Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
Create an Action Plan
You can create an action plan to automate tasks using one or more action runbooks.
Steps:
In the Pulse UI, go to Actions on the left navigation bar and select Actions. The list of existing action plans appears.
On the Actions page, click Create Action. The available action runbooks are displayed.
On the Action Runbooks page, drag a runbook into the Action Workflow box.
Note: You can create an action plan using one or more action runbooks.
Configure the runbook settings and click Submit.
For details on configuring runbooks, see below.
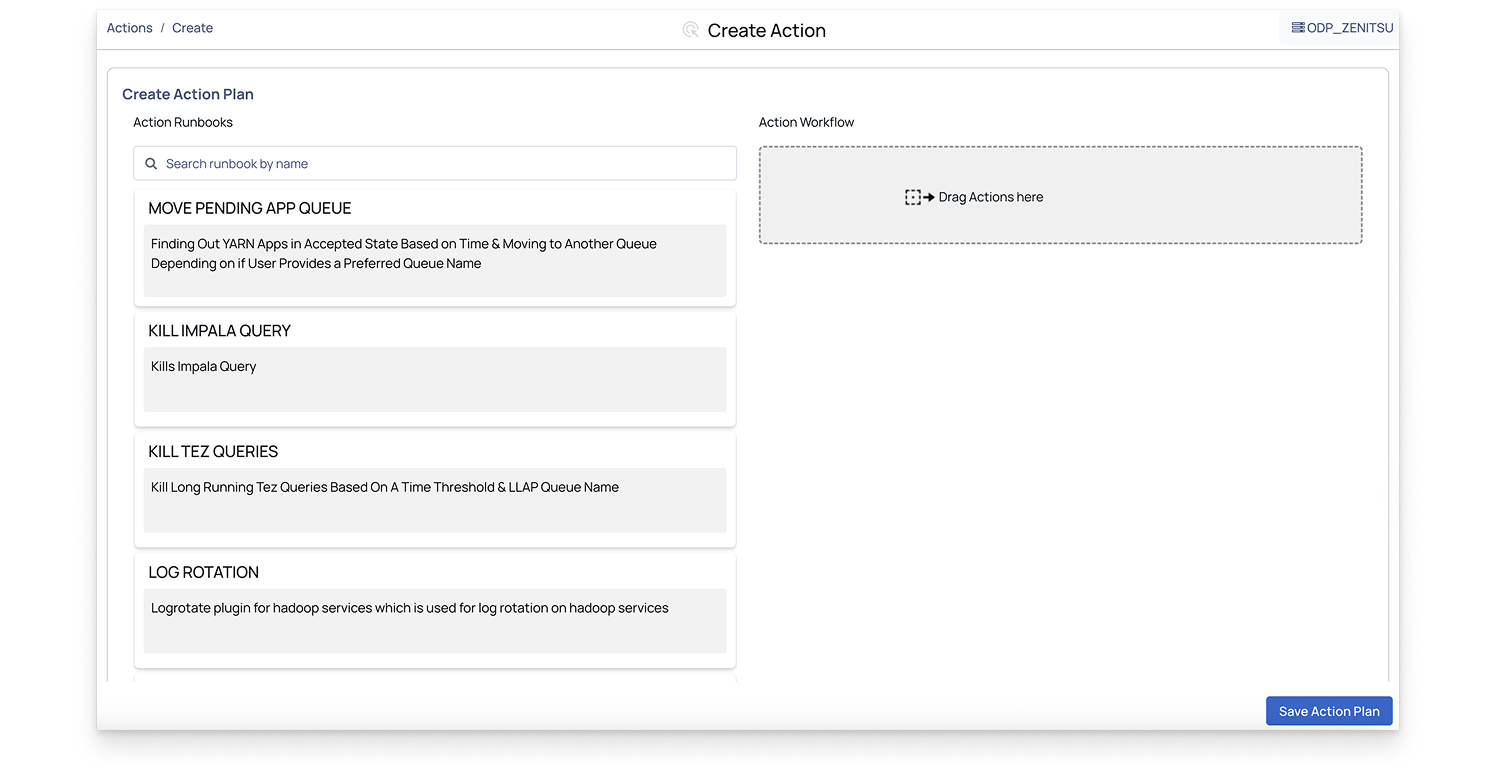
An action plan is created and listed on the Actions page with an overview and available options. For details, see Actions Overview and Action Plan Options.
