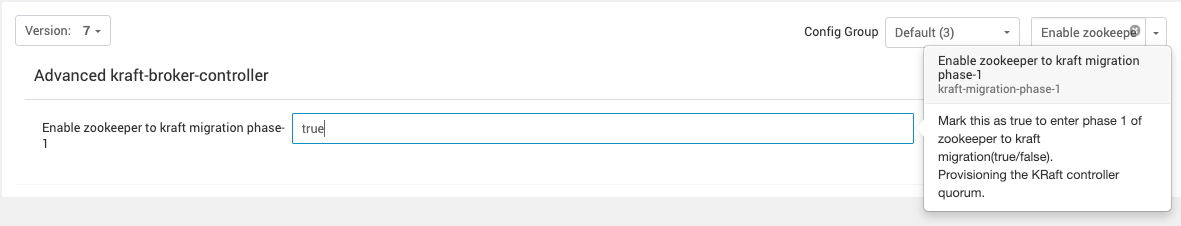
- Under
Advanced kraft-broker-controller, setEnable zookeeper to kraft migration phase-1as true.
The properties mentioned below must never be set to true simultaneously. At any given time, only one of these configurations can be true.
Advanced kraft-broker-controller
The configurations under Advanced Kraft-Broker-Controller are very important and do not be alter unless you fully understand their impact, as improper changes can cause the Kafka service to go down.
- To provide
cluster.idfor your Kafka 3 cluster, you can use the following command on one of the nodes where Kafka 3 is running in Zookeeper mode, the result of the below command needs to be provided incluster-uuidunderAdvanced kraft-broker-controller.
cat /kafka3-logs/meta.properties | grep cluster.idcluster.id=q0xuVvVLSGS5c9hClJ2KlwNote: The log directory of Kafka3 might differ based on the location specified in Ambari under Advanced kafka3-broker as log directories.

Advanced kafka3-broker
- Provide a list of of comma separated
node.id@hostname, which you want to select as controllers inkraft-controller-listunderAdvanced kraft-broker-controller.
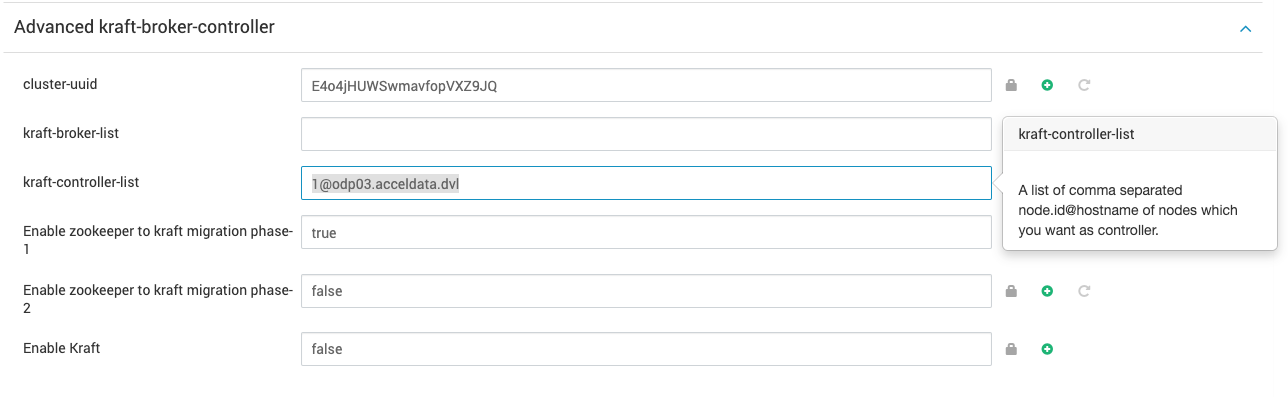
- Set
node.idin controller list, for example, on controller1,node.idmust be set to 1, and so forth. Each node ID must be unique across all the servers in a particular cluster. No two servers can have the same node ID regardless of theirprocess.rolesvalues. (Even if a node is both controller and broker, still a differentnode.idmust be provided under the controller and broker list.) - The
kraft-broker-listmust be empty in this phase.
