Actions
Actions is a scheduling automation system that integrates a playbook with an alert module to manage administrative tasks in a Pulse UI-interactive mode. You can, for example, implement an action that kills an application that has been operating for longer than the given SLA duration.
You need a private key for authorized user on respective server for running defined playbook. Only an Admin or Data Steward type of user can create, edit, and run an action.
To create a playbook, see Custom Playbook.
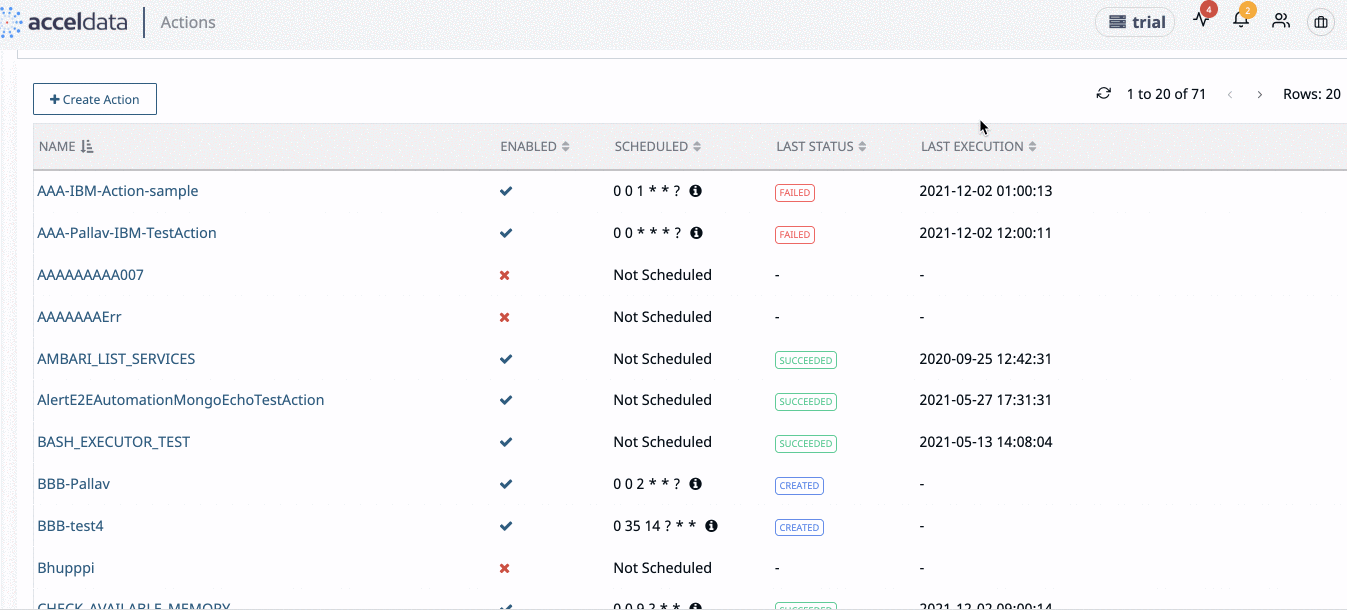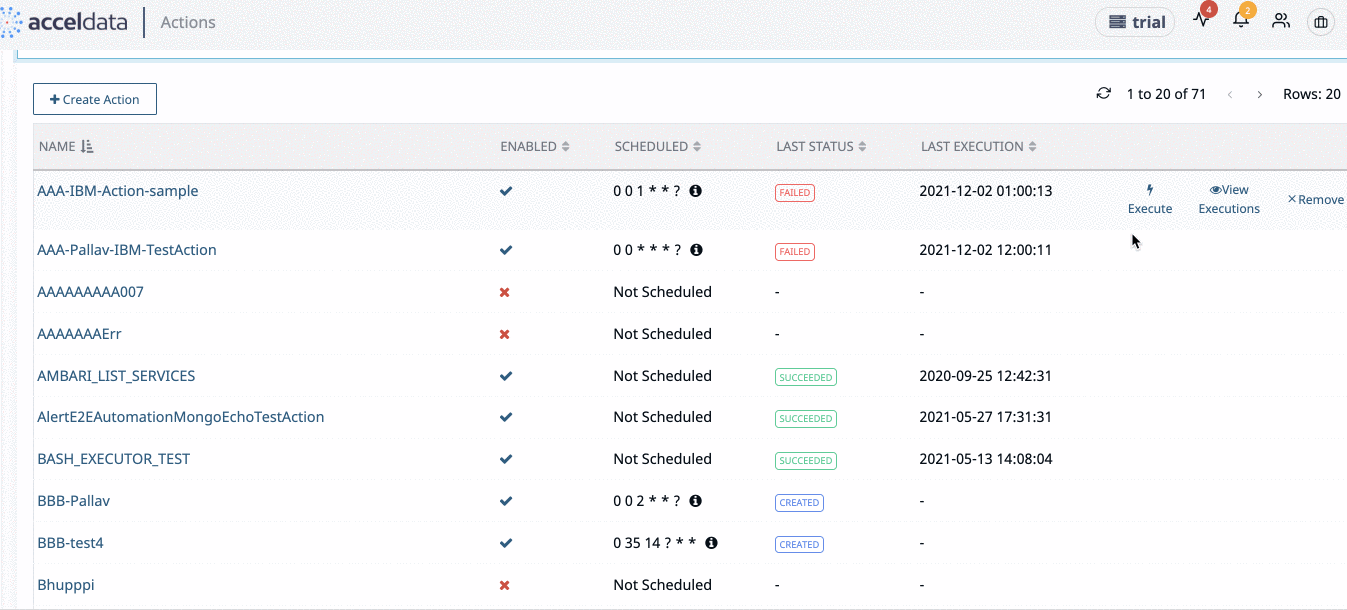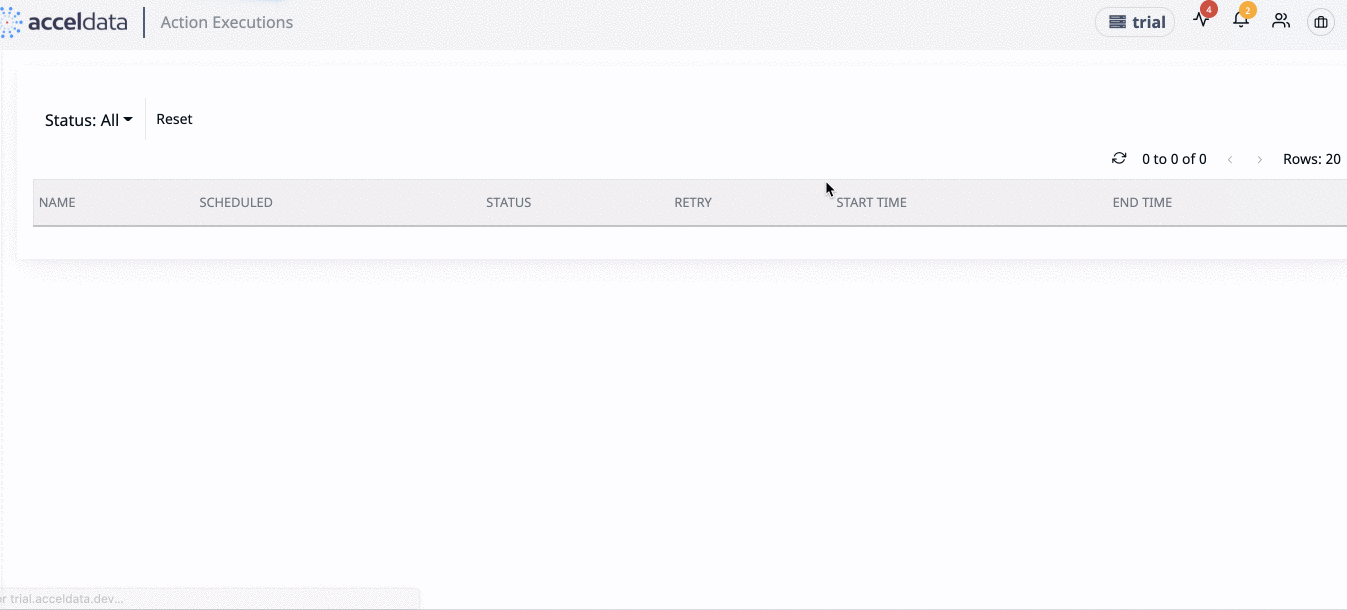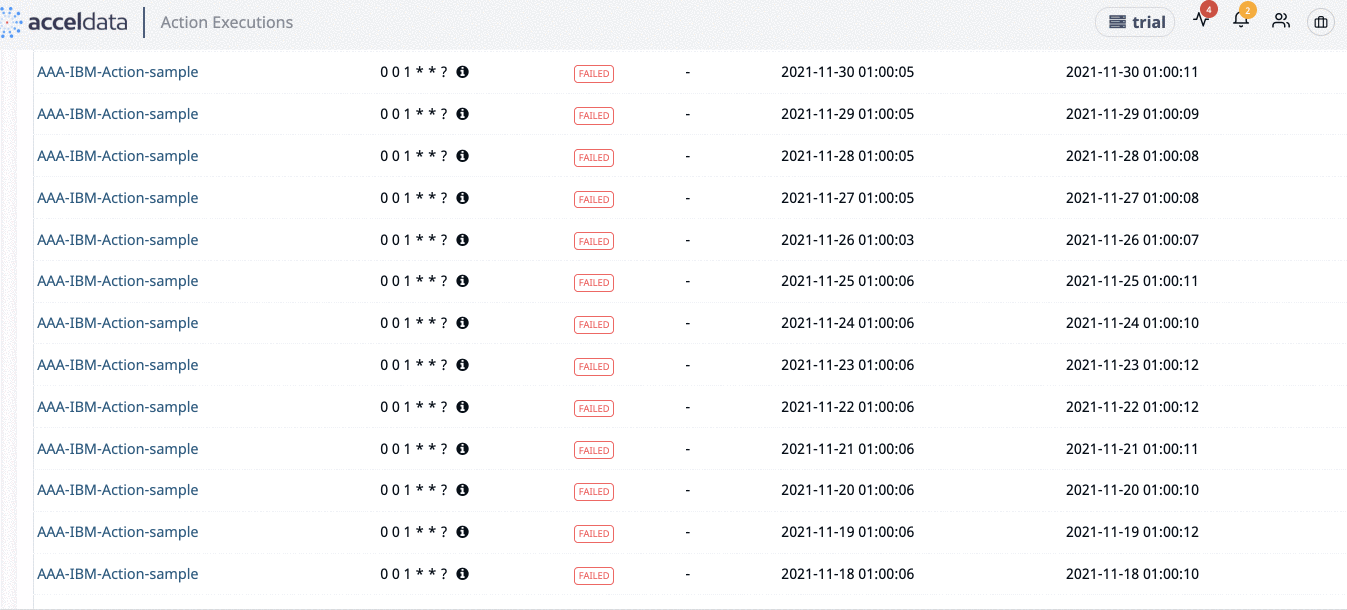
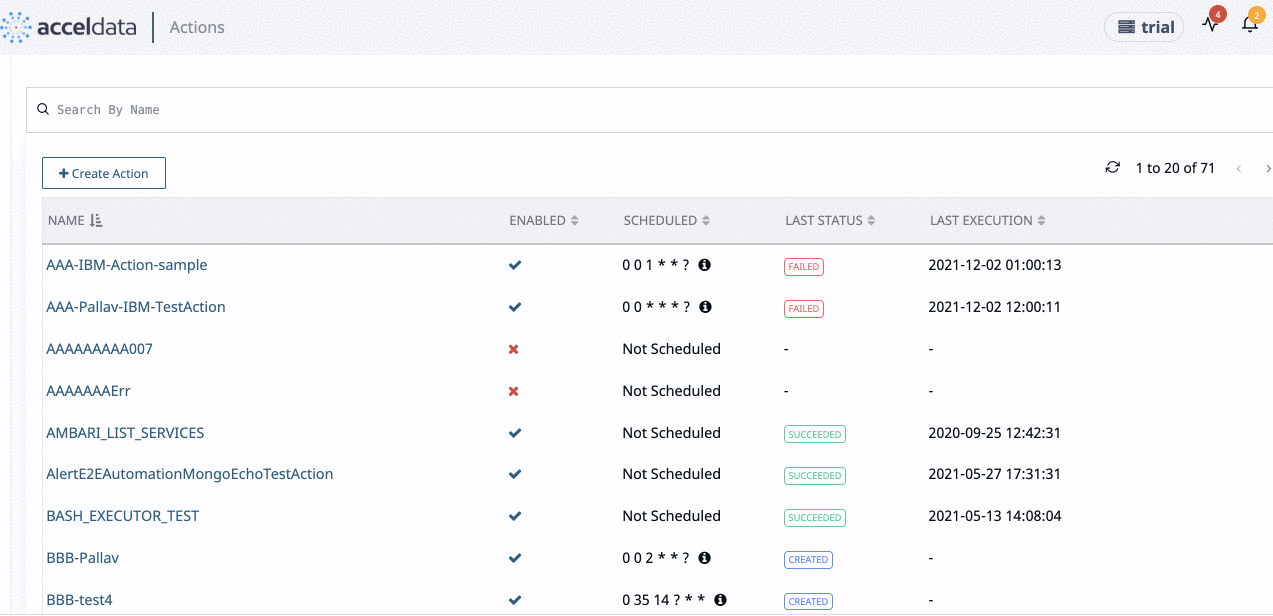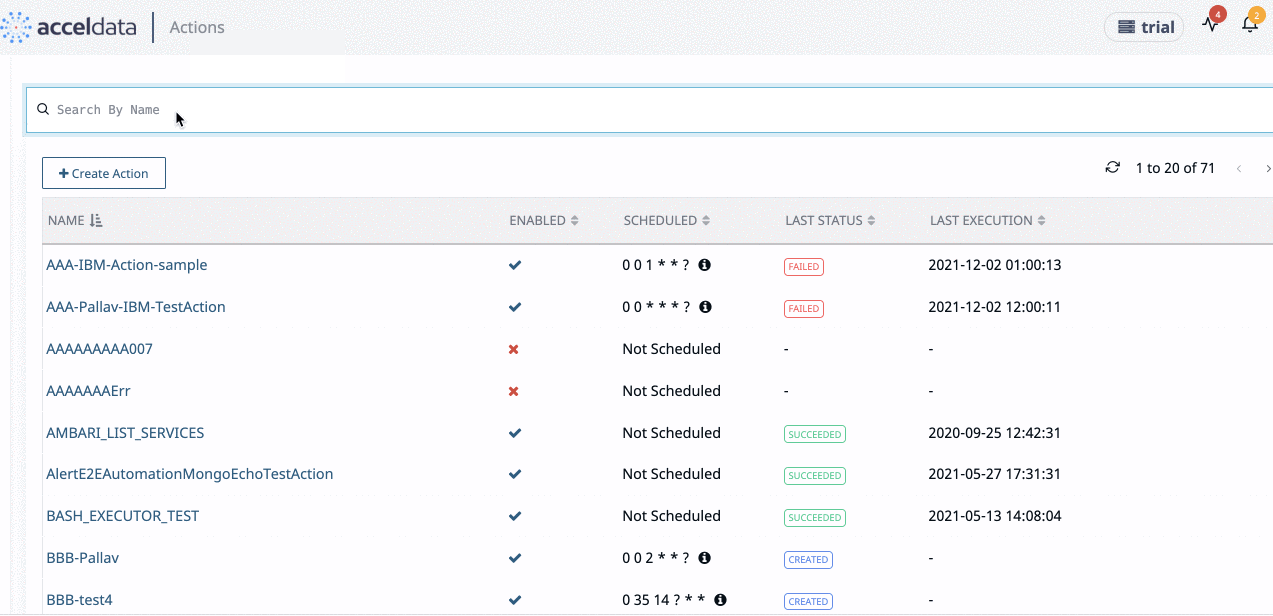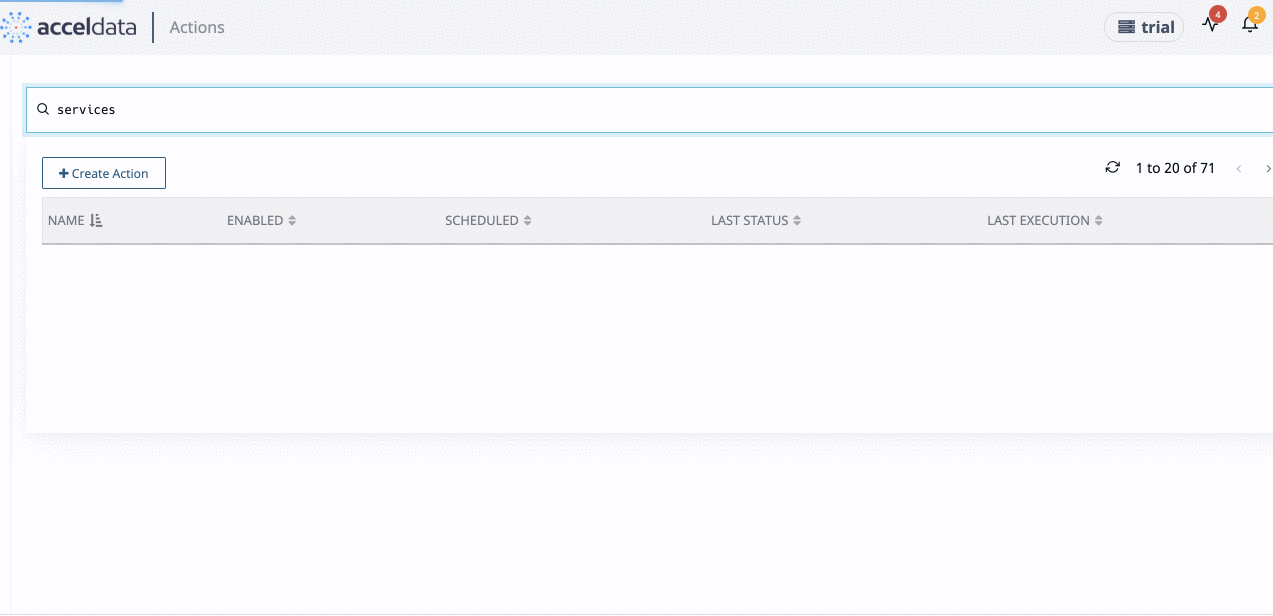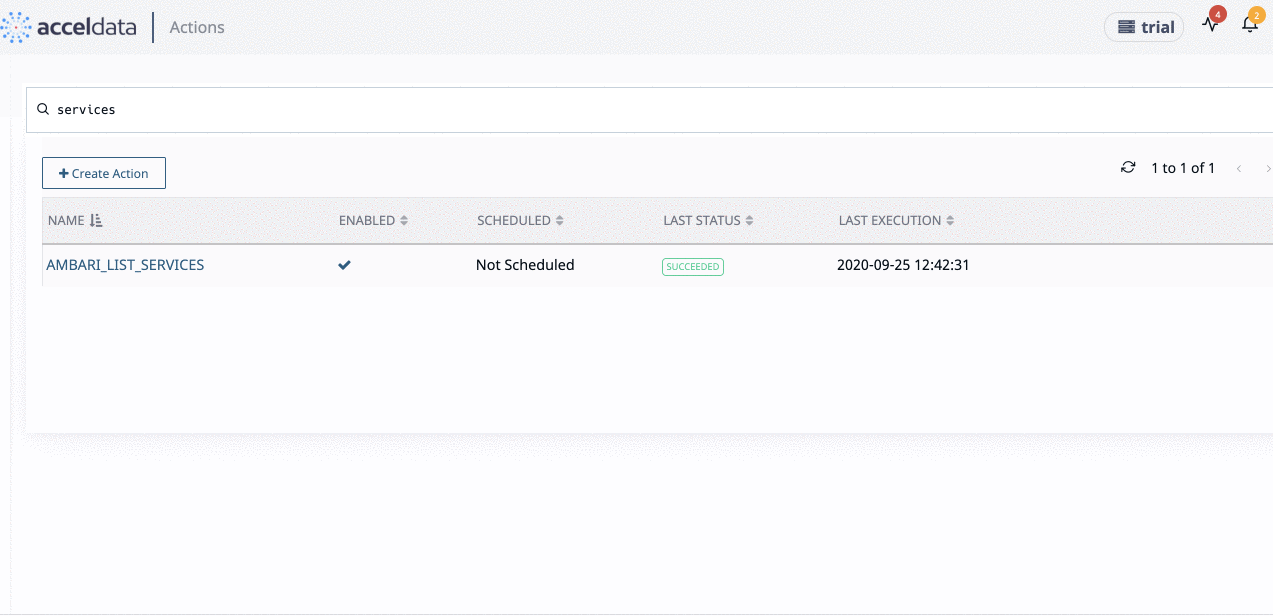
Click Actions > Actions from the left navigation bar to view the list of actions. The Actions page is displayed.
Action Table
The following table describes the details displayed in the action table:
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Specifies the name of the action that was provided while creating the action. |
| Enabled | Displays if the action is enabled or disabled. |
| Scheduled | Specifies the status of the Action. If the action is scheduled, displays the time at the the action is scheduled. If the action is unscheduled, displays Not Scheduled. |
| Last Status | Specifies the status of the action whether action had succeeded or failed or created. |
| Last Execution | Specifies the date and time for when the action was last executed. |
Creating an Action
To create an action, click the Create Action button from the Actions page. The Create Actions page is displayed. Select a runbook to create an action. An Action Wizard is displayed. The Action Wizard consists of stock playbooks provided by Acceldata, if you choose to create playbook of your choice, click here.
Action Wizard is followed by the following four steps:
Step 1
The following are the runbooks available; select the runbook for which you want to create an action:
You can click on the Info (“i”) icon next to each input field in every Action to view detailed information about the corresponding parameter.
- Hive Canary Action
- Validate Kerberos Ticket Generation
- DNS Lookup
- Ambari Admin Utilities
- ZK open connections
- HDFS top-10 Directories
- Local Log Cleanup
- HDFS data Utilities
- Check Path Accessibility
- Echo Text
- Open Port Text
- API Call
- HDFS Log Cleanup
- Hbase Compact Tables
- HDFS Admin Utilities
- Hbase Hbck Action
- Fire Command
- HDFS Balancer
- Kill Tez Queries
- YARN Kill App
- Kill Impala Queries (CDP)
- Kill Impala Queries
Step 2
Enter the following parameters in the step 2 and click Next:
(Mandatory) Include Hosts: Specify the host(s) where an action will be executed. You can select the hosts by the following two methods:
- Click the Include Host box, select the hosts from the drop-down menu.
- (Optional) Click the icon next to the include host box, Select Host window pop-ups. Select the host and click Select. The hosts is selected.
