By default, JupyterHub uses an SQLite database. For production environments, it is recommended to use a more robust database like MySQL or PostgreSQL. Below are the steps to configure each database.
Default Database (SQLite)
If no database configuration is provided, JupyterHub defaults to SQLite. No additional setup is required.
MySQL Configuration
- Install MySQL (if not already installed): Install MySQL Server and ensure it is running.
- Create a MySQL Database and User
CREATE DATABASE jupyterhub;CREATE USER 'jupyterhub'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'jupyterhub';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON jupyterhub.* TO 'jupyterhub'@'%';FLUSH PRIVILEGES;- Configure JupyterHub to Use MySQL: Update your
jupyterhub_config.pyfile to include the database URL.
c.JupyterHub.db_url = "mysql+pymysql://jupyterhub:jupyterhub@10.100.6.29:3306/jupyterhub"Replaced 10.100.6.29 with your MySQL server's IP address.
- Add database configuration in the jupyerhub-conf
jupyterhub_username = jupyterhubjupyterhub_password = jupyterhubjupyterhub_database_name = jupyterhubdatabase_type = mysql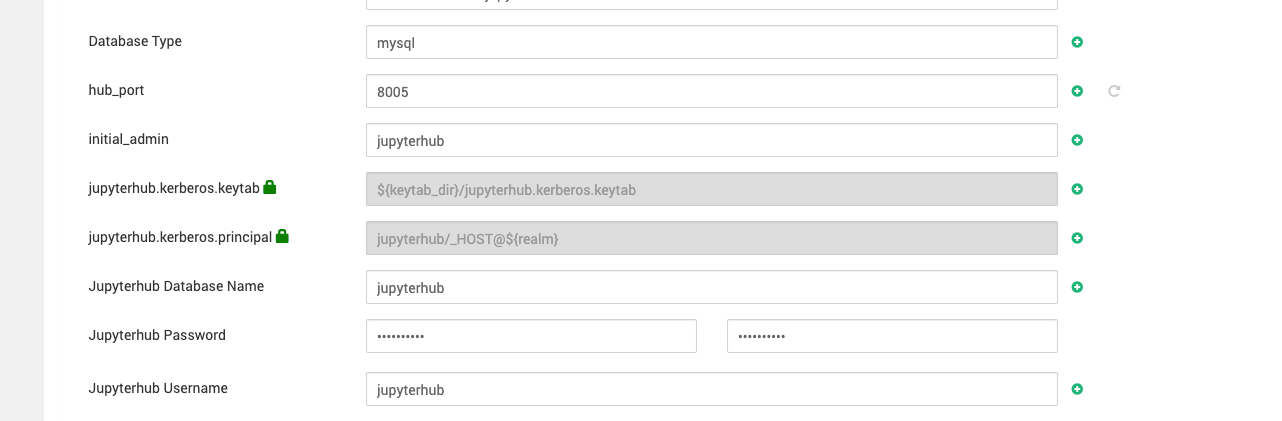
Make sure not to use any special character in the Jupyterhub database password.
PostgreSQL Configuration
- Install PostgreSQL: Run the following commands to install and configure PostgreSQL 12.
sudo dnf install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-8-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpmsudo dnf -qy module disable postgresqlsudo dnf install -y postgresql12-serversudo /usr/pgsql-12/bin/postgresql-12-setup initdbsudo systemctl enable postgresql-12sudo systemctl start postgresql-12- Create a PostgreSQL Database and User: Access the PostgreSQL prompt as the
postgresuser.
sudo -u postgres psqlExecute the following commands:
CREATE DATABASE jupyterhub;CREATE USER jupyterhub WITH PASSWORD 'jupyterhub';GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE jupyterhub TO jupyterhub;CREATE ROLE jupyterhub;GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE jupyterhub TO jupyterhub;\q- Configure PostgreSQL for Remote Access:
- Open the PostgreSQL configuration file.
vi /var/lib/pgsql/12/data/postgresql.confb. Uncomment the listen_addresses and port settings:
listen_addresses = '*'port = 5432c. Update the pg_hba.conf file to allow remote access for the JupyterHub user:
vi /var/lib/pgsql/12/data/pg_hba.confd. Add the following line:
host jupyterhub jupyterhub 10.100.6.29/32 md5Replace 10.100.6.29 with the IP address of the JupyterHub server.