- Add the following configurations under
Custom kraft-controller,which are related to zookeeper and also setzookeeper.metadata.migration.enableas true.
zookeeper.connect=odp02.acceldata.dvl:2181,odp03.acceldata.dvl:2181,odp01.acceldata.dvl:2181/kafka3zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms=25000zookeeper.session.timeout.ms=30000zookeeper.set.acl=truezookeeper.sync.time.ms=2000zookeeper.metadata.migration.enable=true
The zookeeper-related configurations that are mentioned above can be referred from Advanced kafka3-broker.
- Restart the brokers on which the controllers are installed.
Enter the Migration Mode on Brokers
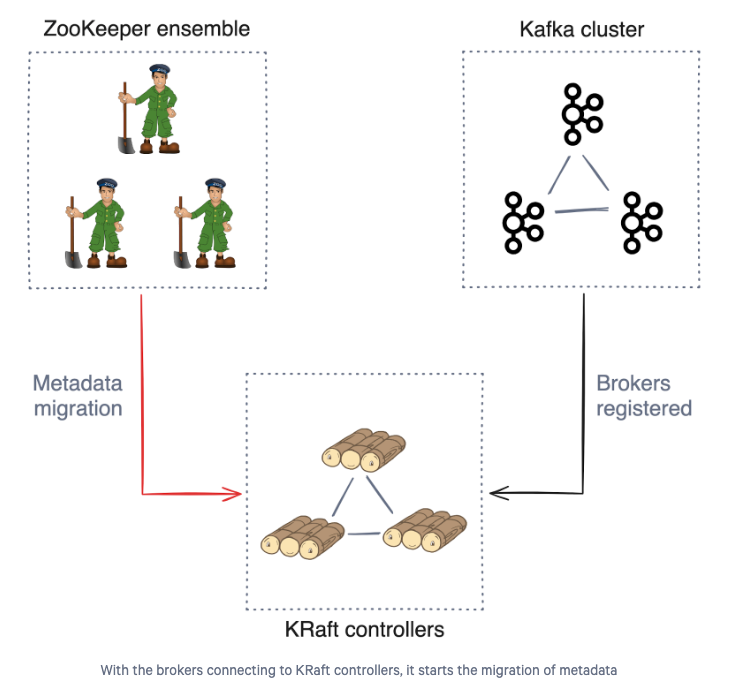
- Before entering this phase, you need to start zk-kraft-migration log-watcher that can be used to check if the migration is completed or not on any one of the nodes that you have selected as controller.
[root@odp03 bin]# source /usr/odp/current/kafka3-broker/config/kafka3-env.sh ; /usr/odp/current/kafka3-broker/bin/log-watcher.shEnter the log directory (e.g., /var/log/kafka3): /var/log/kafka3Monitoring logs in /var/log/kafka3 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafka3.err for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafka-request.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafka-authorizer.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/cruise-control3/kafkacruisecontrol.log.2024-09-26-13 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/cruise-control3/kafkacruisecontrol.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/controller.log.2024-09-26-13 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/controller.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/server.log.2024-09-26-13 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/server.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/state-change.log.2024-09-26-13 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/state-change.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/log-cleaner.log.2024-09-26-13 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/log-cleaner.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log.0 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kraft-controller.err for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log.1 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log.2 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log.3 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log.4 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Pattern not found. Checking again in 3 seconds...- Add the following configurations under
Custom kafka3-brokerrelated tokraft-controllerso that it can connect to kraft controller and start the migration.
controller.listener.names=CONTROLLERcontroller.quorum.voters=1@odp01.acceldata.dvl:7000listener.security.protocol.map=CONTROLLER:SASL_PLAINTEXT,PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT,SSL:SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT:SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL:SASL_SSLThe above configurations must match with the configurations that are used for kraft controller under Advanced kraft-controller.
controller.quorum.voters must have the same value as mentioned in kraft-controller-list along with the port where the kraft controller is running (the kraft controller by default runs on port: 7000).
Apart from the above configurations, there are other configurations required for migration to proceed and needs to be added under Custom kafka3-broker.