Note Include only 1 host name for the kill-based actions.
(Optional) Exclude Hosts: Specify the host(s) where actions should not run. To select the host click the icon, Select Host window pop-ups. Select the host and click Select. This field is populated only when "All" is selected under Include Hosts and certain hosts need to be excluded from the complete list.
Runbook: Shows the current runbook information.
(Mandatory) Remote User: Click the Remote User box with which the playbook will run on host machine, select the Remote User from the drop-down menu. By default the Remote User will be root.
(Optional) Kerberos Enable: Select this check box to enable Kerberos. You must also select a Kerberos principal if you enable Kerberos.
(Optional) To go to the previous step click Prev.
Step 3
To set up notification, click the click here, setup notification option will be displayed. To set up notification perform the following:
Email:
- Type an Email address(es) in the Email To box.
- (Optional) You can CC and BCC the notifications to others as well.
- Click Notify on. Select the status when the action notification has to be notified from the drop-down menu.
Slack:
- Enter the Slack Webhook URL to get notifications on a Slack channel. You can specify multiple Slack Webhook URLs for different groups or channels by adding commas to separate them.
- Click Notify on. Select the status when the action notification has to be notified from the drop-down menu.
JIRA: This notification type creates a new JIRA ticket.
- Click the Use Default Jira Configuration check box to use the JIRA configs set as organization default. If you select this check box, you need not configure any other fields.
- Notify On: Select when you want to receive JIRA notification. you can either select Completed, Succeeded or Failed.
- Project Key: Enter the project key in which you want to create the JIRA.
- Issue Type: Enter the issue type for the JIRA.
- Labels: Enter labels for the JIRA.
- Priority: Enter a priority for the JIRA.
(Optional) To disable the notification, click the *click here. *
Click Next.
You can configure the notification channels Email, Slack, and JIRA, or either one of them or none of them. If you do not want to setup notification Click Next.
Step 4
Perform the following in the final step to create an action:
- Name: Enter a name for the action
- Description: Enter a description for the action.
- Initial Delays: Specify a value in seconds for the initial delay of the action.
- Select the Enabled checkbox to enable the action.
- Select the Scheduled checkbox to schedule the action. Once selected, you can either manually enter a Cron Expression or use the Cron Generator to create one by specifying minutes, hours, days, and other parameters.
- Click Save. An Action is created.
Detailed Information About Each Action
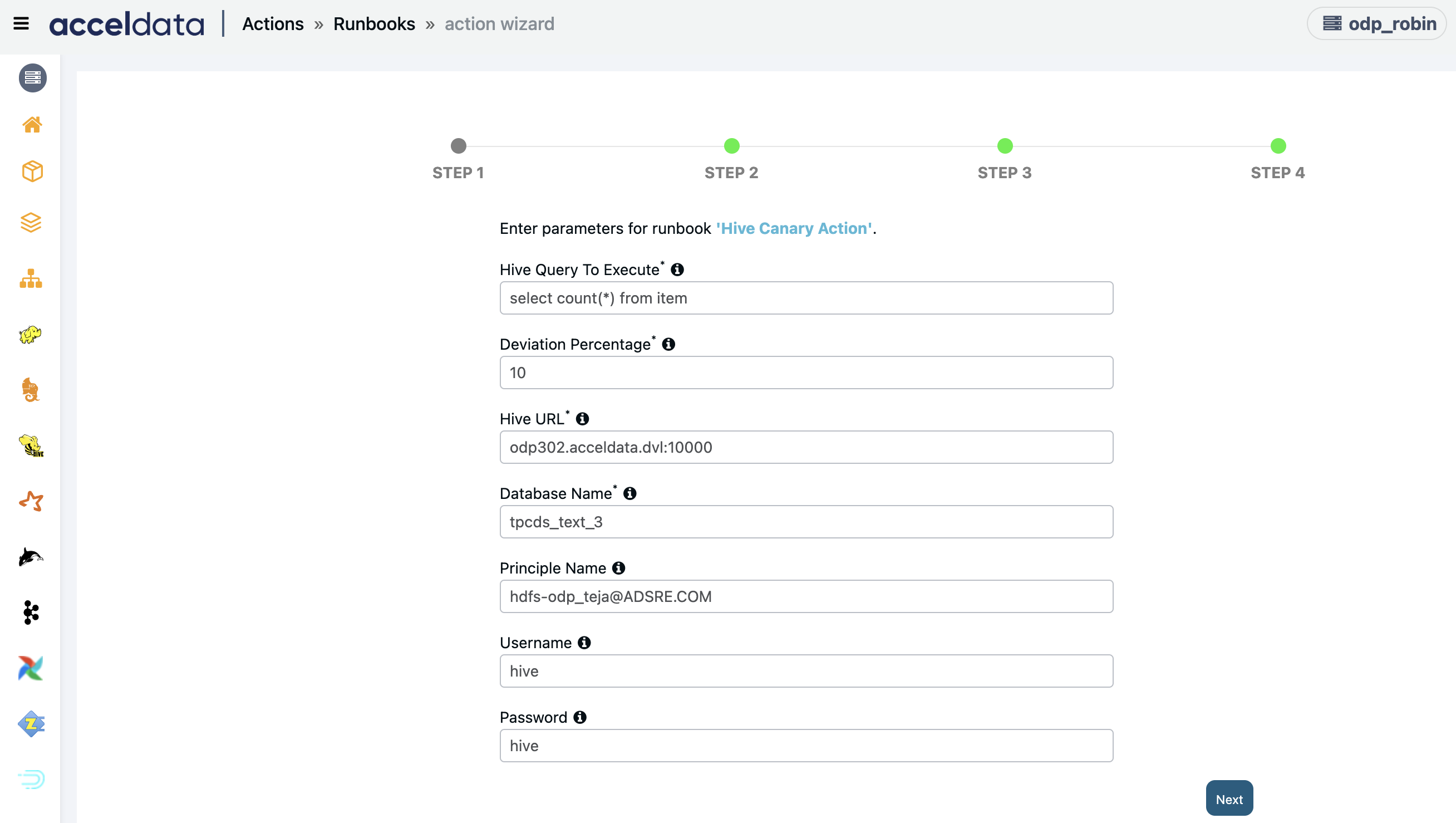
Hive Canary Action
Creates an action script to raise an alert when the hive query time deviation crosses a threshold.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- Hive Query to Execute: Enter the hive query that you want to raise an alert for.
