The current authentication setup for JupyterHub with YarnSpawner and HDFSCM supports both Dummy Authentication for testing purposes and LDAP for production use, providing flexibility based on the deployment requirements.
Choose any one of the following authentication.
Dummy Authentication Setup
The Dummy Authentication in JupyterHub allows users to log in with pre-defined usernames without requiring a real authentication backend. This is typically used for testing purposes. If you are not planning to configure LDAP at the moment, you can set up Dummy Authentication as a temporary solution.
JupyterHub.authenticator_class = jupyterhub.auth.DummyAuthenticatorDummy Password = admin (choose any)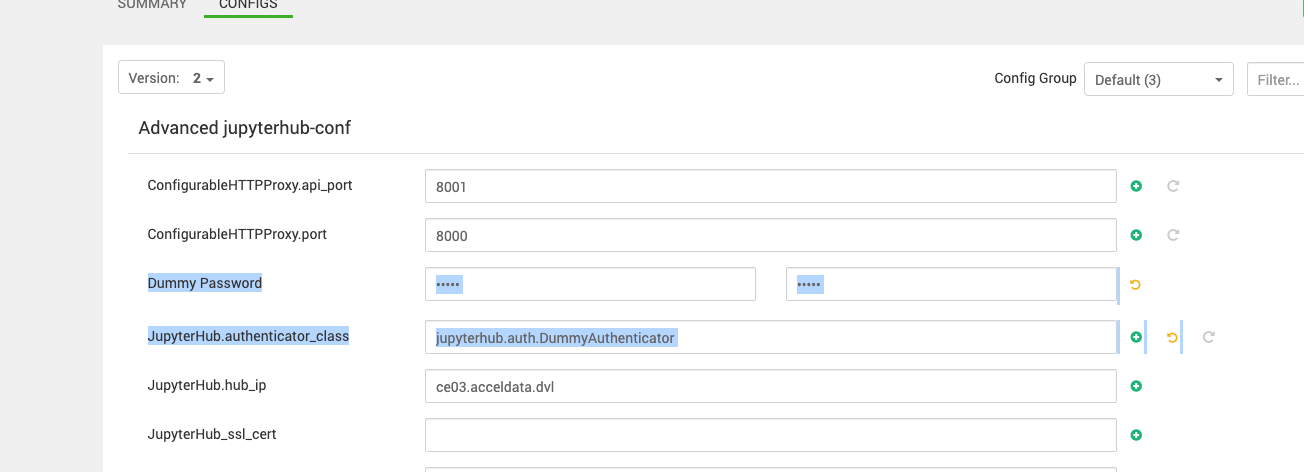

PAM Authentication Setup
PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules) is a framework used to manage authentication on Unix-like systems. It provides a way for system administrators to configure authentication methods and policies, such as password authentication, fingerprint authentication, or even smart cards. PAM allows JupyterHub to authenticate users based on their system-level credentials (e.g., username and password stored in /etc/passwd and /etc/shadow).
In JupyterHub, the PAMAuthenticator class integrates this PAM authentication system, enabling users to log in with their existing operating system accounts without needing separate credentials for JupyterHub.
How to Enable PAM Authentication in JupyterHub?
To enable PAM authentication in JupyterHub, follow these steps:
- Install JupyterHub: Ensure JupyterHub is installed on your system:
pip install jupyterhub- Configure PAMAuthenticator: Edit the
jupyterhub_config.pyfile to specifyPAMAuthenticatoras the authenticator.
c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = 'jupyterhub.auth.PAMAuthenticator'- Optional Configuration:
- You can restrict or allow specific users by setting:
c.PAMAuthenticator.allowed_users = {'user1', 'user2'}- If you want to use a different PAM service, modify the service name:
c.PAMAuthenticator.service = 'my_pam_service'- Ensure PAM is Configured: Make sure PAM is installed and configured on your system. On most Linux systems, PAM is already set up by default.