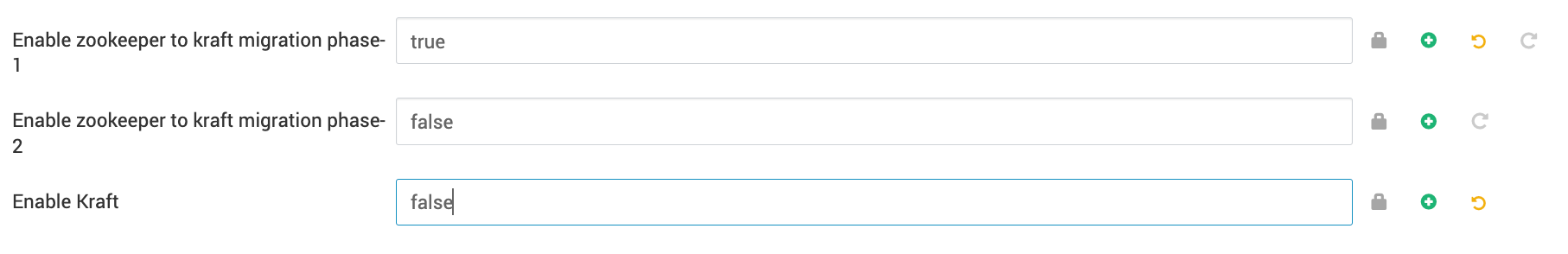
zookeeper.metadata.migration.enable=truereserved.broker.max.id=1000000000- Mark
Enable zookeeper to kraft migration phase-2as true underAdvanced kraft-broker-controllerand setEnable zookeeper to kraft migration phase-1as false.
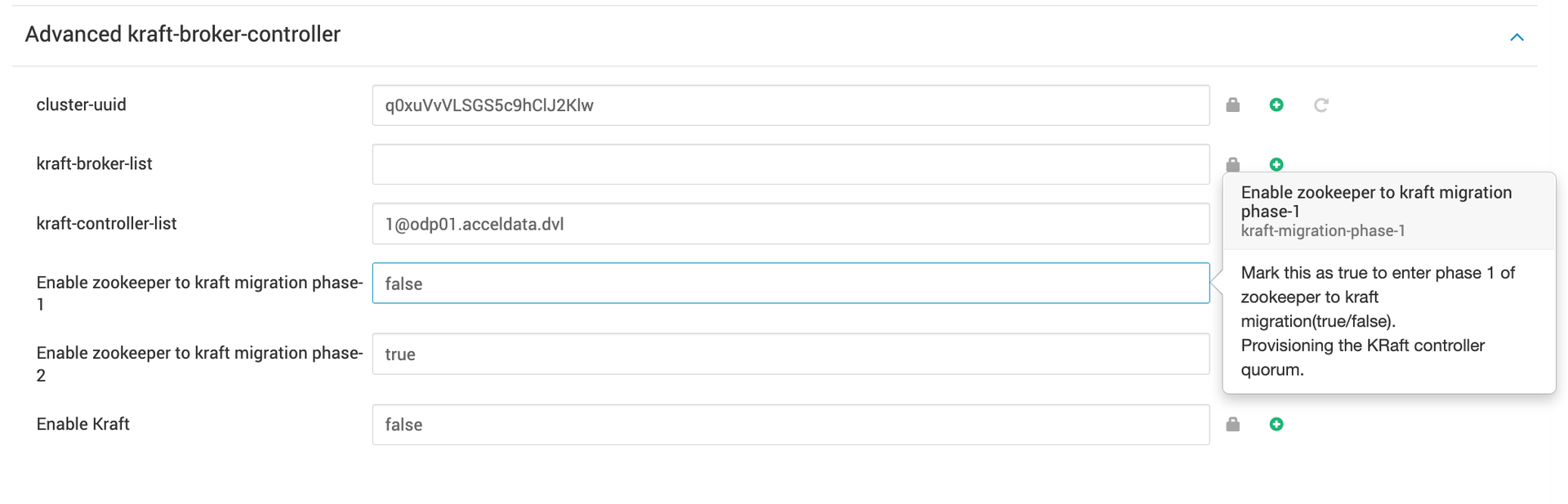
Now you can restart the brokers in a rolling fashion, once the broker has been restarted with the necessary configuration, the migration automatically begins. When the migration is complete, an INFO level log can be observed on the active controller logs:
[root@odp03 bin]# source /usr/odp/current/kafka3-broker/config/kafka3-env.sh ; /usr/odp/current/kafka3-broker/bin/log-watcher.shEnter the log directory (e.g., /var/log/kafka3): /var/log/kafka3Pattern not found. Checking again in 3 seconds...Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafka3.err for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafka-request.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafka-authorizer.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/cruise-control3/kafkacruisecontrol.log.2024-09-26-13 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/cruise-control3/kafkacruisecontrol.log.2024-09-26-14 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/cruise-control3/kafkacruisecontrol.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/controller.log.2024-09-26-13 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/server.log.2024-09-26-13 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/state-change.log.2024-09-26-13 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/log-cleaner.log.2024-09-26-13 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log.0 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kraft-controller.err