Set Configuration for Action Runbooks
To create an action plan, drag and drop an action runbook into the Action Workflow box, then configure the details for each runbook as described below.
Perform HDFS Non-Admin Operations
The HDFS NON-ADMIN OPERATIONS action lets you perform the most common HDFS operations:
- Copying files or directories from a local source to a destination in HDFS or vice versa
- Moving files or directories from a local source to a destination in HDFS or vice versa
- Copying files or directories within HDFS, i.e, where the source and destination are both on HDFS
- Moving files or directories within HDFS, i.e,. where the source and destination are both on HDFS.
This configuration allows non-admin users to perform specific HDFS operations (like copying or moving files) while using Kerberos for secure authentication.
Configure the action runbook details as below:
- Is Cluster Kerberized?: Enable this option if the cluster is Kerberized.
- krb5.conf File Path: Enter the
Krb5.conffile path. - Name Node Address: Enter the NameNode address. Refer to the value of
dfs.namenode.rpc-address/dfs_namenode_servicerpc_addressto ensure the address to be entered. - Destination File/Directory: Enter the path to the destination file or directory in HDFS where you want to copy or move the file.
- HDFS Operation Type: Enter the HDFS operation type from the drop-down list.
- Source File/Directory: Enter the path to the source file or directory, either from the local system or HDFS, depending on the operation type.
- Kerberos Principal: Enter the Kerberos principal for authentication.
- Kerberos Realm: Enter the Kerberos realm, which defines the administrative domain for Kerberos.
- Service Principal Name: The name of the service principal for the HDFS NameNode. This is required if the cluster is Kerberized. For example,
hdfs/node_hostnameon CDP andhdfs/node_hostnameon HDP.
HDFS Top 10 Directories
The HDFS top 10 Directories action runbook enables you to get the top 10 HDFS directories in your ecosystem.
Configure the action runbook details as below:
- Is Cluster Kerberized?: Enable this option if the cluster is Kerberized.
- Krb5.conf File Path: Enter the
Krb5.conffile path. - Name Node Address: Enter the NameNode address. Refer to the value of
dfs.namenode.rpc-address/dfs_namenode_servicerpc_addressto ensure the address is entered. - Kerberos Principal: If Kerberos is enabled, enter the Kerberos principal in the format for secure authentication. If Kerberos is disabled, the value of this field must be simply the HDFS username.
- Kerberos Realm: Enter the name of the Kerberos realm your system will authenticate against.
- Service Principal Name: Enter the service principal name.
Kerberos
The Kerberos action lets you perform the most common Kerberos operations. You can use it to do kinit, kdestroy, etc., before and after performing actions in a Kerberized environment.
Configure the action runbook details as below:
- Keytab: Enter the Keytab file path.
- krb5.conf File Path: Enter the
Krb5.conffile path. - Logout (Delete Ticket): Toggle this setting based on whether you want the Kerberos ticket to be deleted after logout. Set to ON to delete the ticket or OFF to retain it.
- Output: Toggle this based on whether you want the Kerberos authentication process to display output logs. ON for logging or OFF for no logs.
- Kerberos Principal: Enter the Kerberos Principal used for
kinit.
Log Rotation
The Log Rotation action is a plugin for Hadoop services that facilitates log rotation. This action allows you to specify custom log patterns, log directory paths, and retention policies for their Hadoop service logs.
Configure the action runbook details as below:
- Custom Log Pattern: Enter the custom log patterns for the service logs, separated by commas. If not specified, the default log pattern for the service will be used.