- Deviation Percentage: Enter the deviation percentage.
- Hive URL: Enter the hive URL along with the host.
- Database Name: Enter the name of the database from which the query is executed.
- Username: (Optional) Enter the username to login.
- Password: (Optional) Enter the password.
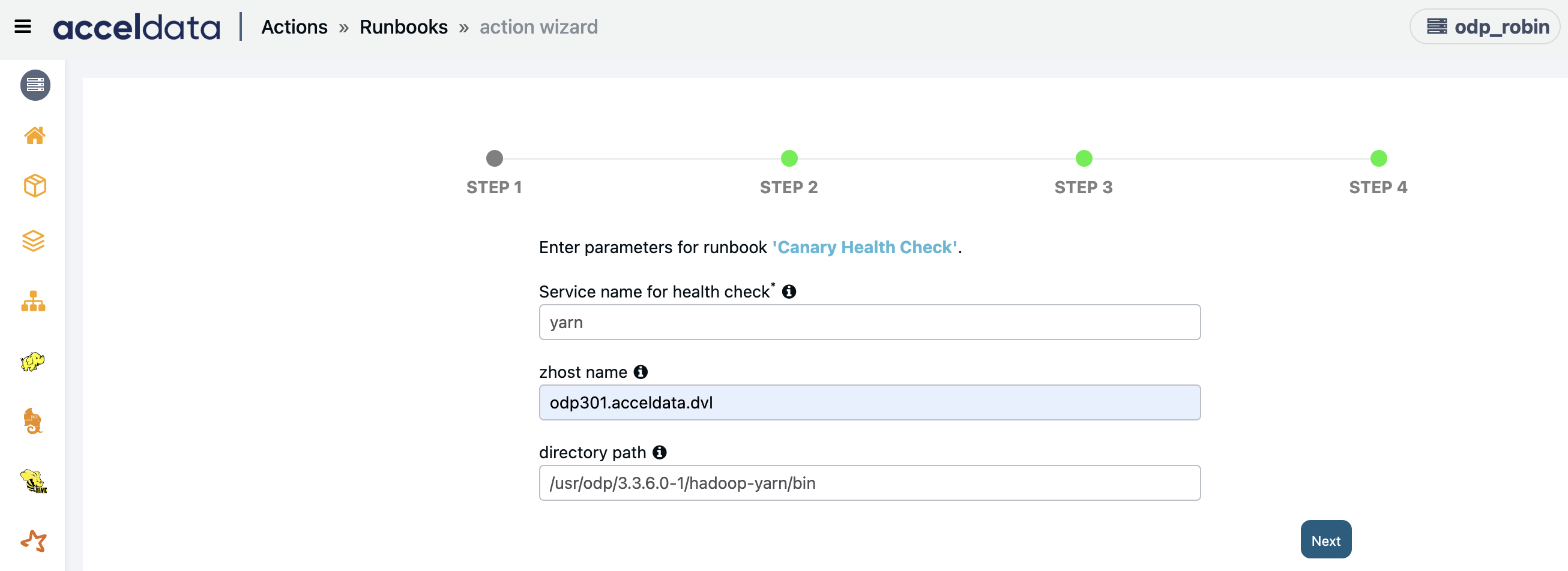
Canary Health Check
Create an action script to check canary health.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- Service name for health check: Enter the service name to perform a health check.
- zhost name: Enter Zookeeper host name to perform health check.
- Directory path: Enter path to service directory as <$SPARK_HOME>/bin/ or <$ZOOKEEPER_ HOME>/bin/ or <KAFKA_HOME>/bin/.
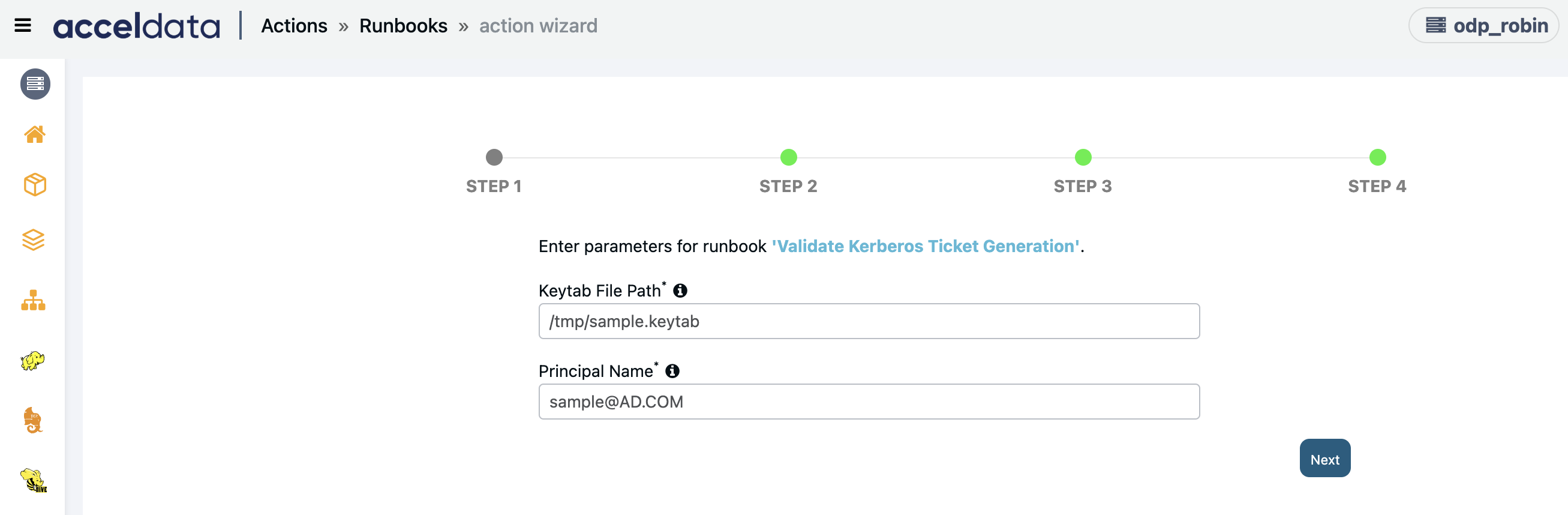
Validate Kerberos Ticket Generation
Creates an action script to check if kerberos is generating tickets or not.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- Keytab File Path: Path of the keytab file of kerberos.
- Principal Name: Name of the principal for which tickets need to be generated.
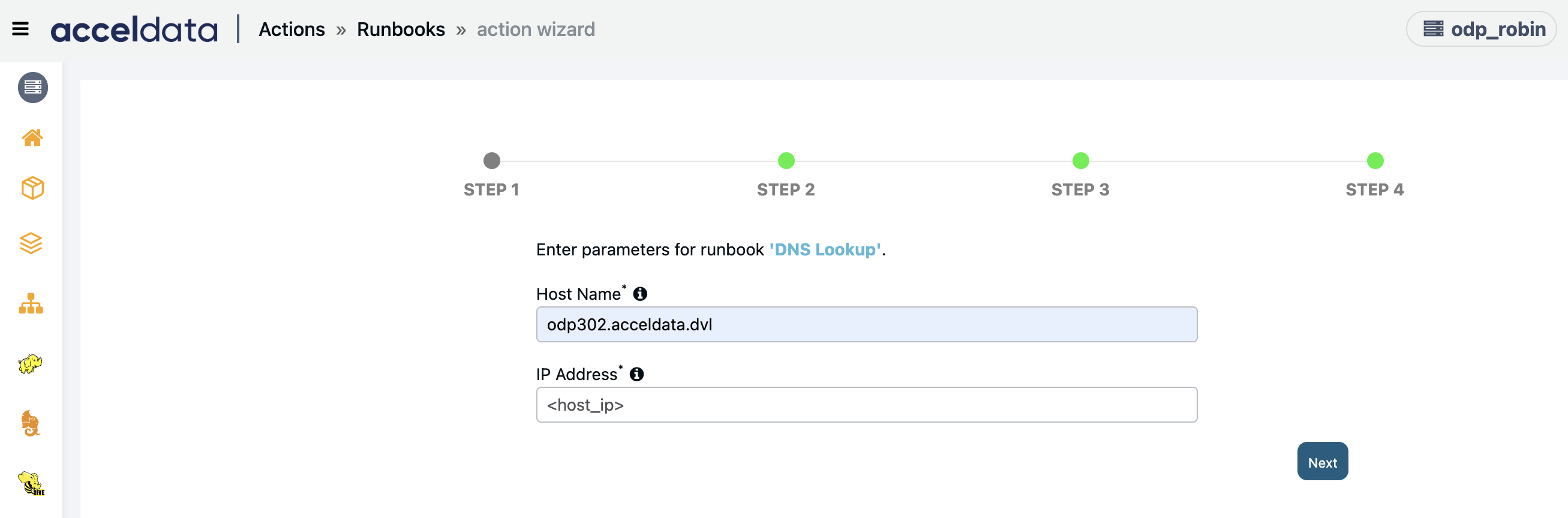
DNS Lookup
Creates an action script to check and validate forward/reverse DNS lookup for given host against all cluster hosts.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- Host Name: Enter the Hostname for forward lookup.
- IP Address: Enter an IP Address for reverse lookup.
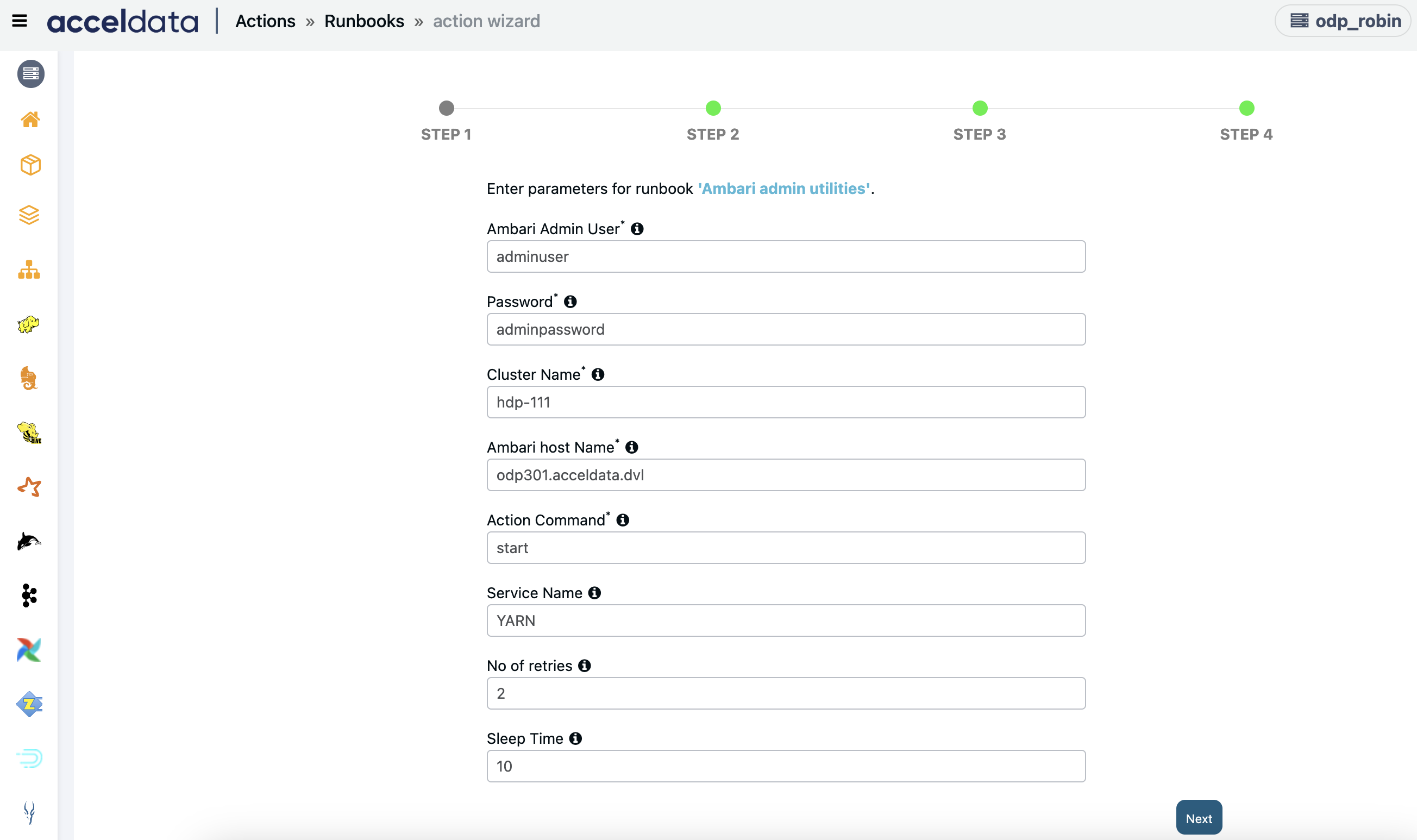
Ambari Admin Utilities
Creates an action script to execute multiple Ambari Actions.