for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log.1 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log.2 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log.3 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/kafkaServer-gc.log.4 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/server.log.2024-09-26-14 for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Searching /var/log/kafka3/server.log for the message: "Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft"Found: "/var/log/kafka3/server.log:[2024-09-26 15:01:03,364] INFO [KRaftMigrationDriver id=1] Completed migration of metadata from ZooKeeper to KRaft. 57 records were generated in 242 ms across 1 batches. The average time spent waiting on a batch was 13.00 ms. The record types were {TOPIC_RECORD=2, PARTITION_RECORD=51, CONFIG_RECORD=3, PRODUCER_IDS_RECORD=1}. The current metadata offset is now 806 with an epoch of 2. Saw 1 brokers in the migrated metadata [1001]. (org.apache.kafka.metadata.migration.KRaftMigrationDriver)"Pattern found. Exiting...Migrating Brokers to KRaft
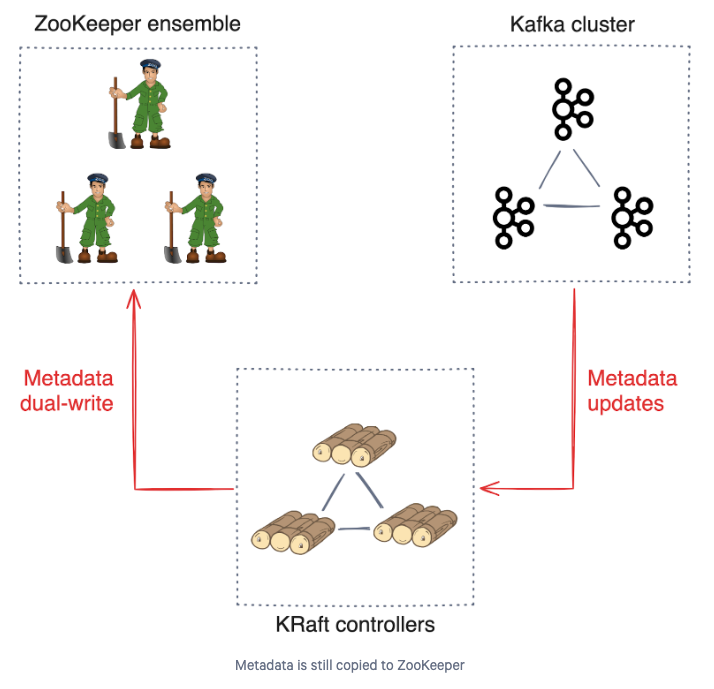
- In this phase you need to migrate Kafka brokers running in the Zookeeper mode. Also, update
kraft-broker-listunderAdvanced kraft-broker-controllerthat is a list of of comma separatednode.id@hostname.

Advanced kraft-broker-controller
This is the same property that is obtained above using the script broker-list.sh :
kraft-broker-list: 1003@odp01.acceldata.dvl,1001@odp02.acceldata.dvl,1002@odp03.acceldata.dvlAlso, make sure that the log directory for kraft-broker must be the same as kafka3 brokers.

Advanced kraft-broker
- Mark the
Enable Kraftmode as true underAdvanced kraft-broker-controller. Also set the value ofEnable zookeeper to kraft migration phase-2to false.