- Log Directory Path: The path of the log directory where the service logs are being stored. If not specified, the default log directory will be used for that service, which is
/var/log/hadoop. - Output: Click the checkbox if you want the log rotation output to be sent to the logs.
- Retention Days: Enter the number of days’ worth of logs to retain. If not specified, the default retention period of 30 days will be used.
- Service Name: Enter the name of the Hadoop service for which you want to rotate logs.
- Timeout (in seconds): Specify the timeout duration in seconds for the log rotation to complete.
Make API Request
The Make API Request action allows you to execute REST API calls with ease directly from our platform. By providing configurable parameters such as method, URL, and host tags, you can tailor your requests to fetch specific data. Optionally, you can log the API call output for further analysis.
Configure the action runbook details as below:
- Timeout (in seconds): Specify the timeout duration for the API request in seconds.
- Headers: Enter headers for the API call and specify them as a string. Each header must be separated and prefixed with -H. For example, -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Host: VM001".
- Skip SSL Certificate Verification: If you set it to
true, the API call ignores the SSL certificate verification. - Is Kerberized: Set this to
trueIf the API call needs Kerberos authentication. - krb5.conf File Path: Enter the path to the
krb5.conffile for Kerberos authentication. - Method: Enter the HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) for the API request.
- Output: Check this box to log the output of the API call to the platform's logs.
- Password For Basic Authentication: Provide the password for basic authentication if it applies to the API call.
- URL: Enter the endpoint URL of the REST API to be called in the format (http|https)://host.domain[]/path.
- Username For Basic Authentication: Enter the Username for basic authentication if it applies to the API call.
Copy Item
The Copy Item runbook in our product enables you to copy files and directories, functioning similarly to the cp command. You can specify various parameters such as the source and destination paths, whether to overwrite existing files and ownership details.
Configure the action runbook details as below:
- Destination File/Directory: Enter the path where the file or directory will be copied to. The destination can be a directory or a file.
- Force Copy: Indicate whether the copy should be overwritten if the destination file already exists.
- Group: Specify the group for the copied item.
- Owner: Specify the owner of the copied item.
- Permission: Enter the permissions for the copied item (e.g., 644).
- Source File/Directory: Enter the path from where the file or directory will be copied. The source can be a directory or a file.
Execute Command
The Execute Command action is a test plugin for Axn that allows you to run shell commands on specified hosts. You can specify the command to be executed and choose to log the output.
Configure the action runbook details as below:
- Specify Command Parameters:
- Command: Enter the shell command to be executed (default is ls -al).
- Output: Check this box if you want the output of the provided command to be written to the logs.
Run Script
The Run Script action allows you to execute a script on specified hosts and optionally return the output. You can choose the script to run and decide whether to wait for the script to finish execution.
Important: The maximum script file size supported is 8 MB.
Configure the action runbook details as below:
- Specify Script Parameters:
- Output: Check this box if you want the output of the provided script to be written to the logs.
- Script File: Choose the file or enter the script to run.
- Wait to Finish: Check this box if you want to wait for the script to finish running before proceeding.
Kill Tez Queries
Terminates non-LLAP Tez queries that have been running for an extended period.
Is Cluster Kerberized: Turn on this option if the cluster is Kerberized.
Krb5.conf File Path: Enter the path to the
krb5.conffile.LLAP Queue Name: Specify the LLAP queue name to exclude from killing long-running queries.
RM URL: Enter the YARN Resource Manager URL for your cluster.
- Example:
http[s]://<RM Hostname>:<Web Port>/
- Example:
Threshold in Minutes: Specify the threshold duration in minutes. Queries running longer than this value will be terminated.
Kill Impala Query
Terminates an Impala query that has been running for an extended period.
Coordinator Host: Enter the coordinator host for the specified Impala query ID.
Coordinator URL: Enter the Impala coordinator URL.
- Example:
http[s]://<hostname>:<port>
- Example:
Is Kerberized: Turn on this option if the cluster is Kerberized.