Enter the Action Command and click Next:. Click
ZK open connections
Creates an action script to find an active and the number of connections opened on the ZK clients.
- Click Next.
HDFS top-10 Directories
Creates an action script to find the top 10 large directories in the HDFS.
- Click Next.
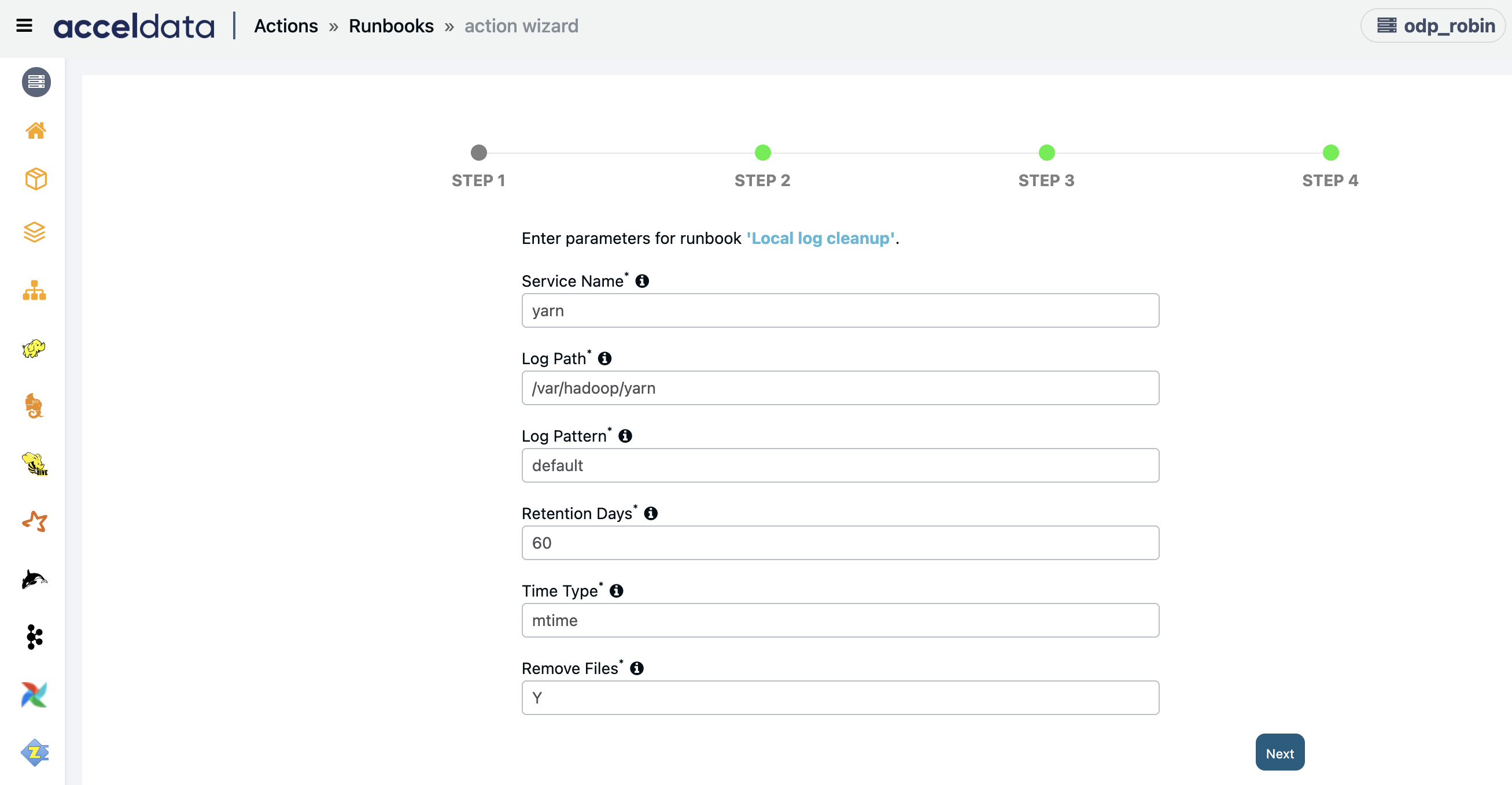
Local Log Cleanup
Creates an action script to remove the old service logs on the local.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- Service Name: Enter the Name of service's log(s) to be removed.
- Log path: Enter the configured log directory for given service, type 'default' for default service's log path
- Retention Days: Enter the logs to be removed older than above input days.
- Time Type: Enter either access time (atime) or modified time (mtime) to clean up the logs based on atime or mtime.
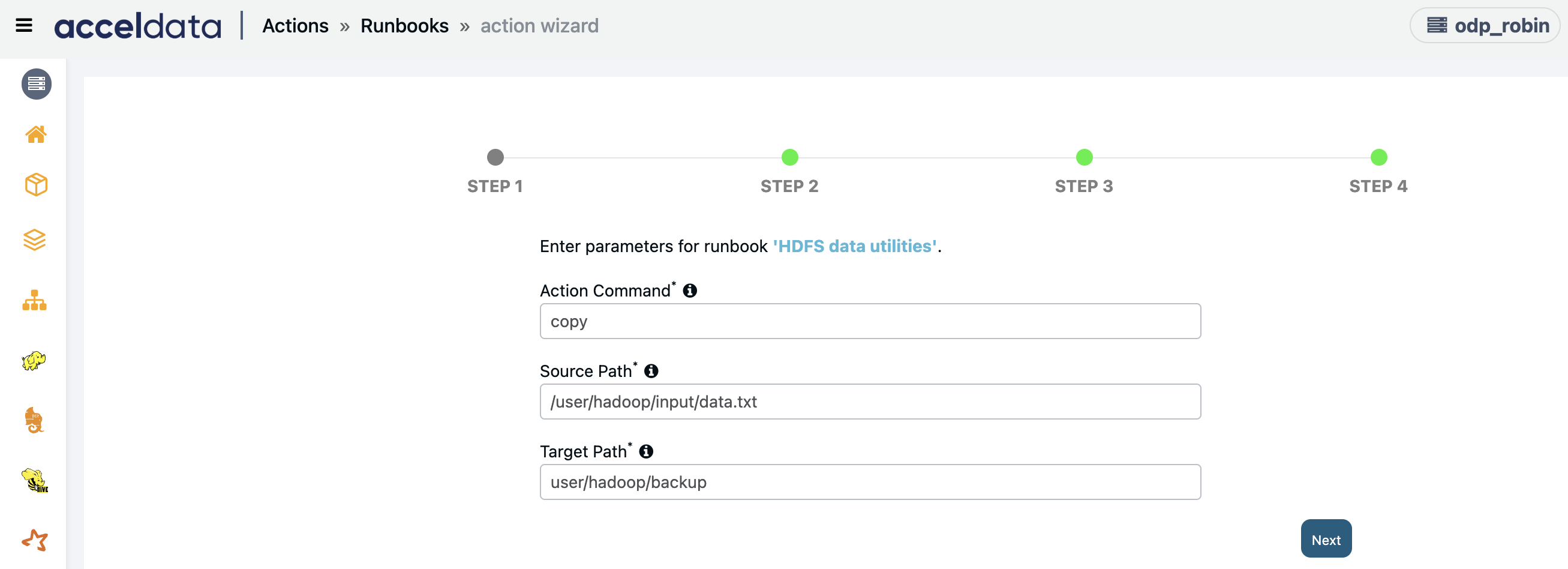
HDFS data Utilities
Creates an action script to run HDFS admin utilities related data, containing copy, move.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- Action Command: Enter the action command to run HDFS admin utilities.
- Source path: Enter the source path HDFS URL.
- Target Path: Enter the Destination path HDFS URL.
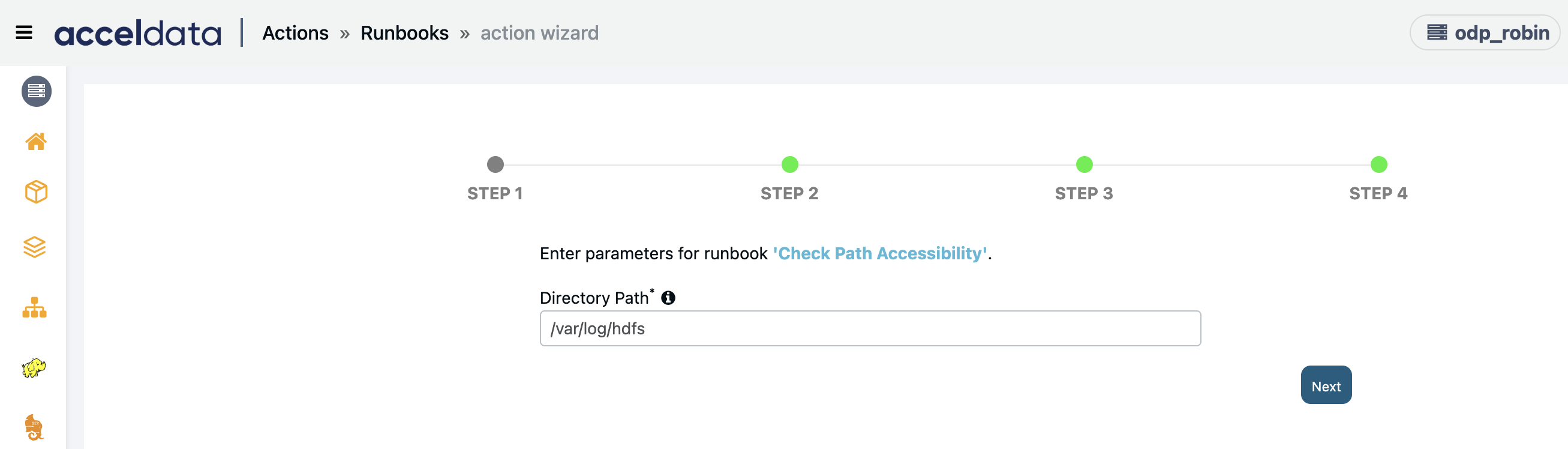
Check Path Accessibility
Creates an action to checks if given path is accessible.
Enter the Directory Path to check accessibility and click Next.
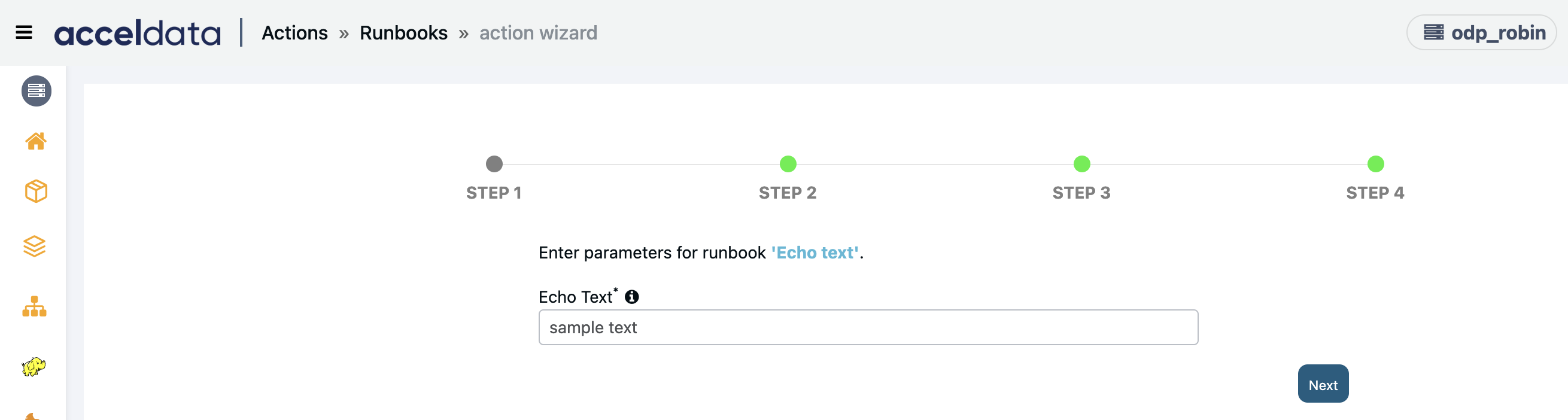
Echo Text
Creates an action to Echo a text to the remote machine.
Enter the Echo Text and click Next.