- Start JupyterHub: Run JupyterHub, and users will authenticate using their system credentials.
jupyterhub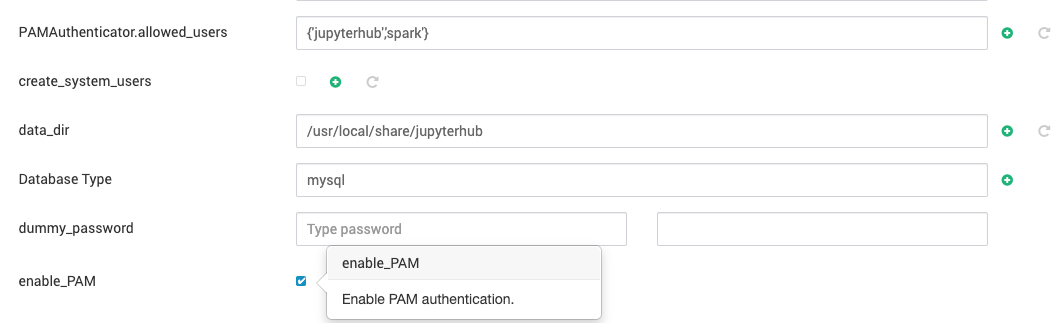
Summary
Enabling PAM authentication in JupyterHub allows users to log in using their operating system credentials. By setting the PAMAuthenticator in the jupyterhub_config.py file, you can integrate system-level authentication seamlessly. PAM provides flexibility, letting you use various authentication mechanisms supported by your operating system.
LDAP Authentication Setup
JupyterHub supports LDAP for user authentication. Due to limitations in the default LDAP package, we recommend using a different LDAP integration project for JupyterHub. Below are the steps for configuring LDAP authentication and ensuring smooth operation with HDFS and YarnSpawner.
Configure through Ambari UI
Add the LDAP configuration in Ambari UI.
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------# LDAP configuration#------------------------------------------------------------------------------# Set LDAPAuthenticator as the authenticator class#c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = 'ldapauthenticator.LDAPAuthenticator'# LDAP