Krbconfig: Enter the path to the
krb5.conffile.Op Type: Select the operation type based on where the query needs to be killed:
- Kill Query on ODP
- Kill Query on CDP
Query ID: Enter the Impala query ID.
Kill Spark - K8S Job
Terminates Spark applications that have been running for an extended period.
Namespace: Specify the Spark namespace.
Spark Value: Enter the Spark job identifier used to locate the application to be terminated.
- Client Mode: Enter the Spark application POD name.
- Cluster Mode: Enter the PID of the Spark application
Spark Job Execution Mode: Select the Spark execution mode for your application.
- Client Mode: Select this option when the Spark driver runs inside the Kubernetes cluster.
- Cluster Mode: Select this option when the Spark driver may run on either the Kubernetes cluster or a virtual machine (VM), and the executors run on the target cluster.
Note: Choose the execution mode that matches your Spark environment configuration.
This action runbook is applicable only for Standalone Spark on Kubernetes.
Kill YARN Applications
Terminates YARN applications that have been running beyond the defined threshold or meet specific filter criteria.
Application ID: Enter the Application ID to terminate a specific application. Enter
anyto automatically select applications based on threshold parameters.Confirm Application Was Killed Successfully: Select this option to verify whether the application was successfully terminated. The system checks the application status five seconds after sending the kill request.
Filter Criterion: Filter applications by allocated memory, allocated vCore, or user.
Is Cluster Kerberized: Turn on this option if the cluster is Kerberized.
Queue Name: Enter the queue name to terminate applications running on a specific queue. This field applies only when the filter option is User; otherwise, leave it blank.
RM URL: Enter the YARN Resource Manager URL for your cluster.
- Example:
http[s]://<RM Hostname>:<Web Port>/
- Example:
Value: Enter the threshold value based on the selected filter criterion:
- Memory: Specify in megabytes (for example,
100→100 MB). - vCore: Specify the number of cores (for example,
10→10 vCore). - User: Enter in CSV format (for example, single user →
user1; multiple users →user1,user2,user3).
- Memory: Specify in megabytes (for example,
Kill Trino Query
Terminates a Trino query that has been running for an extended period.
Password: Enter the Trino user password for authentication.
Trino Query ID: Enter the Trino query ID.
- Example:
20250912123456_00001_abcd1
- Example:
Trino Coordinator URL: Enter the Trino Coordinator URL for your cluster.
- Example:
http[s]://<Coordinator>
- Example:
Username: Enter the Trino username associated with the query.
This action runbook is applicable only for Trino on Kubernetes.
Move Pending App Queue
This runbook allows you to change the queue of a YARN application that is pending.
Application ID: Enter the ID of the pending application that needs to be moved. Enter
anyto automatically select applications based on threshold parameters.Elapsed Time: Enter the elapsed time in seconds to filter and move pending applications. Enter
0if you provided an application ID.Is Cluster Kerberized: Turn on this option if the cluster is Kerberized.
Queue Name: Enter the preferred leaf queue name (or names, separated by commas) where the pending application should be moved. You can enter
anyto automatically select a queue with available resources.Note: The user must have permission to submit jobs to the target queues.
RM URL: Enter the YARN Resource Manager URL for your cluster.
- Example:
http[s]://<RM Hostname>:<Web Port>/
- Example:
Make Ambari API Request
Performs a start, stop, or restart action on cluster services or components through the Ambari API.
Select Start, Stop, or Restart Action: Choose the action to perform on the cluster services.
- Stop
- Start
- Restart
Select Single Service, All Services, or a Host Component: Specify the target scope for the action—single service, all services, or a host component. Provide additional parameters as required.
Timeout (in Seconds): Specify the timeout duration in seconds for the Ambari API call.
Cluster Name for Ambari Action: Enter the cluster name for the Ambari API call.
Hostname of the Component: Enter the hostname of the component on which the action will be performed.
Skip SSL Certificate Verification: Select this option to skip SSL certificate verification.