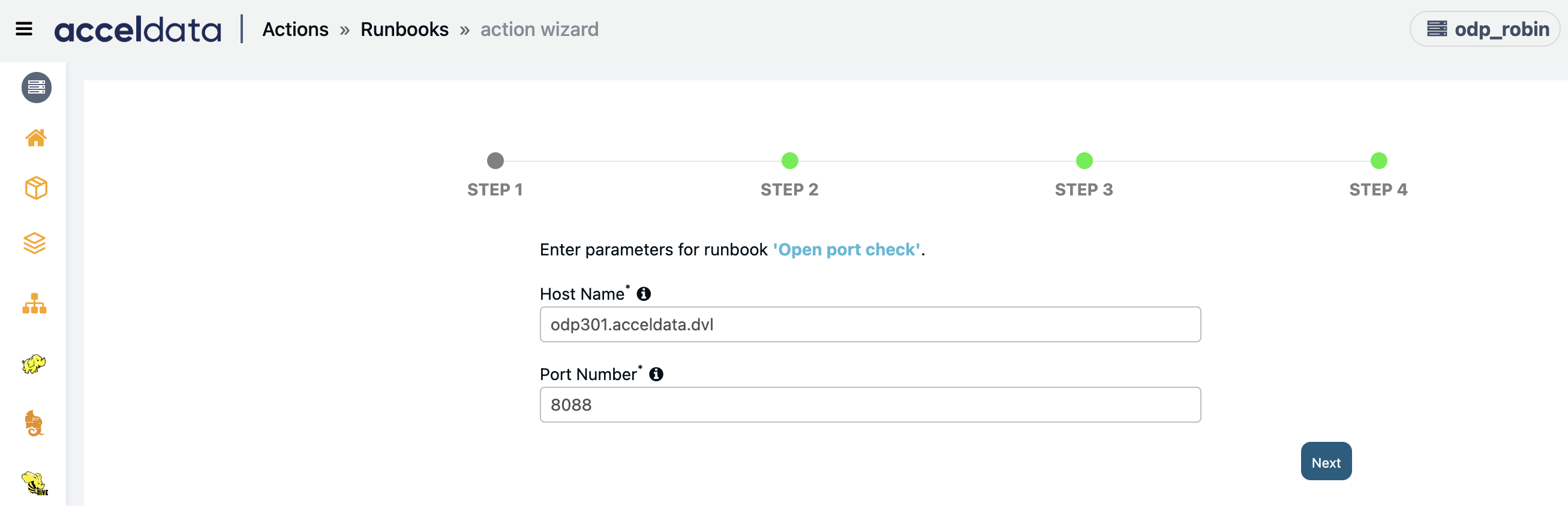
Open Port Text
Creates an action script to test the connection status for given server and port from specified host(s).
Enter the following parameters and click Next.
- Host Name: Enter the destination host name.
- Port Number: Enter the destination port number.
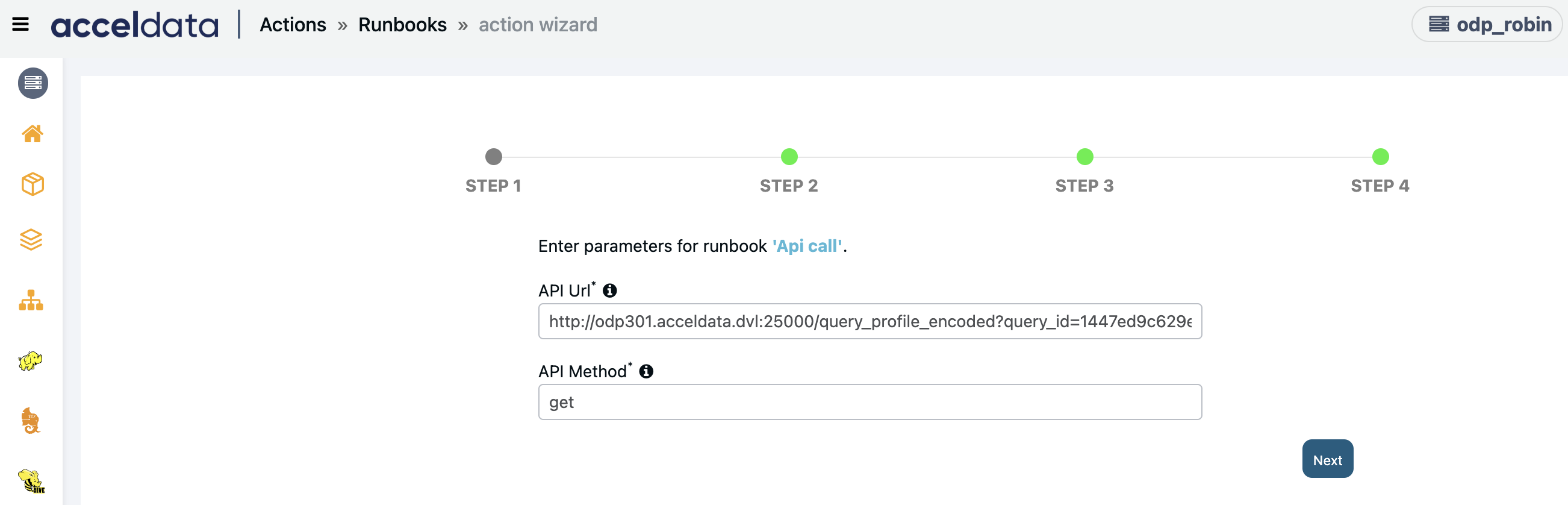
API Call
Creates an action to call an API.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- API URL: Enter the API URL.
- API Method: API method to be used to call the API.
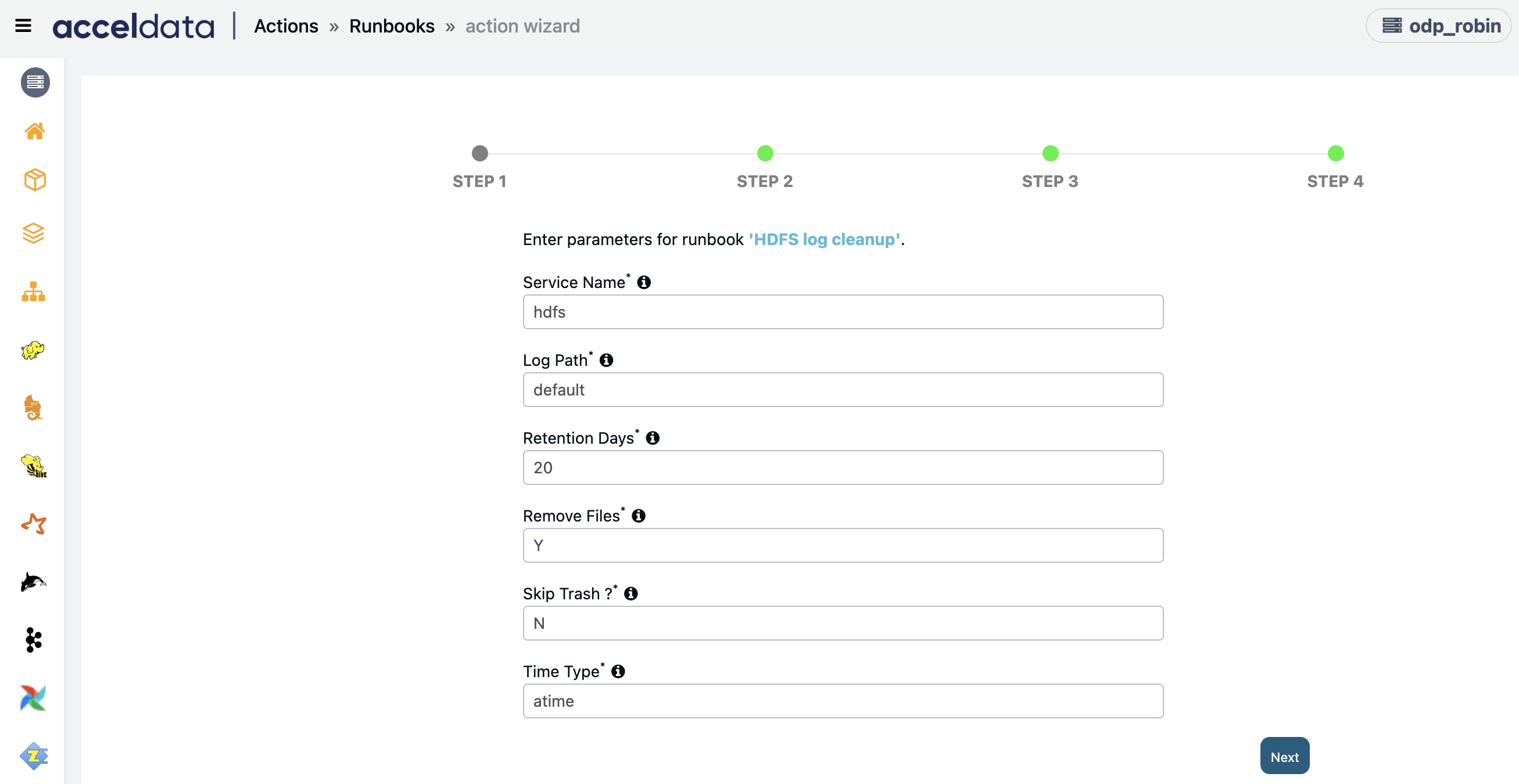
HDFS Log Cleanup
Creates an action script to remove the old service logs on the HDFS.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- Service Name: Enter the Name of service's log(s) to be removed.
- Log path: Enter the configured log directory for given service, type 'default' for default service's log path
- Retention Days: Enter the logs to be removed older than above input days.
- Remove files: Enter Y/N.
- Skip Trash: Skip trash when removing files (Y/N).
- Time Type: Enter either access time (atime) or modified time (mtime) to clean up the logs based on access time or modification time.
For HDFS log cleanup, using atime takes significantly more time compared to mtime, as it executes stat command for each file which is an expensive command. The time required to complete the action with atime is directly dependent on the total number of files being scanned, and it requires more time than usual.
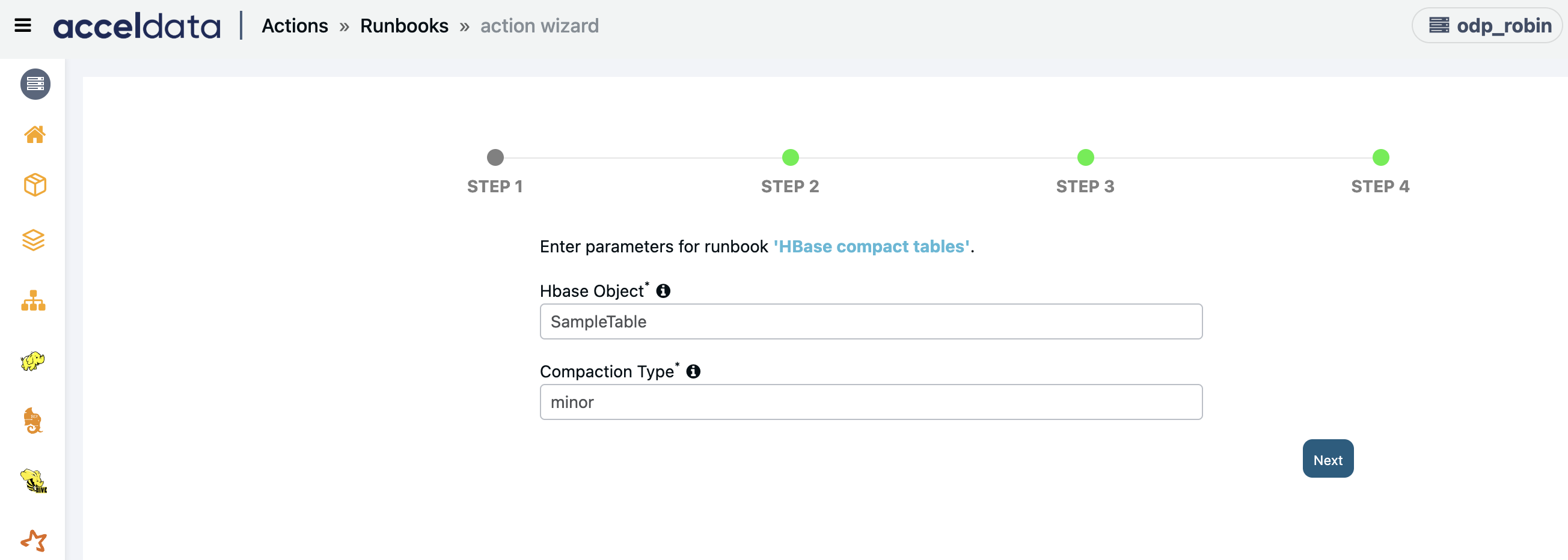
Hbase Compact Tables
Creates an action script to compact Hbase region/table/column family.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- Hbase Object: Enter the HBase object to be compacted.
- Compaction Type: Enter the HBase compaction type 'major' / 'minor'.
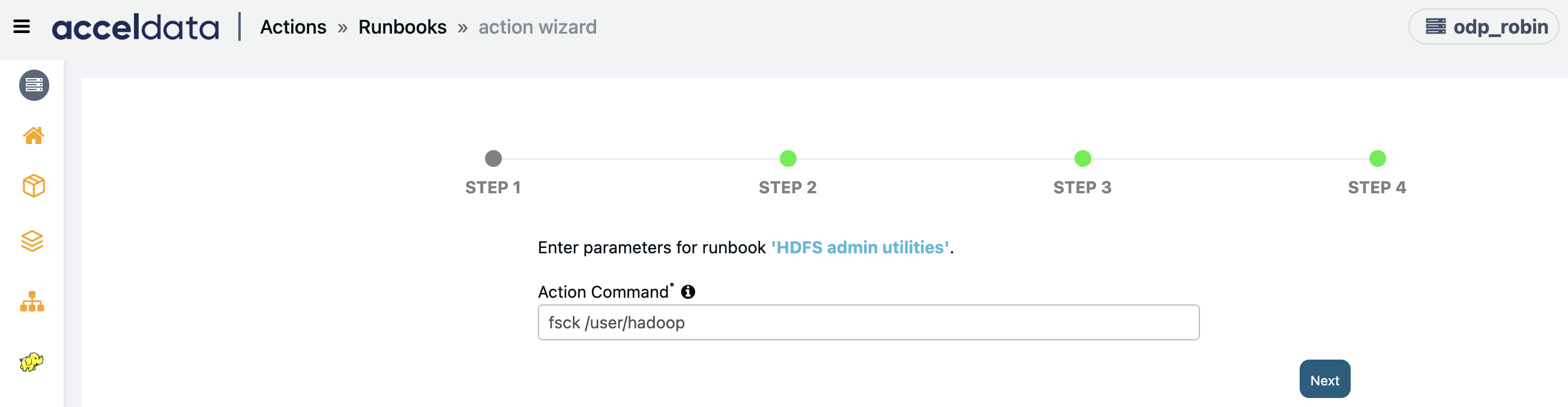
HDFS Admin Utilities
Creates an action script to run HDFS admin utilities containing fsck, image backup and balancer.