- Restart PostgreSQL.
sudo systemctl restart postgresql-12- Configure JupyterHub to Use PostgreSQL: Update your
jupyterhub_config.pyfile to include the database URL.
c.JupyterHub.db_url = "postgresql+psycopg2://jupyterhub:jupyterhub@10.100.6.29:5432/jupyterhub"Replace 10.100.6.29 with your PostgreSQL server's IP address.
- Add the database configuration in the
jupyerhub-conf.
jupyterhub_username = jupyterhubjupyterhub_password = jupyterhubjupyterhub_database_name = jupyterhubdatabase_type = postgresql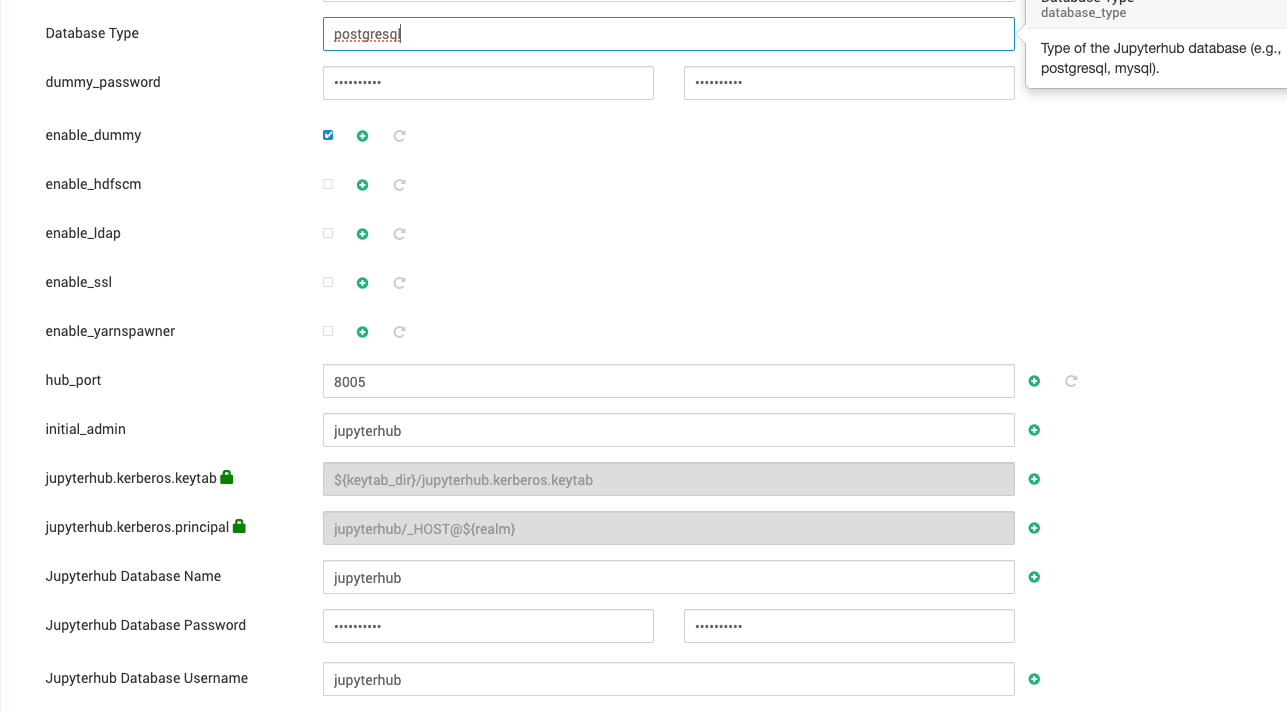
Make sure not to use any special character in the Jupyterhub password.
- Dependencies for MySQL: Ensure
pymysqlis installed for MySQL support. - Dependencies for PostgreSQL: Install the required library with:
pip3 install psycopg2-binary- Test the database connection before starting JupyterHub to confirm proper configuration.