Is Kerberized: Turn on this option if the Ambari UI is Kerberized.
Output: Select this option to write the output of the Ambari REST API call to the logs.
Password for Basic Authentication: Enter the password for basic authentication, if applicable to the Ambari API call.
Service Name / Component Name for Executing Action: Enter the service or component name on which to perform the action. (If you are applying the action to all services, you can leave this field blank.)
Ambari URL: Enter the Ambari HTTP or HTTPS URL.
- Example:
http[s]://<host>.<domain>[:port]
- Example:
Username for Basic Authentication: Enter the username for basic authentication, if applicable to the Ambari API call.
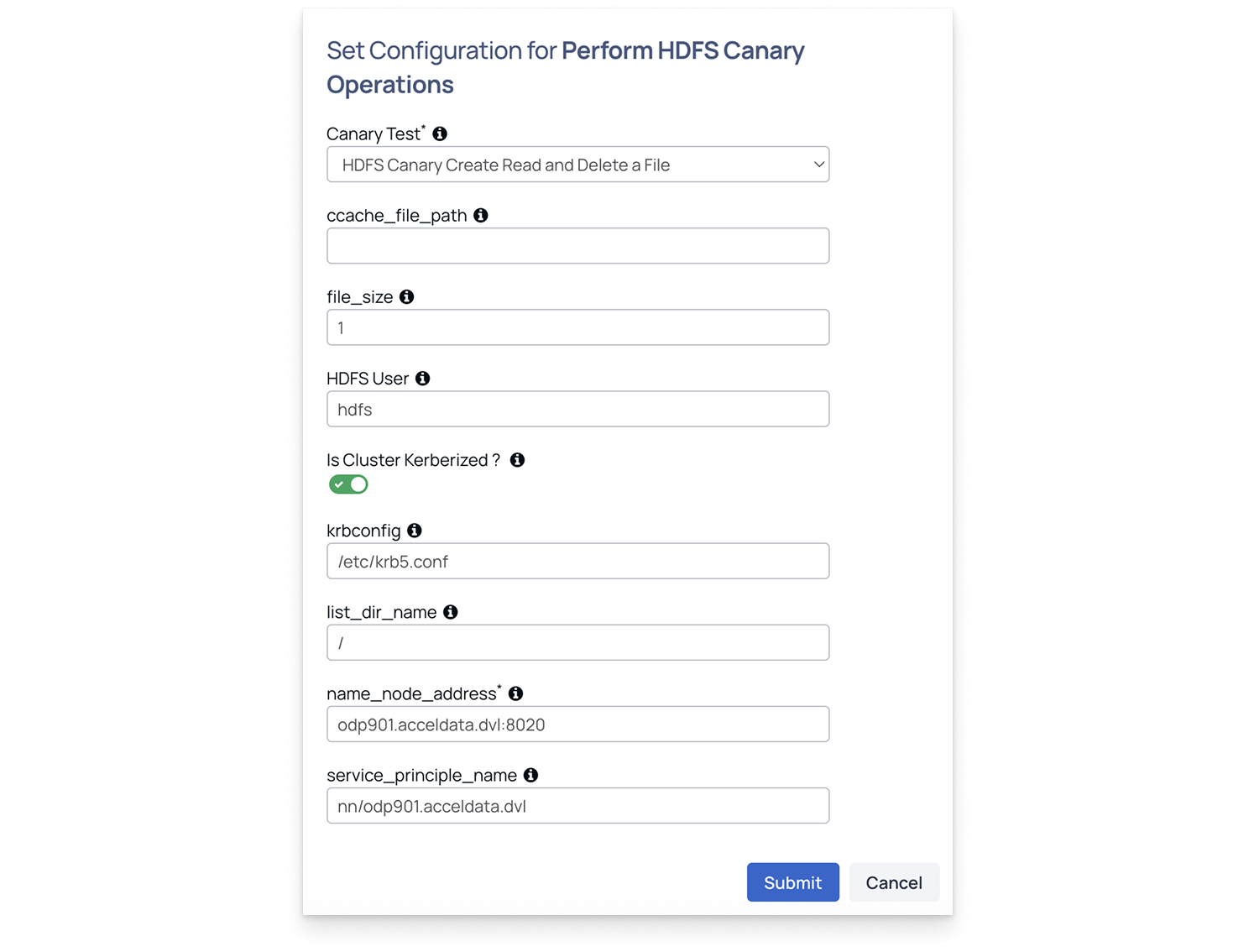
Perform HDFS Canary Operations
Performs HDFS canary tests to validate read, write, list, and delete performance in HDFS, ensuring cluster health and responsiveness.