Enter the Action Command to run HDFS admin utilities. Click
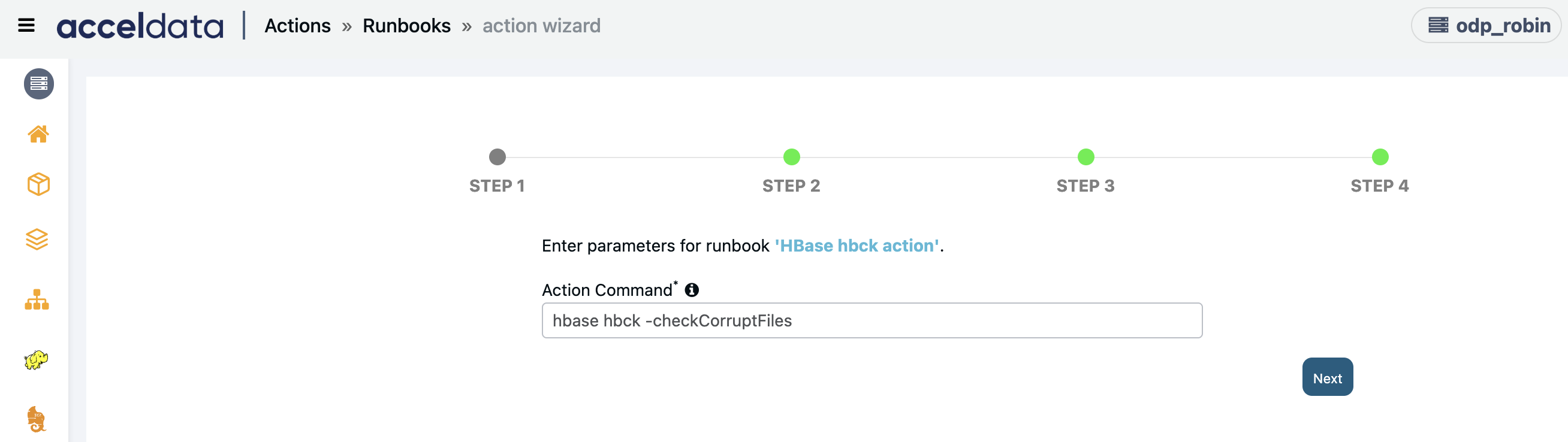
Hbase Hbck Action
Creates an Action script to run Hbck command to detect and fix the region inconsistencies.
Enter the Action Command. Enter the single operation in the field.
####
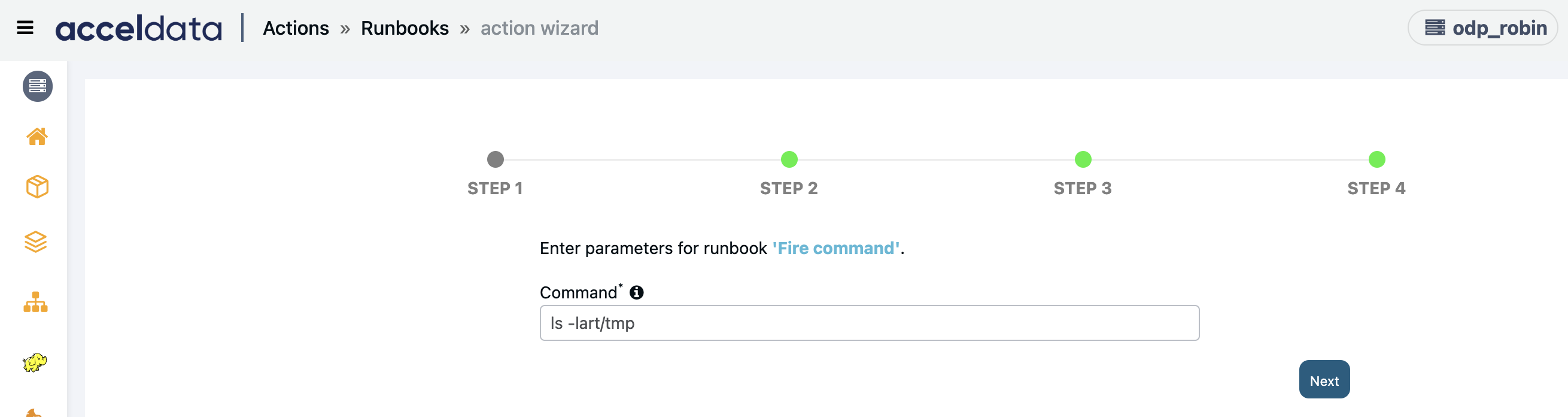
Fire Command
Creates an action script to run any command on the given host(s).
Enter the Command to be fired and click Next.
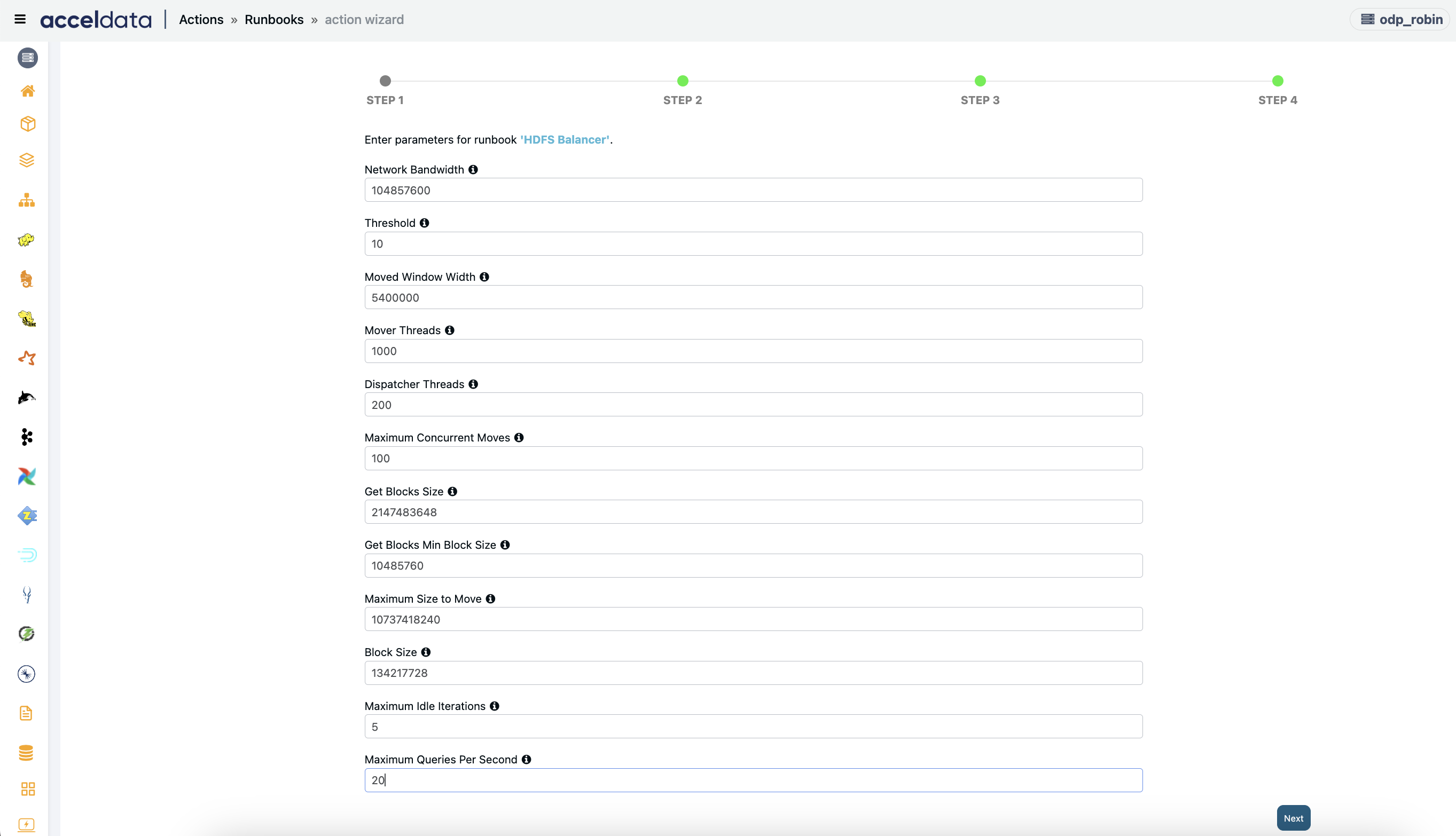
HDFS Balancer
Creates an action script to run HDFS datanode balancer with network bandwidth option. User requires path privileges and permissions.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- (Optional) Network Bandwidth: Enter the network bandwidth consumed by each DataNode, default bandwidth is 500MB/s.
- (Optional) Threshold: Enter the threshold(%) limit for balancer to move data, default threshold is 5.
- (Optional) Moved Window Width: Time window for moved blocks to avoid redundant moves. Default value = (from hdfs-site.xml OR 5400000 ms).
- (Optional) Mover Threads: Enter the number of threads to move blocks during balancing. Default value = (from hdfs-site.xml OR 1000).
- (Optional) Dispatcher Threads: Enter the size of the thread pool for the HDFS balancer block mover. Default value = (from hdfs-site.xml OR 200).__
- (Optional) Maximum Concurrent Moves: Enter the maximum number of concurrent block moves allowed for the balancer. Default value = (from hdfs-site.xml OR 100).
- (Optional) Get Blocks Size: Size of blocks fetched from data nodes during balancing. Default value = (from hdfs-site.xml OR 2147483648 bytes (2GB)).
- (Optional) Get Blocks Min Block Size: Enter the minimum size of blocks to be considered during balancing. Default value = (from hdfs-site.xml OR 10485760 bytes (10MB)).
- (Optional) Maximum Size to Move: Enter the maximum size of a single block to move during balancing. Default value = (from hdfs-site.xml OR 10737418240 bytes (10GB)).
- (Optional) Block Size: The HDFS block size. Default value = (from hdfs-site.xml OR 134217728 bytes (128MB)).
- __(Optional) Maximum Idle Iterations: Enter the maximum number of idle iterations before exit. Default value = (from hdfs-site.xml OR 5).
- (Optional) Maximum Queries Per Second: Enter the maximum number of getBlocks RPCs, data movement utilities can make to a NameNode per second. Default value = (from hdfs-site.xml OR 20).
####
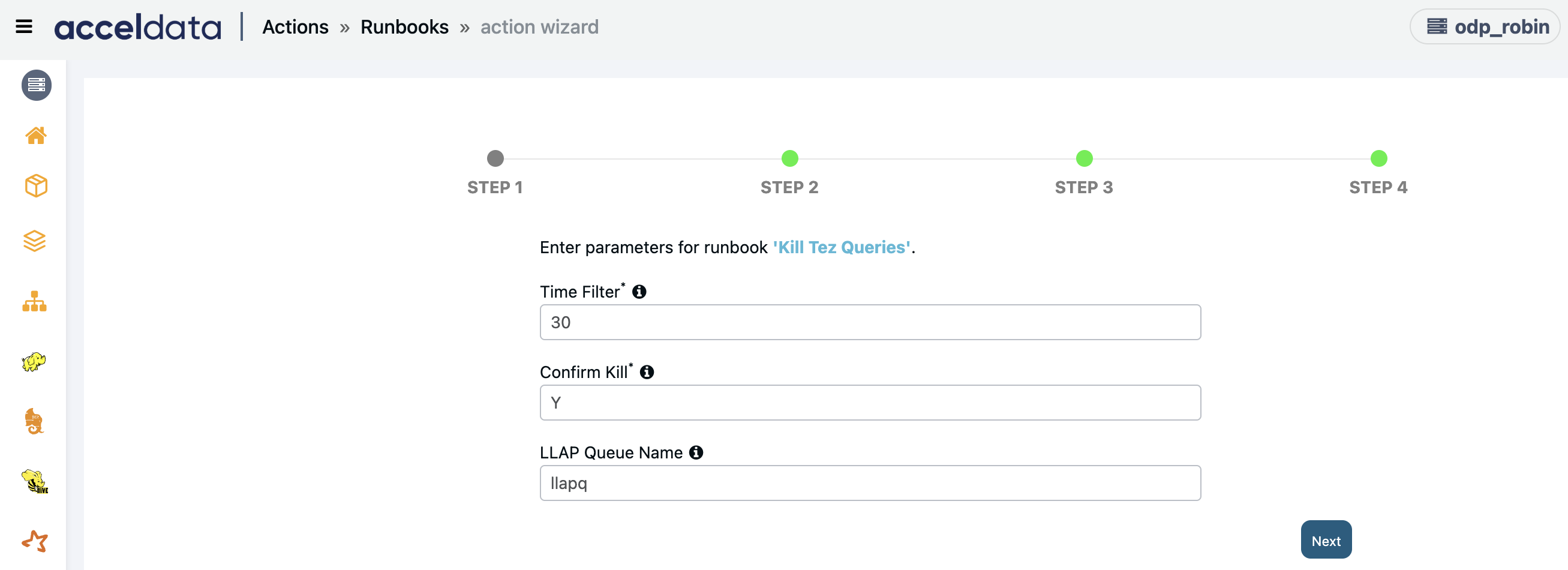
Kill Tez Queries
Ends non-LLAP Tez queries that have been running for a long time.
Enter the following parameters and click Next:
- Time Filter: Enter a time limit (in minutes) to kill queries.
- Confirm Kill: To confirm terminating apps, type Y, and to list apps, type N.
- LLAP Queue Name: To avoid stopping long-running apps, add the LLAP queue name.
