Yarn Optimizer Configuration
You can make the configuration as per your requirement by navigating to the Yarn Optimizer > Config page to influence the optimization.
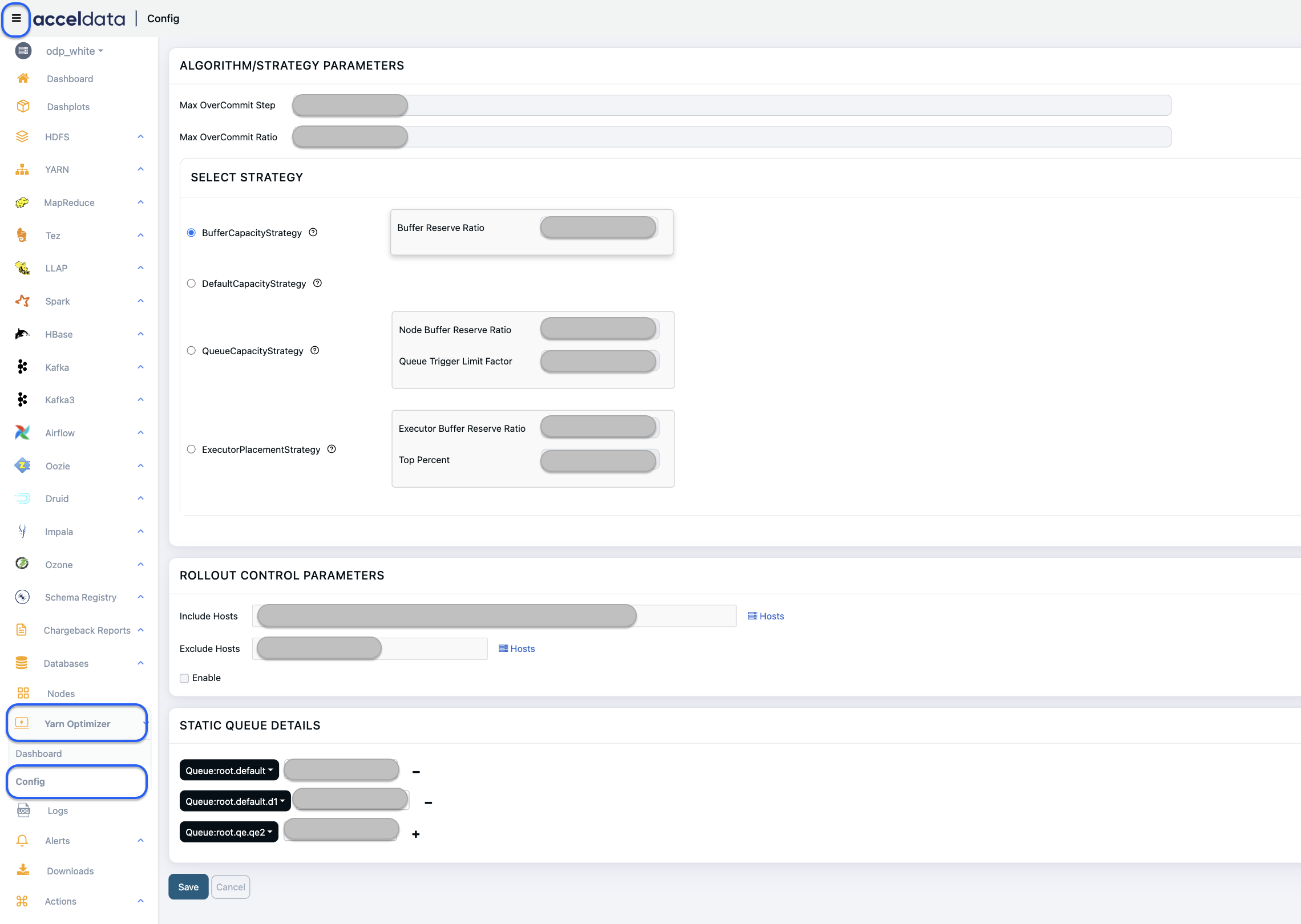
Algorithm or Strategy Parameters
You can configure the below functionalities as needed:
- Maximum OverCommit Step: Enter a value to increment by which memory overcommit is updated for each iteration. The value needs to be in %. For example, 0.02 (2 %).
- Maximum OverCommit Ratio: The ratio between overcommitted and physical memory.
Select Strategy
You can select one of the strategies to configure the YARN Optimizer.
Buffer Capacity Strategy
- Buffer Reserve Ratio: The percentage of total memory or resources that must be kept in reserve and not overcommitted. For example, suppose a system has 100 GB of physical memory and a Buffer Reserve Ratio of 0.05. The system reserves 5 GB as a buffer, meaning only 95 GB of the memory is available for allocation or overcommitment. This helps prevent scenarios where overcommitment could cause the system to run out of critical resources, leading to performance degradation, swapping, or even crashes.
Queue Capacity Strategy
- Node Buffer Reserve Ratio: This is the amount of memory that must remain unallocated on a node. For example, suppose a node in a Hadoop cluster has 100 GB of physical memory, and the Node Buffer Reserve Ratio is set to 20% (0.2). In this case, 2 0 GB (20% of 100 GB) is reserved for the system, leaving 80 GB available for Hadoop tasks such as MapReduce jobs, HDFS operations, or other distributed processing tasks. This ensures that the node has enough memory left in reserve to handle spikes in workload, process system overhead, or maintain stability if certain processes require more memory than expected.
- Queue Trigger Limit Factor: The required amount of queue to be in use for optimization to trigger.
The Buffer Capacity Strategy optimization starts only when the value set in Node Buffer Reserve Ratio and Queue Trigger Limit Factor exceeds.
Execute Placement Strategy
- Executor Buffer Reserve Ratio: The ratio of memory reserved for the non-YARN processes. For example, suppose an executor has 10 GB of memory allocated to it, and the Executor Buffer Reserve Ratio is set to 0.1 (10%). In this case, 1 GB (10% of 10 GB) of the executor's memory will be reserved and not used for regular task execution, leaving 9 GB available for processing.
The reserved 1 GB ensures that the executor can handle any unexpected workload surges or system overhead without crashing.
- Top percent: The ratio of the most unused nodes and total nodes.
If the value is set to 0.5 (50 percent), the 50 percent of the total nodes in a cluster with the most unused physical memory will be overcommitted for the new job allocation.
The Default Capacity Strategy disables the optimization.
Rollout Control Parameters
You can include or exclude hosts from the configuration.
- Include Hosts: Click Hosts and select the checkbox for hosts to include.
- Exclude Hosts: Click Hosts and select the checkbox for hosts to exclude.
Ensure to select Enable to rollout control parameters. Otherwise, all hosts will be included.
Static Queue Details
Pulse YARN Optimizer supports optimization of static queues along with dynamic queues within the total available resources.
Dynamic Queues are automatically optimized when the YARN optimizer is deployed on the nodes. However, for Static Queues, manual configuration in the UI is required for optimization.
Steps for the configuration:
- In the Static Queue Details, select a queue from the drop-down. You can add multiple static queue names and configure them accordingly.
- Configure the optimization ratio in percentage (0.1, 0.2, etc.,) to optimize the queue resources.
For details about the use case on how YARN Optimizer optimizes resource allocation in static queues through a practical example, see Resource Optimization for YARN Static Queues.