Canary Test: Select one of the tests:
- hdfs-canary-create-read-delete-file
- hdfs-canary-list-dir
When hdfs-canary-create-read-delete-file is selected, fill in the details as below.
- Ccache_file_path: Path to Kerberos cache (usually /opt/pulse/actions/tmp/krb5cc*).
- File_size: Enter the file size in GB (minimum: 1 GB).
- HDFS User: Typically hdfs.
- Is Cluster Kerberized: Enable if Kerberos is configured.
- Krbconfig: Path to Kerberos configuration file (must exist on all nodes).
- list_dir_name: Directory to list in HDFS. Enter / for root.
- Name_node_address: NameNode address. For example, odp901.acceldata.dvl:8020.
- Service_principal_name: Required only for Kerberized clusters.
When hdfs-canary-list-dir is selected, fill in the fields as described in Step 2. The only differences are:
- File Size: Not required.
- list_dir_name: Specify any directory in HDFS (defaults to the root directory).
When configuring hosts in the next step for canary operations, specify a single host where the target service is running. This host will internally make requests and fetch the required data.
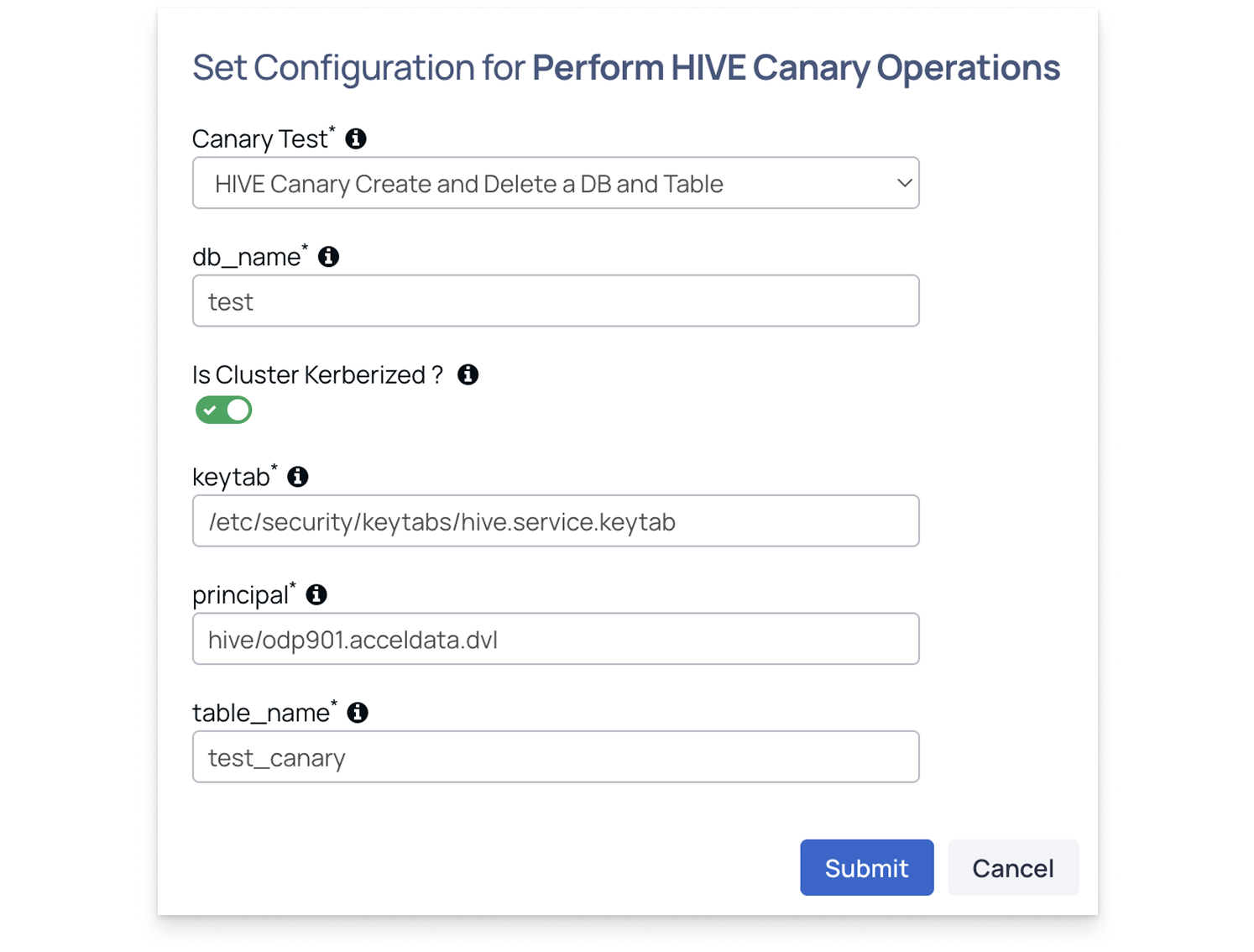
Perform HIVE Canary Operations
Performs Hive canary tests to measure query execution time, table operations, and overall Hive service stability.
- Ensure the Hive shell command-line tool is installed and configured on the host.
- Verify that the host can successfully connect to the Hive service.
- This host is typically the Hive client node specified in the Select Host field when configuring the Hive canary action in Pulse.
Canary Test: Select one of the tests:
- hive-canary-create-delete-table: Creates and deletes a table to measure query execution and error rates.
- hive-canary-select: Runs a select query to measure execution time and query latency.
When hive-canary-create-delete-table is selected, configure the following parameters to run the test:
- db_name: Enter the database name. Ensure that the database already exists.
- Is cluster kerberized: Enable this option if Kerberos authentication is enabled on the cluster.