server host and port#c.LDAPAuthenticator.server_hosts = ['ldap://65.21.223.155:389']# Bind DN and password for LDAP connection#c.LDAPAuthenticator.bind_user_dn = 'cn=admin,dc=netflux,dc=com'#c.LDAPAuthenticator.bind_user_password = 'admin'# Base DN and search filter for user lookup#c.LDAPAuthenticator.user_search_base = 'dc=netflux,dc=com'#c.LDAPAuthenticator.user_search_filter = '(cn={username})'#c.LDAPAuthenticator.lookup_dn = True#c.LDAPAuthenticator.use_ssl = False# Username pattern (valid characters for usernames)#c.LDAPAuthenticator.username_pattern = '[a-zA-Z0-9_.][a-zA-Z0-9_.-]{0,252}[a-zA-Z0-9_.$-]?'# Create home directory on login#c.LDAPAuthenticator.create_user_home_dir = True#c.LDAPAuthenticator.create_user_home_dir_cmd = ['mkhomedir_helper']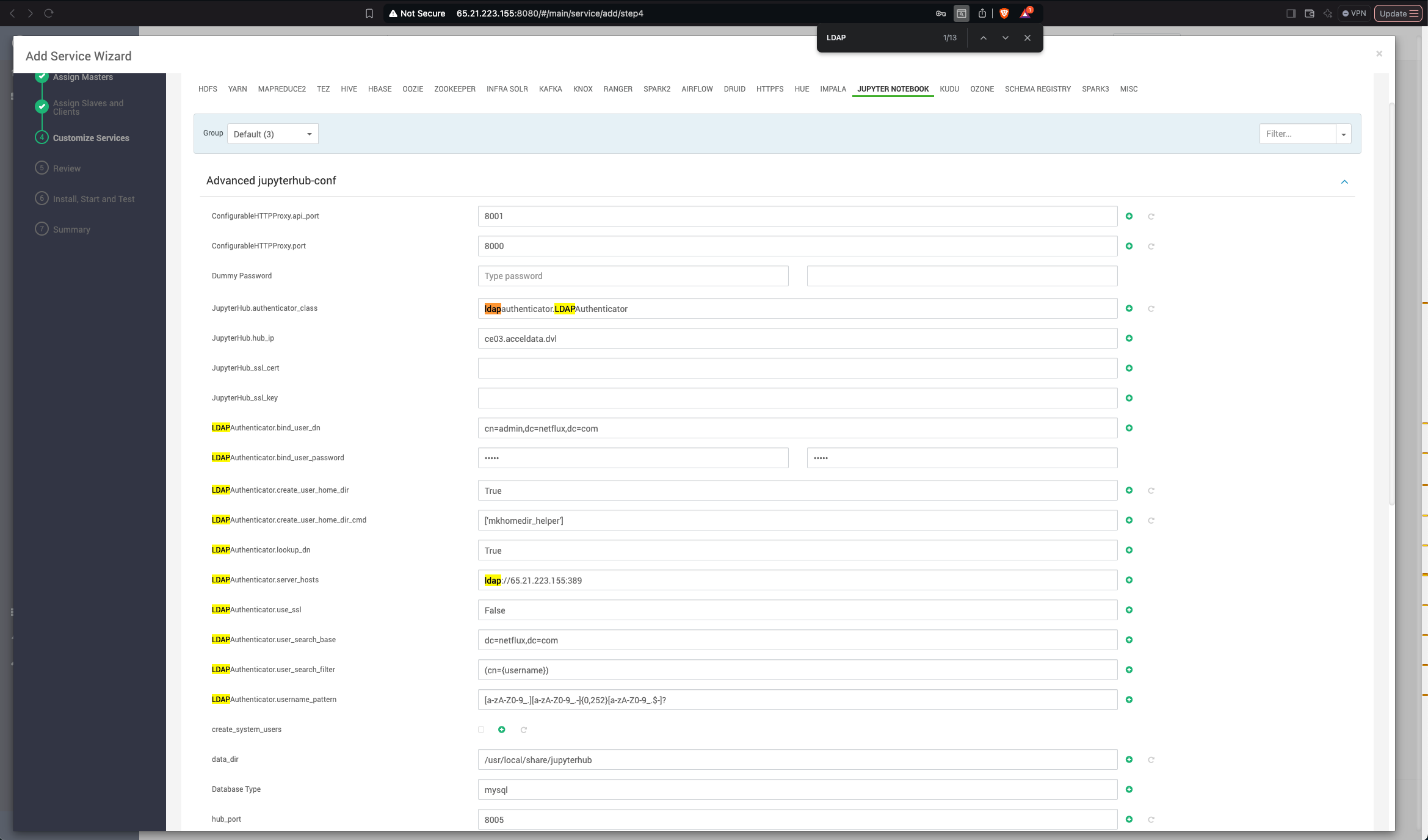
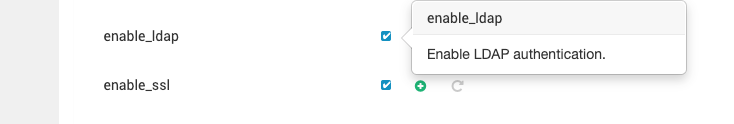
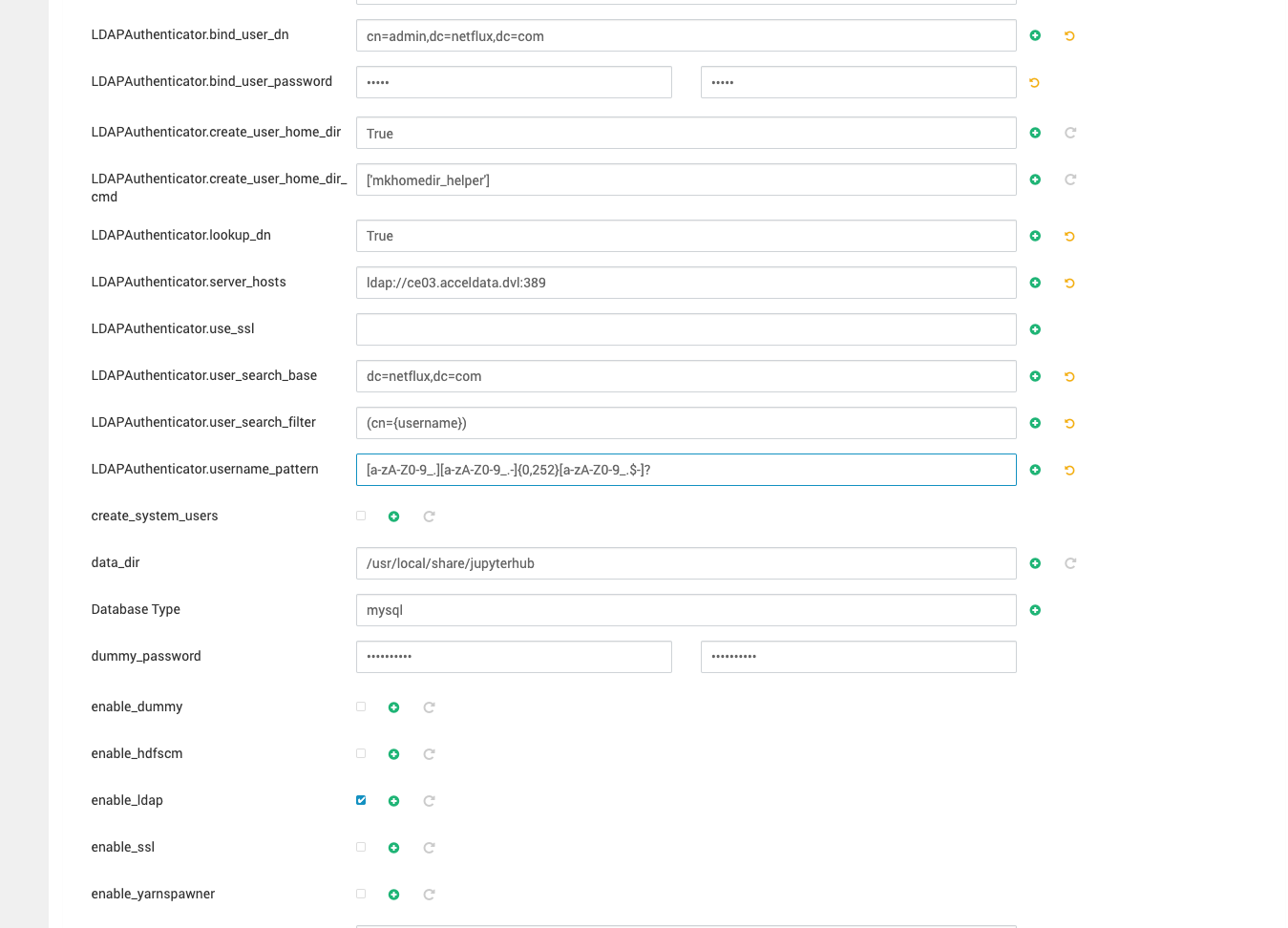
Save the configurations and restart the service. Ensure the user is added to the YARN queue to grant them permission to submit jobs.
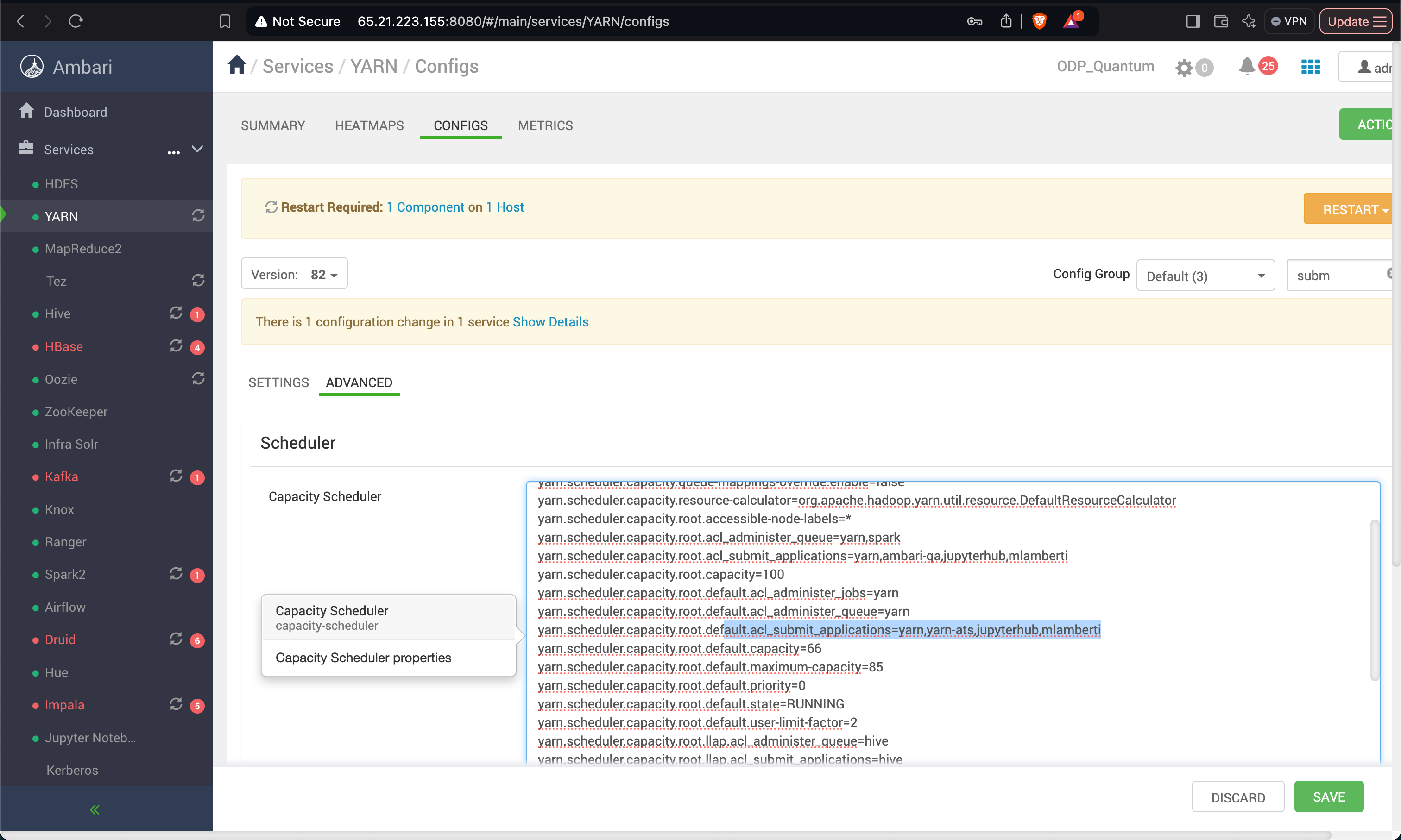
Add Users and Set Permissions