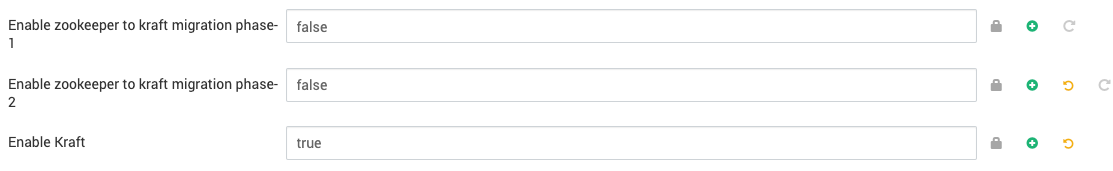
Advanced kraft-broker-controller
- Restart all the Kafka3 brokers in a rolling fashion.
- Before entering the step of Finalizing the Migration, you need to keep in mind that after finalizing the migration, it is not possible to revert to the Zookeeper mode.
- Check Reverting to ZooKeeper mode During the Migration for steps to revert the migration.
Finalizing the Migration
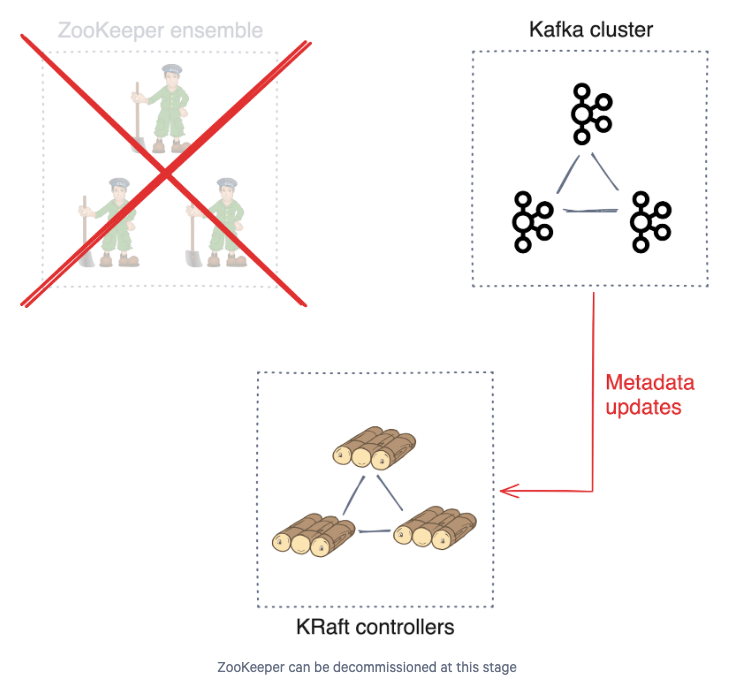
- Once all brokers are restarted in the KRaft mode, the last step is to finalize the migration to take the KRaft controllers out of migration mode.
- This is done by removing
zookeeper.metadata.migration.enableand other zookeeper related properties underCustom kraft-controller. - After this point, it is no longer possible to revert to ZooKeeper mode.
- Remove the below zookeeper related configurationss from
Custom kraft-controller,which were added in the above steps.