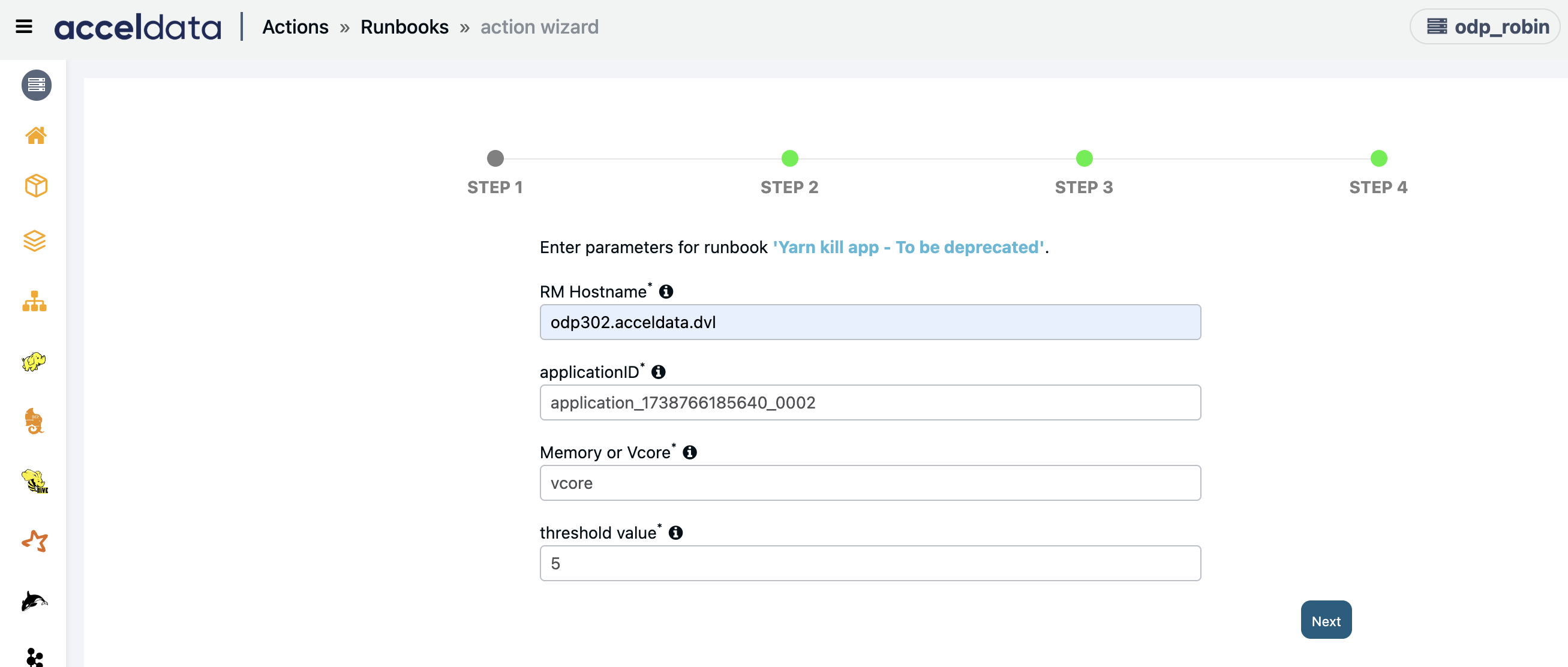
YARN Kill App
This runbook creates an action script to delete a YARN application.
This action will soon be deprecated. Users are encouraged to switch to the Yarn Application - Auto Killer Action, which offers enhanced capabilities, including more flexible termination conditions and improved control over application management.
- RM Hostname: Enter the hostname or IP address of the resource manager of your cluster.
- applicationID: Enter the ID of the application to be killed. You can enter "any" to automatically select applications based on threshold parameters.
- Memory or Vcore: You must either enter memory or vcore. The threshold will be set for the variable chosen here.
- Threshold Value: Enter the threshold value for the variable selected in the previous step.
- Click Next.
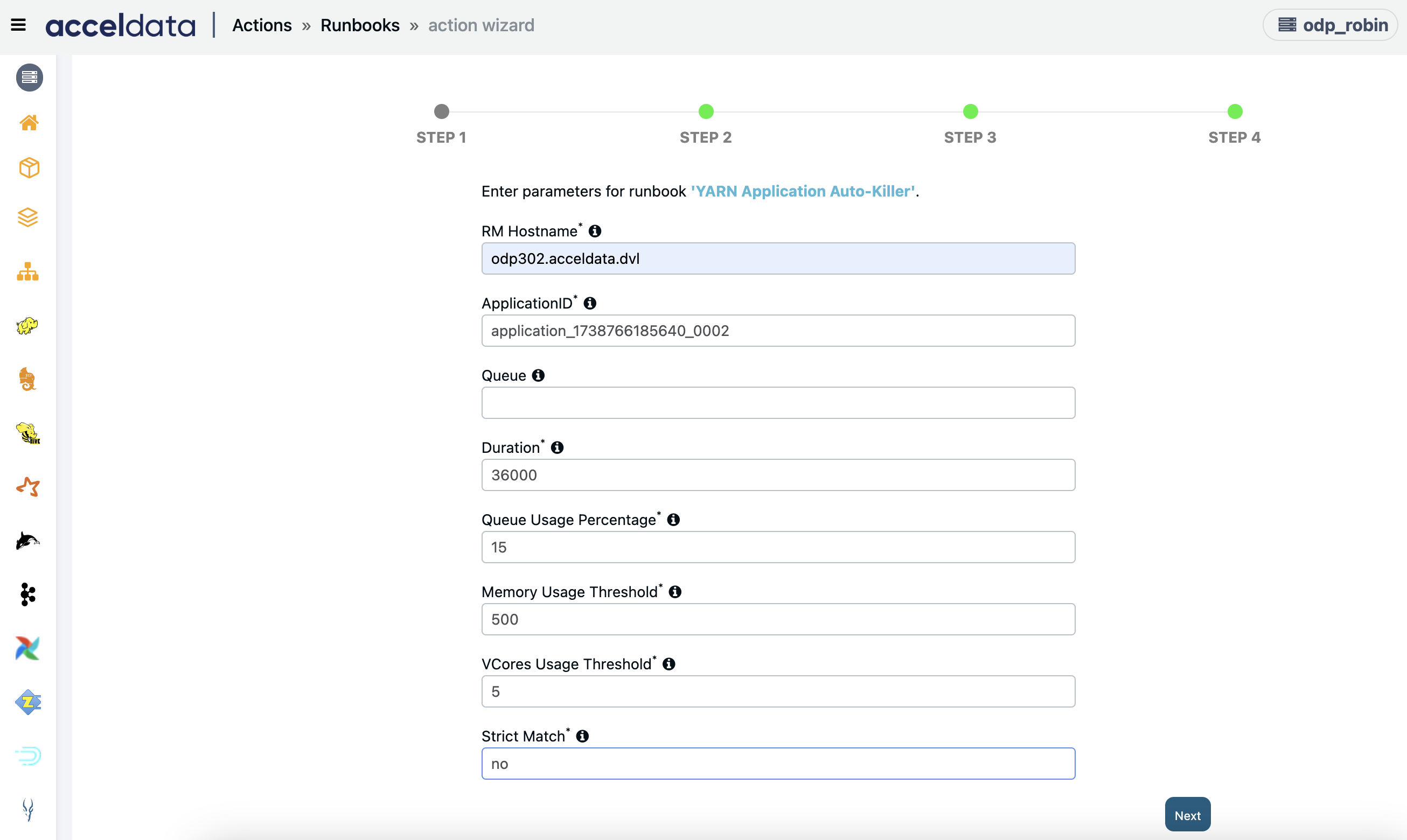
Yarn Application Auto Killer
This runbook allows you to kill applications with multiple criteria. This is an enhanced version of the action YARN Kill App.
Enter “any” when creating a standalone action with other criteria. If an action is associated with an alert, the Application ID will be automatically passed from the alert to the action, and all the other fields and corresponding fields hold no value. So, for mandatory fields, enter “0,” and for optional fields, leave them empty.
- RM Hostname: Enter the hostname or IP address of the resource manager of your cluster.
- applicationID: Enter the ID of the application to be killed. You can enter "any" to automatically select applications based on threshold parameters.
- Queue: Enter queues where applications should not be terminated.
- Duration: Enter the duration threshold in milliseconds. The applications running longer than this threshold gets killed.
- Queue Usage Percentage: Enter the queue usage threshold percentage. The applications with queue usage percentage greater than this threshold gets killed.
- Memory Usage Threshold: Enter the memory usage threshold in MB. The applications with allocated memory greater than this threshold gets killed.
- vCores Usage Threshold: Enter the vCores usage threshold in numbers. The applications with greater than this threshold gets killed.
- Strict Match:
- Set to "Yes" to kill applications only if all conditions are met.
- Set to "No" to terminate applications even if any one condition is met.
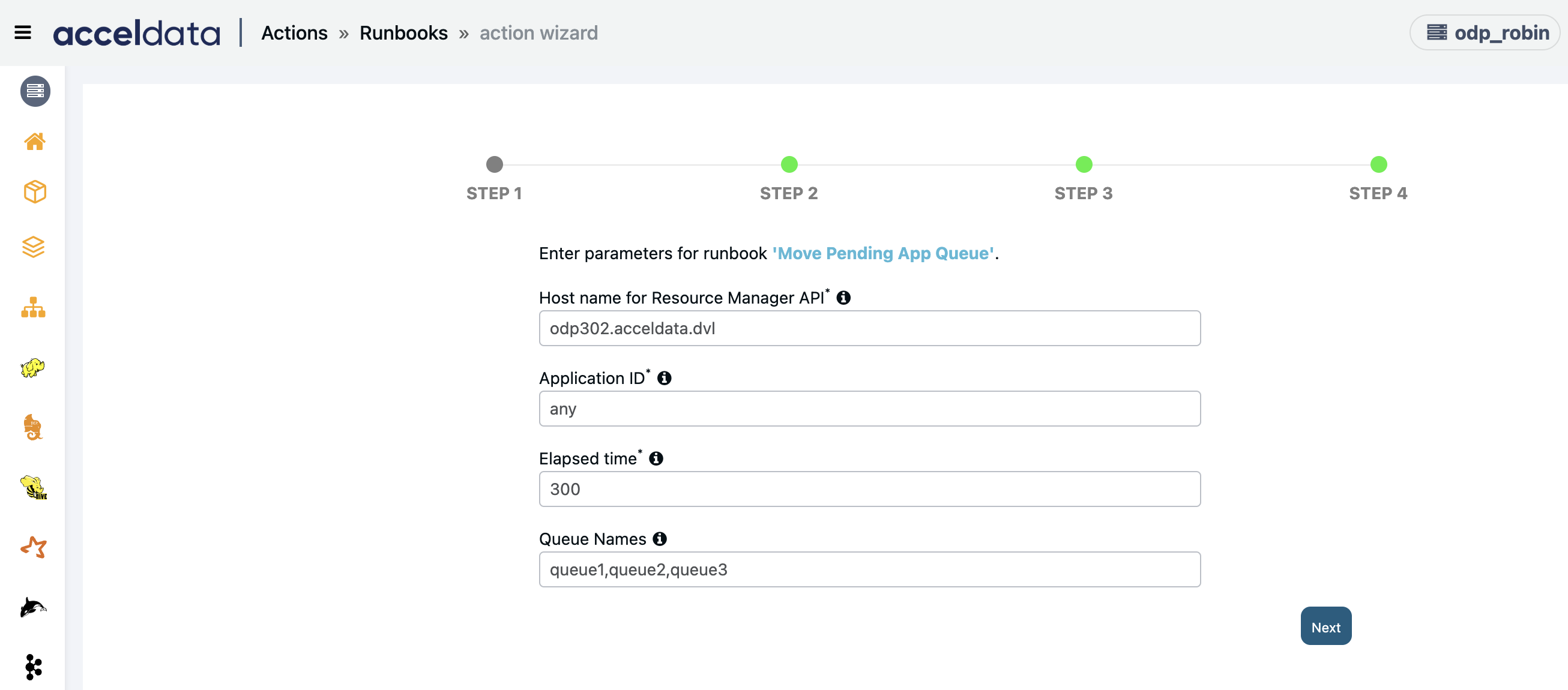
Move Pending App Queue
This runbook allows you to change the queue of a YARN application which is in pending state.
- Hostname for Resource Manager API: Enter the hostname of the resource manager with port number.
- applicationID: Enter the ID of the application which is pending and needs to be moved. You can enter "any" to automatically select applications based on threshold parameters.
- Elapsed Time: Enter time (in seconds) to filter and move pending applications. Type "na" if you have entered application ID in the previous step.
- Queue Name: Enter the preferred leaf queue names (comma-separated) to which the pending application must be moved. You can enter the key word "any" to automatically select a leaf queue with available resources.
Note The user must have the permission to submit jobs to those queues. - Click Next.