The error indicates that the user mlamberti does not have sufficient write permissions on the HDFS path /user. The issue arises because the YarnSpawner is trying to create a directory or file in /user, but mlamberti lacks the necessary permissions.
To resolve this, follow these steps:
Verify HDFS Permissions
Check the current permissions of the /user directory:
hdfs dfs -ls /You must see something like this for /user:
drwxrwxr-x - hdfs hadoop 0 2024-11-29 /userThis means:
- Owner:
hdfshas full permissions. - Group:
hadoophas read, write, and execute permissions. - Others: Only read and execute permissions (no write).
Grant Specific Permissions to mlamberti
If the default HDFS behavior is to create a directory for the user at /user/mlamberti, ensure that mlamberti has write permissions to /user or manually create and set permissions for /user/mlamberti.
Option A: Manually Create and Set Permissions for /user/mlamberti
- Create a directory.
hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/mlamberti- Set the owner and permissions.
hdfs dfs -chown mlamberti:jupyterhub /user/mlambertihdfs dfs -chmod 700 /user/mlambertiOption B: Grant Group Write Access to /user
If multiple users need write access to /user (not recommended unless necessary).
- Add mlamberti to the hadoop group.
sudo usermod -aG hadoop mlamberti- Adjust
/userpermissions to allow group write.
hdfs dfs -chmod 775 /userAdd Permission for the LDAP User
Add permission for the LDAP user to /home directory.
sudo chown -R mlamberti:jupyterhub /home/mlambertisudo chmod -R g+rwx /home/mlambertisudo chmod -R g+s /home/mlambertiSteps to Fix the Permission Issue (Perform on all the Nodes)
- Verify Ownership and Permissions Check the ownership and permissions of the
/home/jupyterhub/.jupyterand/home/jupyterhub/.jupyter/runtimedirectories.
ls -ld /home/jupyterhub/ls -ld /home/jupyterhub/- Change Ownership If the directories are not owned by the
jupyterhubgroup or themlambertiuser does not have access, modify the ownership.
sudo chown -R jupyterhub:jupyterhub /home/jupyterhub/sudo chmod -R 777 /home/jupyterhub/- Ensure Group Access To allow all members of the
jupyterhubgroup (includingmlamberti) to write.
sudo chmod -R g+rwx /home/jupyterhub/- Set SGID for Consistent Group Ownership Enable the SGID bit on the
.jupyterdirectory so that files and subdirectories inherit thejupyterhubgroup.
