Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Introduction to Apache Pinot
What is Apache Pinot?
Apache Pinot is a real-time, distrishbuted OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) datastore designed for fast, low-latency analytics on large-scale data. It enables businesses to run real-time queries on high-volume data with millisecond response times.
It is widely used for dashboard analytics, anomaly detection, and business intelligence (BI) applications where quick insights from streaming and batch data are required.
Apache Pinot can be thought of as an ultra-fast search engine for numerical data. Similar to how Google enables rapid discovery of webpages, Pinot empowers businesses to extract critical insights from massive volumes of data within milliseconds.
- Google = Search engine for words (For example, "Best restaurants near me")
- Apache Pinot = Search engine for numbers (For example, "Top 5 most ordered dishes in the last 10 minutes")
How does Apache Pinot Work?
Apache Pinot functions as a highly efficient, large-scale digital library, organizing vast amounts of information in a structured manner to enable extremely fast and precise retrieval.
Data Ingestion
Apache Pinot supports two types of data ingestion:
Real-time Ingestion (For example, Kafka)
- Data flows continuously from streaming sources into Pinot.
- Each incoming record is indexed immediately and becomes available for querying within seconds.
Batch Ingestion (For example, HDFS, S3, etc.)
- Historical data is periodically ingested from offline storage.
Data Storage and Indexing
- Columnar Storage: Stores data in a column-oriented format for fast aggregations.
- Indexing: Uses Inverted, Sorted, Range, and Star-Tree indexes to optimize query speed.
- Immutable Segments: Data is stored in read-only segments to enhance performance.
Query Execution
Users can query Pinot using SQL-like queries via:
- Pinot UI (Query Console)
- REST API
- Pinot CLI
- JDBC for BI tools
When a query is sent, Pinot’s Broker Node distributes it across multiple Server Nodes, retrieves results, and returns the response within milliseconds.
In simple terms:
Data Comes In:
- From real-time sources (like orders coming in from Swiggy/Zomato).
- From old data (historical records stored in databases like Hadoop).
Data Gets Indexed (Organized)
- Just like a book has an index to help you find topics quickly, Pinot organizes data smartly so searches are lightning fast.
You Ask a Question (Query)
- Example: "Show me the top 5 best-selling dishes in Bangalore right now."
- Pinot finds and returns the answer in less than a second.
Apache Pinot Architecture
The diagram below illustrates the architecture of Apache Pinot, a real-time distributed columnar storage system designed for low-latency analytics. It highlights the key components such as the controller, broker, server, and the data ingestion pipeline, showcasing how Pinot efficiently handles large-scale data processing and enables real-time querying.
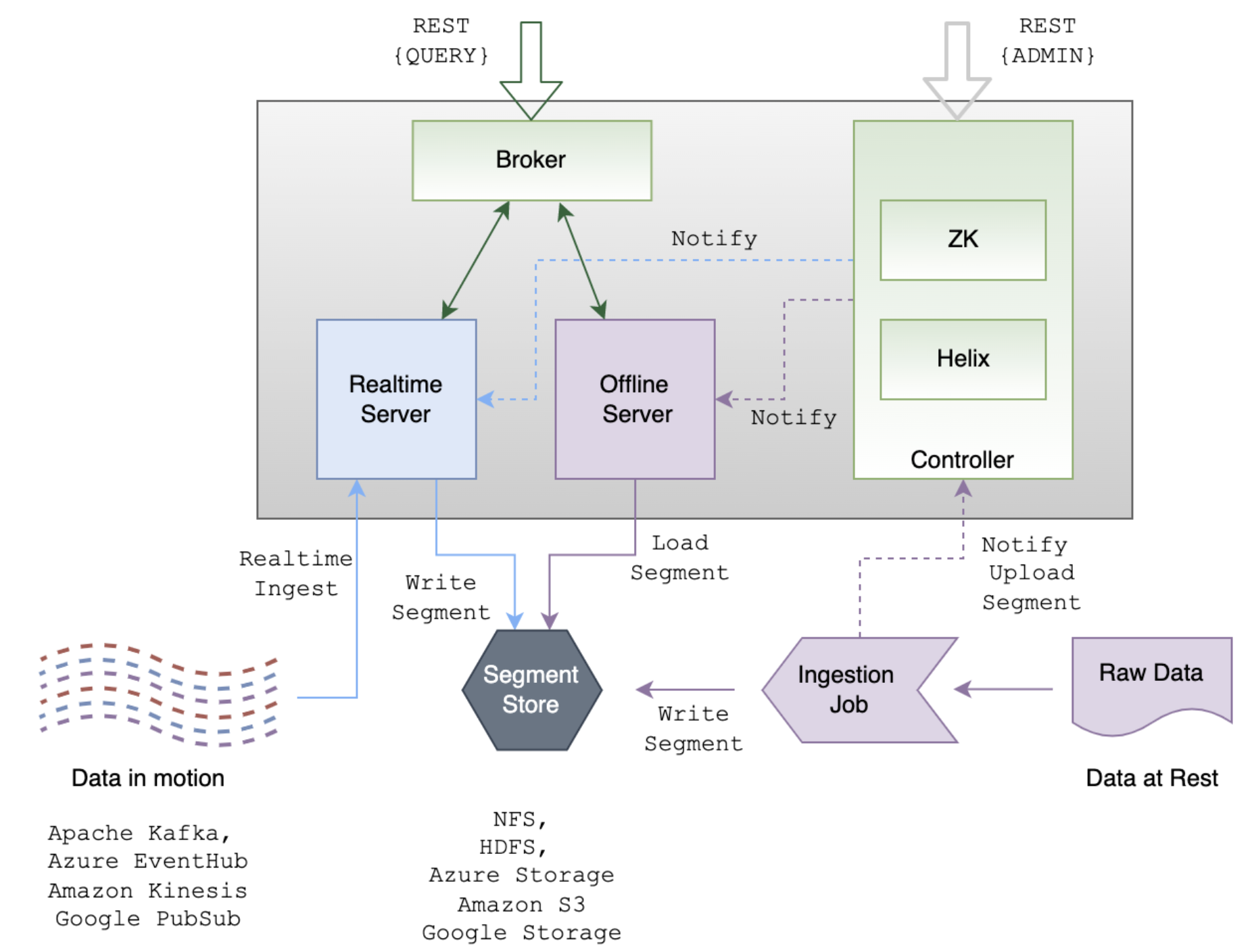
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| Apache Pinot Cluster || || +---------------------+ +---------------------+ +---------------------+ || | Broker | | Server | | Controller | || | | | | | | || | - Query Routing | | - Segment Storage | | - Cluster Management| || | - Query Processing |<--> | - Realtime Ingestion|<-->| - Schema Management | || | - Result Merging | | - Query Execution | | - Segment Assignment| || +---------------------+ +---------------------+ +---------------------+ || ^ || | || v || +---------------------+ || | Client | || | | || | - Query Submission | || | - Result Retrieval | || +---------------------+ || |+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ ^ | v+---------------------+ +---------------------+ +---------------------+| Data Source | | Zookeeper | | Deep Storage || | | | | || - Kafka/S3/HDFS/etc | | - Cluster Metadata | | - Segment Backups || - Batch/Streaming |<--->| - Coordination |<--->| (S3/HDFS/etc) |+---------------------+ +---------------------+ +---------------------+Pinot follows a distributed architecture with multiple components working together to ingest, store, and query data efficiently.
Key Components
Brokers:
- Acts as the query layer of Pinot.
- Receives queries from clients and forwards them to the appropriate servers.
- Aggregates results from multiple servers and returns the final response.
Servers:
- Store the actual data in segment files.
- Execute queries on the stored segments.
- Supports both real-time and offline segments.
Controllers:
- Manages cluster metadata and coordination.
- Handles segment assignment, retention policies, and schema management.
- Uses Apache Helix for cluster management.
Minions:
- Performs background tasks like segment merging, data compaction, and optimization.
Zookeeper:
- Maintains cluster state and metadata coordination among controllers, brokers, and servers.
- Ensures high availability and fault tolerance.
Apache Pinot has four main components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Controller | Manages cluster coordination, table configurations, and metadata. |
| Broker | Handles queries, distributes them across servers, and returns results. |
| Server | Stores and processes data segments. |
| Zookeeper | Ensures cluster coordination and leader election. |
Who Uses Apache Pinot?
Many big companies use Pinot, including:
- LinkedIn (for real-time analytics on user activity).
- Uber (for tracking ride demand in different areas).
Key Features of Apache Pinot
- Real-time and Batch Data Ingestion – Supports data from Kafka, Pulsar, Hadoop, S3, and more.
- Ultra-Low Latency Queries – Processes complex queries in milliseconds.
- Columnar Storage – Optimized for analytical queries.
- Flexible Indexing – Includes Inverted, Sorted, Star-tree, and Range Indexing for fast lookups.
- SQL-Like Query Language – Supports familiar SQL queries.
- Highly Scalable – Can handle terabytes to petabytes of data efficiently.
- Integration with BI Tools – Works with Tableau, Superset, Looker, and more.
Summary
- Minimum setup: 1 Controller, 1 Broker, 1 Server, 1 Zookeeper.
- Production HA setup: 3 Controllers, 2+ Brokers, 3+ Servers, 3+ Zookeeper nodes.
- Scale components based on query load, ingestion volume, and fault tolerance needs.
Comparison: Apache Pinot vs Other OLAP Databases
| Feature | Apache Pinot | Druid | ClickHouse | Presto |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real-time Ingestion | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❌ No |
| Columnar Storage | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Query Latency | 🚀 Milliseconds | ⚡ Fast | ⚡ Fast | 🐢 Seconds |
| Indexing Options | ⭐ Star-tree, Inverted | 🔍 Bitmap | 🔍 Sparse | ❌ No Indexing |
| Data Source | Kafka, Hadoop, S3 | Kafka, Hadoop | Filesystem | Databases |
CRUD Operations in Apache Pinot
| Operation | Supported? | Workaround |
|---|---|---|
| Create (INSERT) | ❌ No direct INSERT | Use batch ingestion or Kafka stream |
| Read (SELECT) | ✅ Yes | Standard SQL queries |
| Update (UPDATE) | ❌ No direct UPDATE | Use Upsert (real-time) or re-ingest batch data |
| Delete (DELETE) | ❌ No direct DELETE |