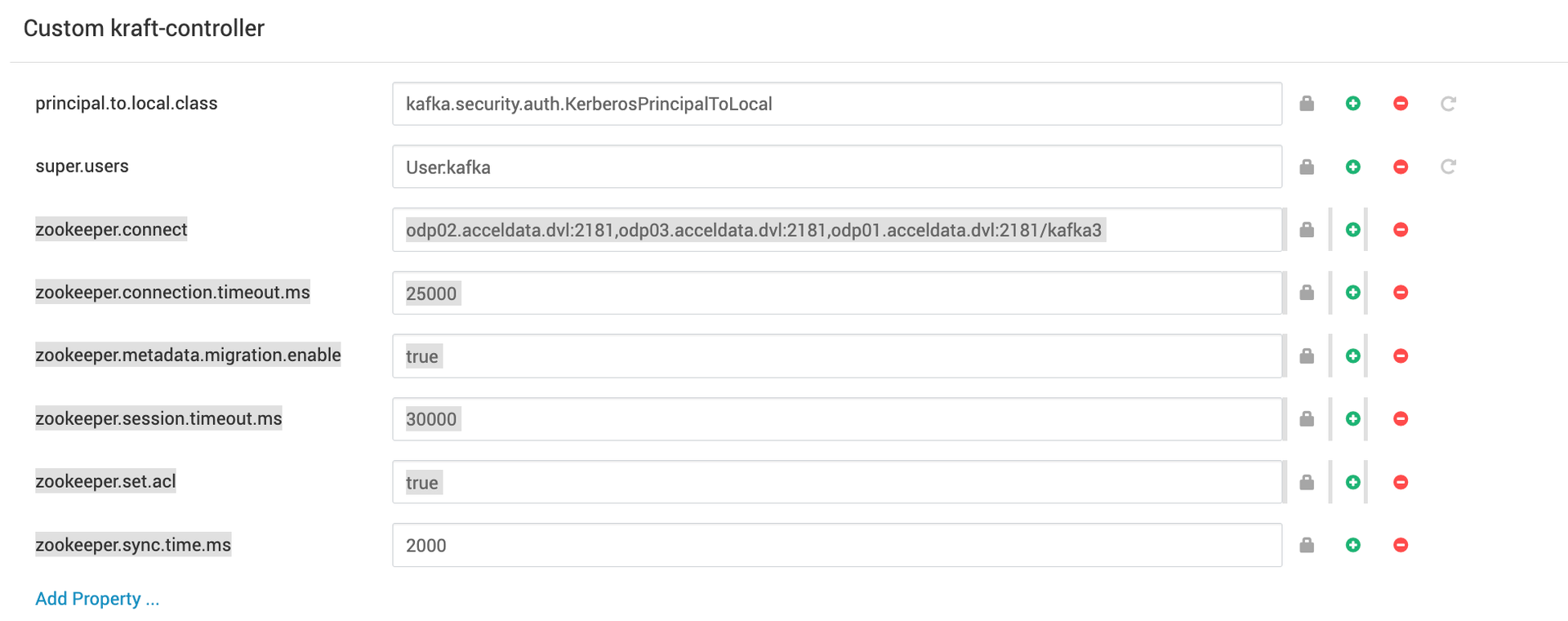
Custom kraft-controller
- At this point, Remove the following property under
Advanced kafka3-log4j:
log4j.logger.org.apache.kafka.metadata.migration=TRACE- Now you can try Kafka commands such as listing, creating, producing, and consuming data that was produced before when Kafka3 brokers were running in zookeeper mode:
######CONSUME######./kafka-console-consumer.sh --topic dilraj --bootstrap-server odp01.acceldata.dvl:6669 --consumer.config /root/tpo/client-kerb.prop --from-beginningReverting to ZooKeeper mode During the Migration
While the cluster is still in migration mode, it is possible to revert to the ZooKeeper mode. The process to follow depends on how far the migration has progressed. To find out how to revert, select the final migration step that you have completed in this table.
Note that the directions given here assume that each step was fully completed, and they were done in order. So, for example, we assume that if Enter Migration Mode on the Brokers was completed, Provisioning the KRaft controller quorum was also fully completed previously.
If you did not fully complete any step, back out from whatever you have done, and then follow revert directions for the last fully completed step.
| Migration Step | Directions for reverting | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Prerequisites and planning for migration | The prerequisites section does not involve leaving the ZooKeeper mode. So, there is nothing to do in the case of a revert. | |
| Step 1: Preparing for migration | The preparation section does not involve leaving the ZooKeeper mode. So, there is nothing to do in the case of a revert. | |
| Step 2: Provisioning the KRaft controller quorum | Deprovision the KRaft controller quorum by reverting the changes made in this step. Then you are done. | |
| Step 3: Enter the Migration Mode on Brokers |
| It is important to perform the zkCli.sh step quickly to minimize the amount of time that the cluster lacks a controller. Until the /controller znode is deleted, you can also ignore any errors in the broker log about failing to connect to the Kraft controller. Those error logs must disappear after the second roll to pure ZooKeeper mode. |
| Step 4: Migrating brokers to KRaft |
|
|
| Step 5: Finalizing the migration | If you have finalized the ZooKeeper migration, then you cannot revert. | Some users prefer to wait for a week or two before finalizing the migration. While this requires you to keep the ZooKeeper cluster running for a while longer, it may help validate the KRaft mode in your cluster. |