sudo chmod g+s /home/jupyterhub/Restart JupyterHub and Log in Using the LDAP User Credentials
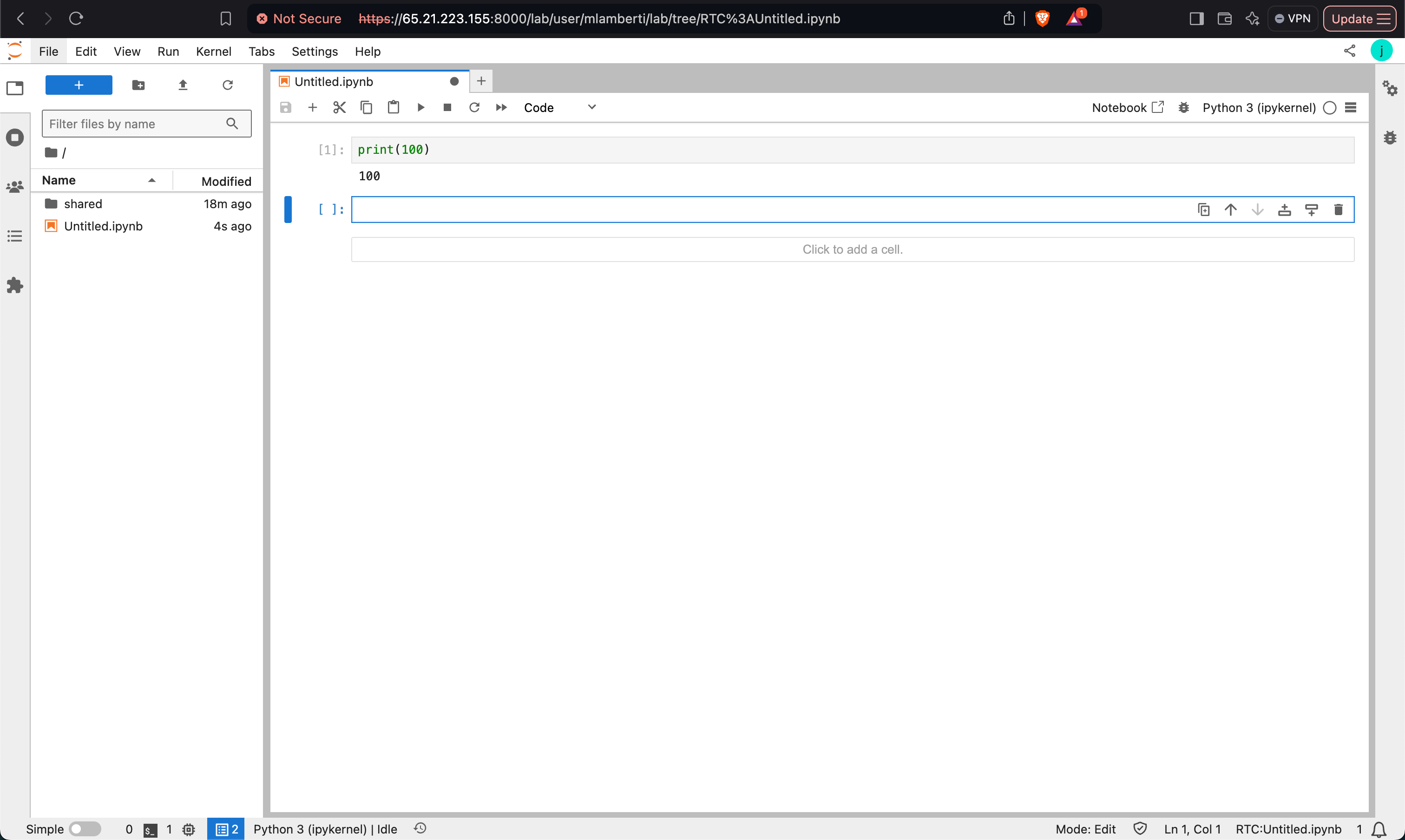
Verify the notebooks on HDFS path for LDAP users.
