To enable seamless interaction between JupyterHub, HDFS, and YARN in a Hadoop cluster, certain configurations must be applied.
- Update core-site.xml: Modify the Hadoop configuration file
core-site.xmlto allow the JupyterHub user to act as a proxy. Add the following properties:
<property> <name>hadoop.proxyuser.jupyterhub.groups</name> <value>*</value> </property> <property> <name>hadoop.proxyuser.jupyterhub.hosts</name> <value>*</value> </property> <property> <name>hadoop.proxyuser.jupyterhub.users</name> <value>*</value> </property>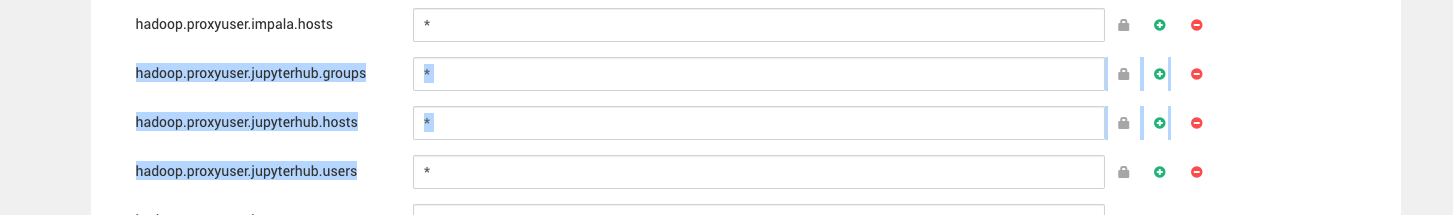
- Update the YARN Queue ACLs: Ensure the YARN queue has the necessary access control lists (ACLs) to permit the JupyterHub user to submit jobs. This can be configured in the YARN ResourceManager settings or queue configuration files.
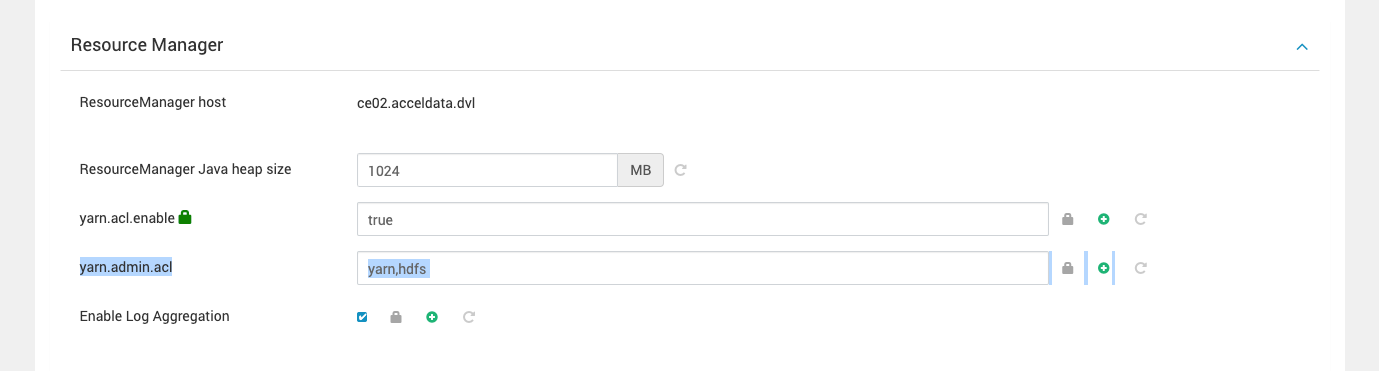
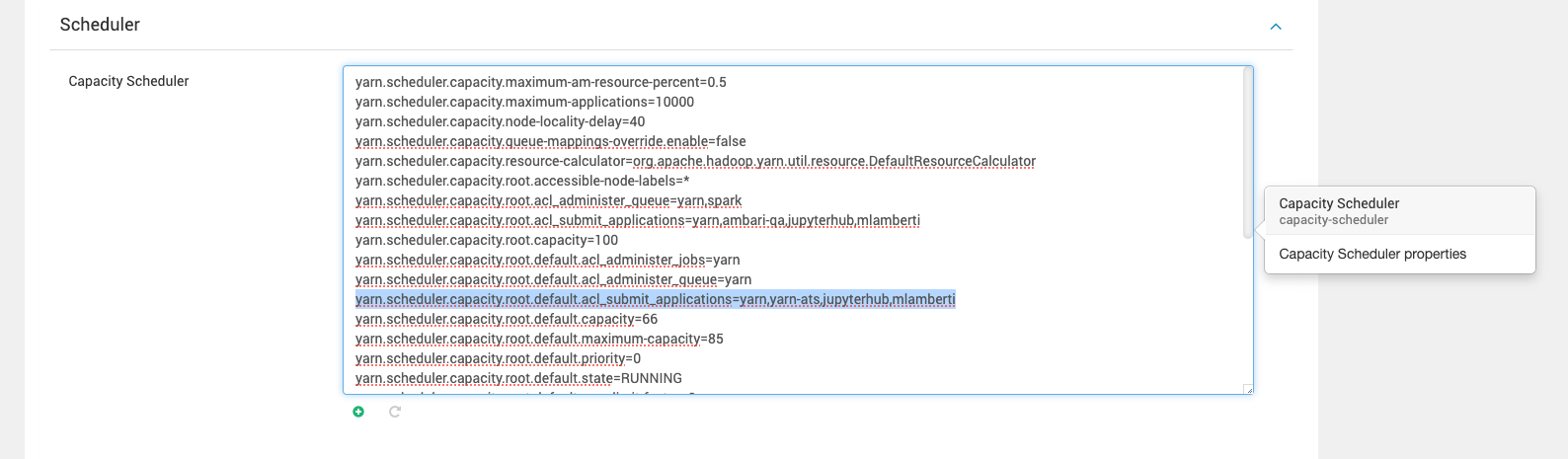
Why These Steps Are Important?
Access Control:
- Configuring proxy permissions in
core-site.xmlallows JupyterHub to interact with HDFS on behalf of its users. - YARN ACLs ensure users can submit jobs through YarnSpawner without encountering permission issues.
- Configuring proxy permissions in
Seamless Execution:
- These configurations eliminate interruptions when users access files stored in HDFS or submit Spark jobs via YARN.
- Streamlined permissions simplify the setup and improve the user experience.
This document serves as a foundation for setting up JupyterHub in a distributed Hadoop environment. Following these steps ensures scalability, security, and smooth integration with essential components like HDFS and YARN.
Was this page helpful?