- Keytab: Provide the location of the Hive keytab file.
- Principal: Enter the node where you want to run the canary test.
- Table: Specify the table name that the canary should create and then delete.
When hive-canary-select is selected, fill in the fields as described in Step 2.
When configuring hosts in the next step for canary operations, specify a single host where the target service is running. This host will internally make requests and fetch the required data.
Perform Impala Canary Operations
Performs Impala canary tests to verify query performance, latency, and service responsiveness across the Impala environment.
- Ensure the Impala shell (impala-shell) command-line tool is installed and configured on the host.
- Verify that the host can successfully connect to the Impala service.
- This host is typically the Impala client node specified in the Select Host field when configuring the Impala canary action in Pulse.
Canary Test: Select one of the tests:
- impala-canary-create-delete-table: Creates and deletes a table in Impala to validate responsiveness and stability.
- impala-canary-select: Executes a select query to measure query latency and success rate.
When impala-canary-create-delete-table is selected, configure the following parameters to run the test:
- db_name: Enter the database name. Ensure that the database already exists.
- Is cluster kerberized: Enable this option if Kerberos authentication is enabled on the cluster.
- Keytab: Provide the location of the Hive keytab file.
- Principal: Enter the node where you want to run the canary test.
- Table Name: Specify the table name that the canary should create and then delete.
When impala-canary-select is selected, fill in the fields as described in Step 2.
When configuring hosts in the next step for canary operations, specify a single host where the target service is running. This host will internally make requests and fetch the required data.
For additional help, contact www.acceldata.force.com OR call our service desk +1 844 9433282
Copyright © 2026