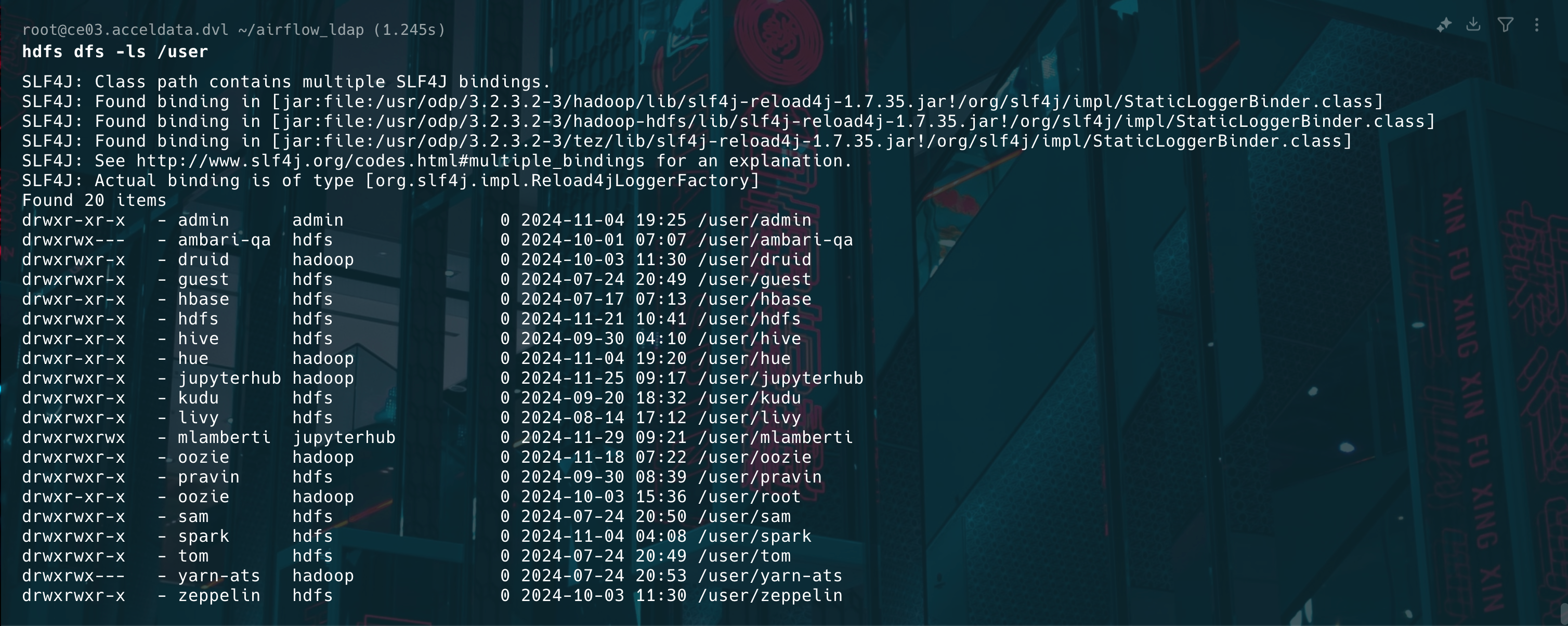
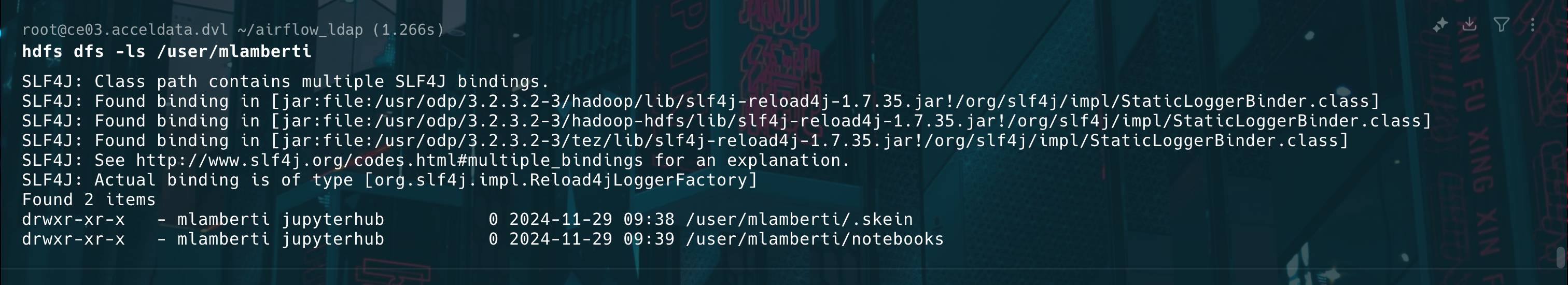
Validate HDFS and Notebook Setup
- Verify the HDFS Directories for Users:
hdfs dfs -ls /user/mlamberti/notebookshdfs dfs -ls /user/jupyterhubhdfs dfs -ls /user/jupyterhub/notebooks hdfs dfs -ls /user/mlambertiSLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/hadoop/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/hadoop-hdfs/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/tez/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.slf4j.impl.Reload4jLoggerFactory]Found 2 itemsdrwxr-xr-x - mlamberti hdfs 0 2024-10-07 16:43 /user/mlamberti/.skeindrwxr-xr-x - mlamberti hdfs 0 2024-10-07 16:38 /user/mlamberti/notebookshdfs dfs -ls /user/mlamberti/notebooksSLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/hadoop/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/hadoop-hdfs/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/tez/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.slf4j.impl.Reload4jLoggerFactory]Found 7 itemsdrwxr-xr-x - mlamberti hdfs 0 2024-10-07 14:36 /user/mlamberti/notebooks/.ipynb_checkpoints-rw-r--r-- 3 mlamberti hdfs 904 2024-10-07 14:36 /user/mlamberti/notebooks/Untitled.ipynb-rw-r--r-- 3 mlamberti hdfs 376 2024-10-07 15:34 /user/mlamberti/notebooks/Untitled1.ipynb-rw-r--r-- 3 mlamberti hdfs 904 2024-10-07 16:19 /user/mlamberti/notebooks/Untitled2.ipynb-rw-r--r-- 3 mlamberti hdfs 376 2024-10-07 16:20 /user/mlamberti/notebooks/Untitled3.ipynb-rw-r--r-- 3 mlamberti hdfs 1410 2024-10-07 16:38 /user/mlamberti/notebooks/Untitled4.ipynbdrwxr-xr-x - mlamberti hdfs 0 2024-10-04 21:58 /user/mlamberti/notebooks/sharedhdfs dfs -ls /user/jupyterhubSLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/hadoop/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/hadoop-hdfs/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/tez/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.slf4j.impl.Reload4jLoggerFactory]Found 3 itemsdrwxr-xr-x - jupyterhub hdfs 0 2024-10-04 21:28 /user/jupyterhub/.skeindrwxr-xr-x - jupyterhub hdfs 0 2024-10-03 22:03 /user/jupyterhub/environmentsdrwxr-xr-x - jupyterhub hdfs 0 2024-09-12 14:38 /user/jupyterhub/notebookshdfs dfs -ls /user/jupyterhub/notebooksSLF4J: Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings.SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/hadoop/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/hadoop-hdfs/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: Found binding in [jar:file:/usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/tez/lib/slf4j-reload4j-1.7.35.jar!/org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class]SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#multiple_bindings for an explanation.SLF4J: Actual binding is of type [org.slf4j.impl.Reload4jLoggerFactory]Found 6 itemsdrwxr-xr-x - jupyterhub hdfs 0 2024-09-10 15:51 /user/jupyterhub/notebooks/.ipynb_checkpointsdrwxr-xr-x - jupyterhub hdfs 0 2024-09-12 14:38 /user/jupyterhub/notebooks/Untitled Folder-rw-r--r-- 3 jupyterhub hdfs 616 2024-09-10 15:51 /user/jupyterhub/notebooks/Untitled.ipynb-rw-r--r-- 3 jupyterhub hdfs 381 2024-09-11 14:53 /user/jupyterhub/notebooks/Untitled1.ipynb-rw-r--r-- 3 jupyterhub hdfs 904 2024-09-11 14:55 /user/jupyterhub/notebooks/Untitled2.ipynbdrwxr-xr-x - jupyterhub hdfs 0 2024-09-10 15:41 /user/jupyterhub/notebooks/shared- Ensure Directories Exist: Check that all required directories are created and owned by the respective users or groups:
/user/mlamberti/user/jupyterhub/user/jupyterhub/notebooks- If not, create them:
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /user/mlamberti/notebookshdfs dfs -mkdir -p /user/jupyterhub/notebooks- Set Correct Ownership:
hdfs dfs -chown -R mlamberti:hdfs /user/mlambertihdfs dfs -chown -R jupyterhub:hdfs /user/jupyterhubStart JupyterHub
- Activate the JupyterHub Environment
source /usr/odp/3.2.3.3-3/jupyterhub_env/bin/activate- Run JupyterHub
jupyterhub -f /path/to/jupyterhub_config.py- Log in with LDAP User Credentials: Confirm that users can log in using their LDAP credentials and access their respective notebooks in HDFS.
Verify Functionality
- Check that users can:
- Submit jobs to the Yarn queue.
- Access and create notebooks in HDFS.
By following these steps, you can successfully configure LDAP authentication for JupyterHub and ensure seamless integration with HDFS and YarnSpawner.