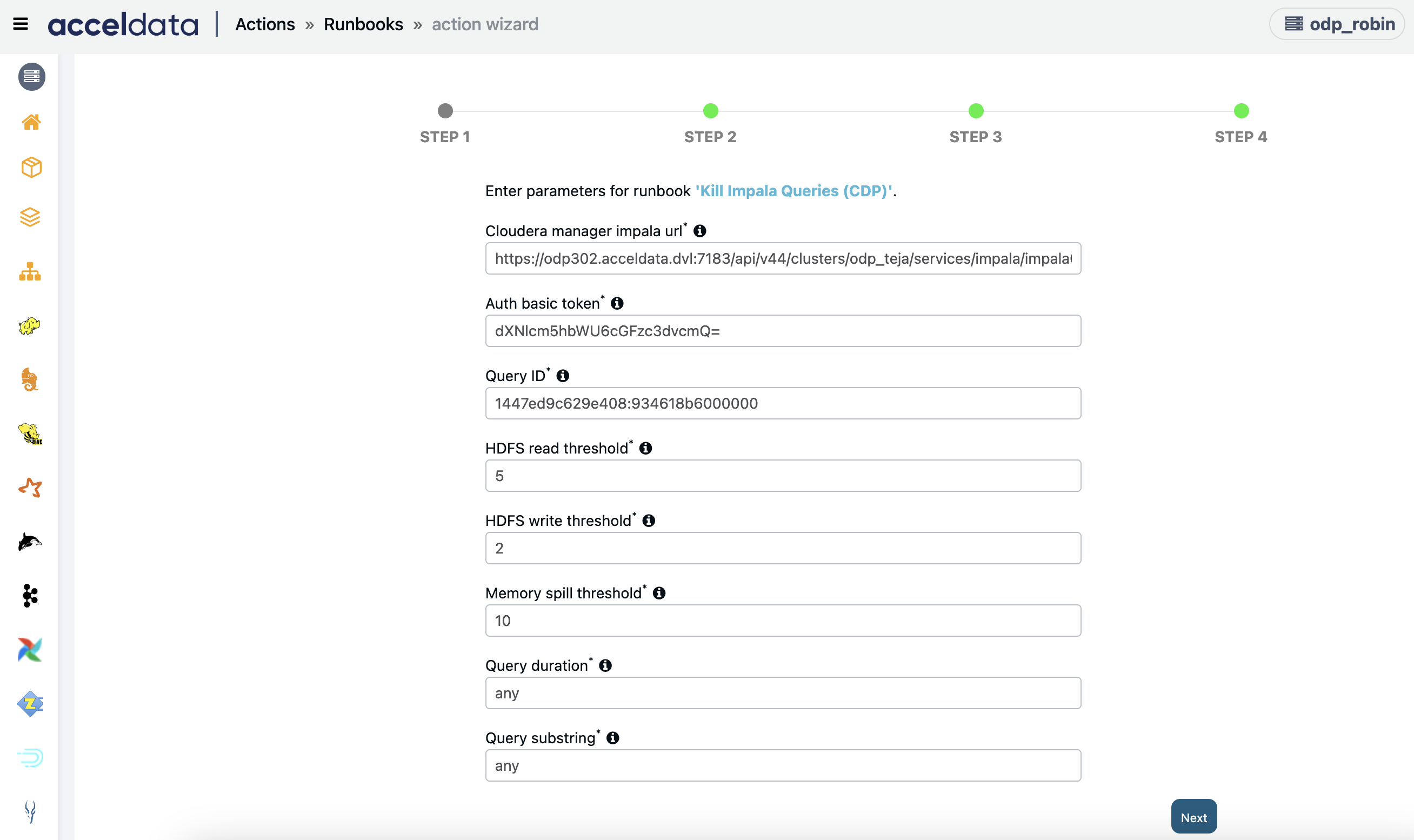
Kill Impala Queries (CDP)
Enter the following parameters:
The query will be killed, if any one of these parameters are matched: HDFS Read Threshold, HDFS Write Threshold, Memory Spill Threshold, Query Duration, and Query Substring.
If you have entered the query id, then the above condition will be ignored.
- Cloudera Manager Host: Cloudera manager host in this format
<ip>:<port> - Cluster Name: Name of the cluster
- Auth Basic Token: Authorization token. You can generate the authorization token using the following code:
echo "username:password" | tr -d '\n' | base64 - Query ID: Query id to kill specific query. Fill 'any' to automatically select query based on other threshold parameters.
- HDFS Read Threshold: HDFS read threshold value (in mb) to filter query. Fill 'any' to automatically select query based on other threshold parameters.
- HDFS Write Threshold: HDFS write threshold value (in mb) to filter query. Fill 'any' to automatically select query based on other threshold parameters.
- Memory Spill Threshold: Memory spill threshold value (in mb) to filter query. Fill 'any' to automatically select query based on other threshold parameters.
- Query Duration: Query duration (in secs) to filter query. Fill 'any' to automatically select query based on other threshold parameters.
- Query Substring: Query substring (ex. CREATE/SELECT) to filter query. Fill 'any' to automatically select query based on other threshold parameters.
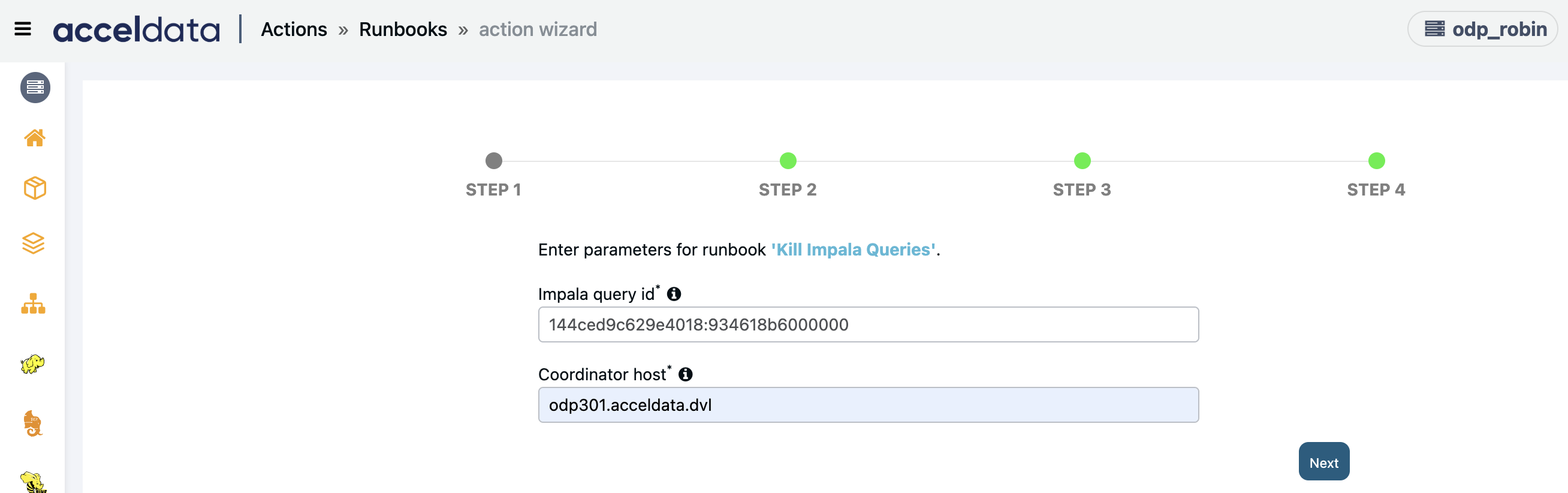
Kill Impala Queries
Enter the following parameters:
- Impala Query ID: Impala query which needs to be killed.
- Coordinator Host: Coordinator host for the given Impala query id.
Execute Actions
To Execute an action, perform the following:
- Click Execute in the Actions page against the name of the action you want to execute.
- A confirmation dialog box is displayed. Click Ok. The selected action is executed.
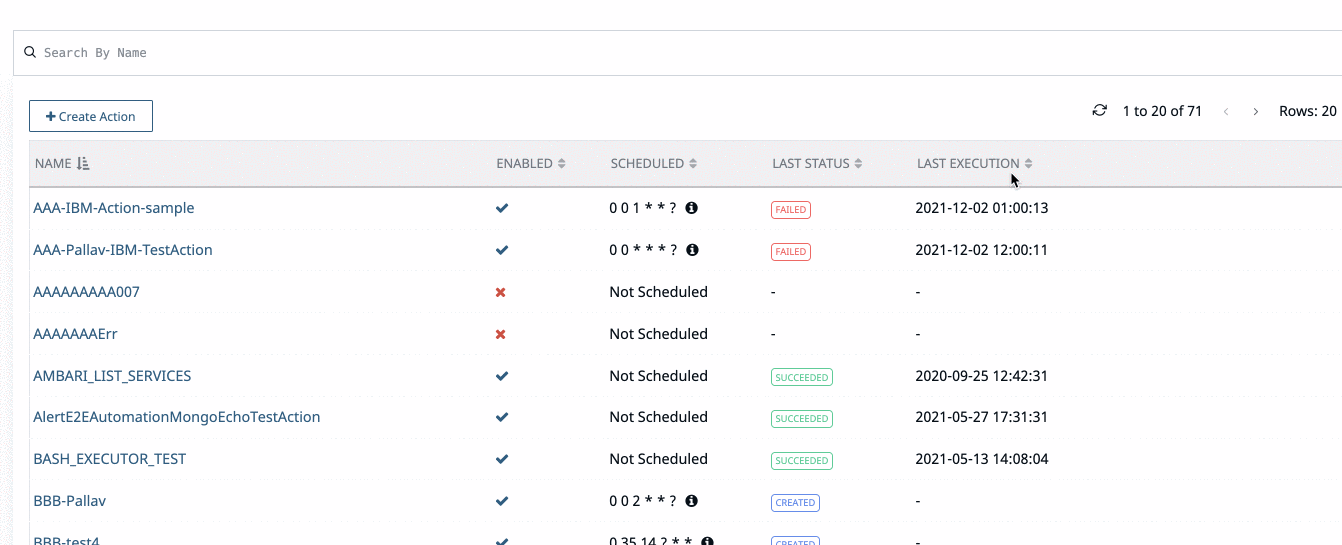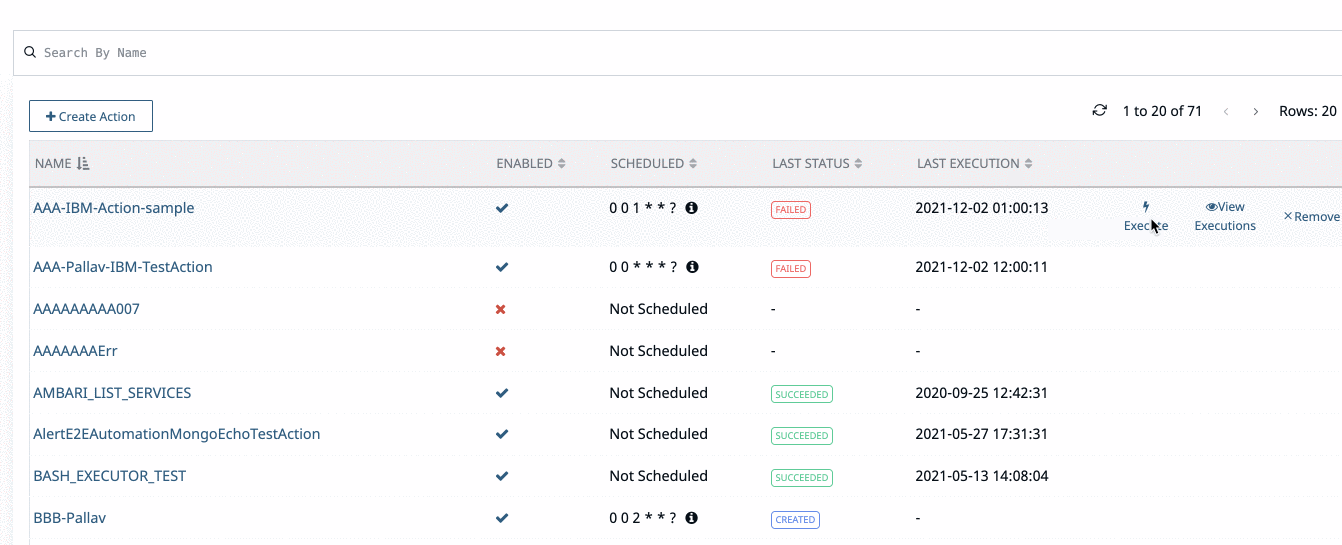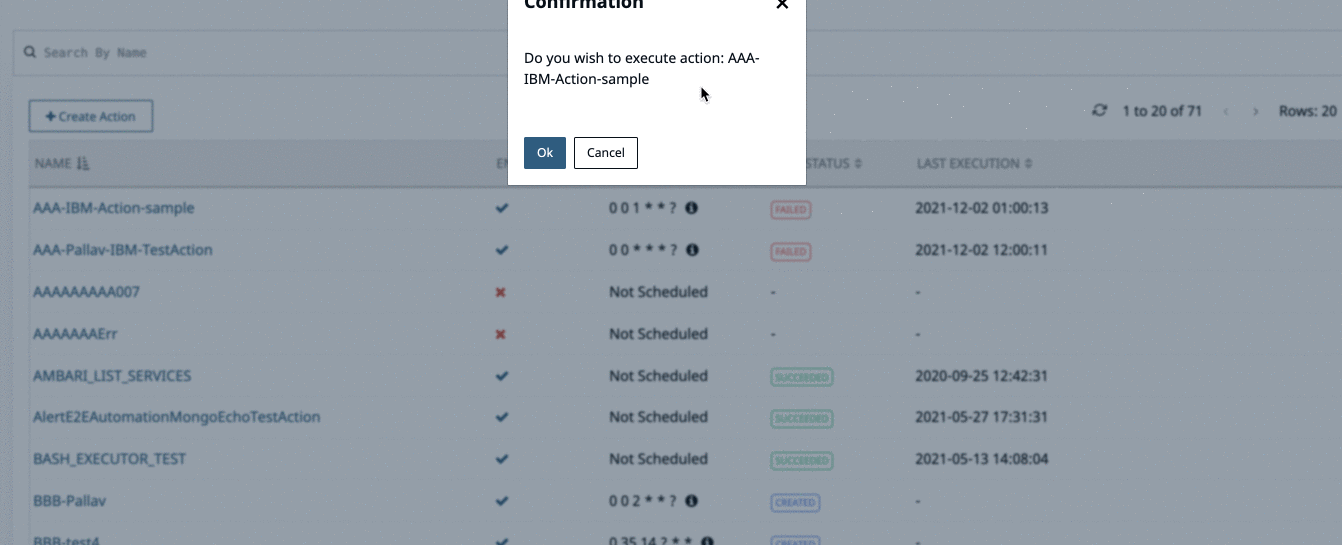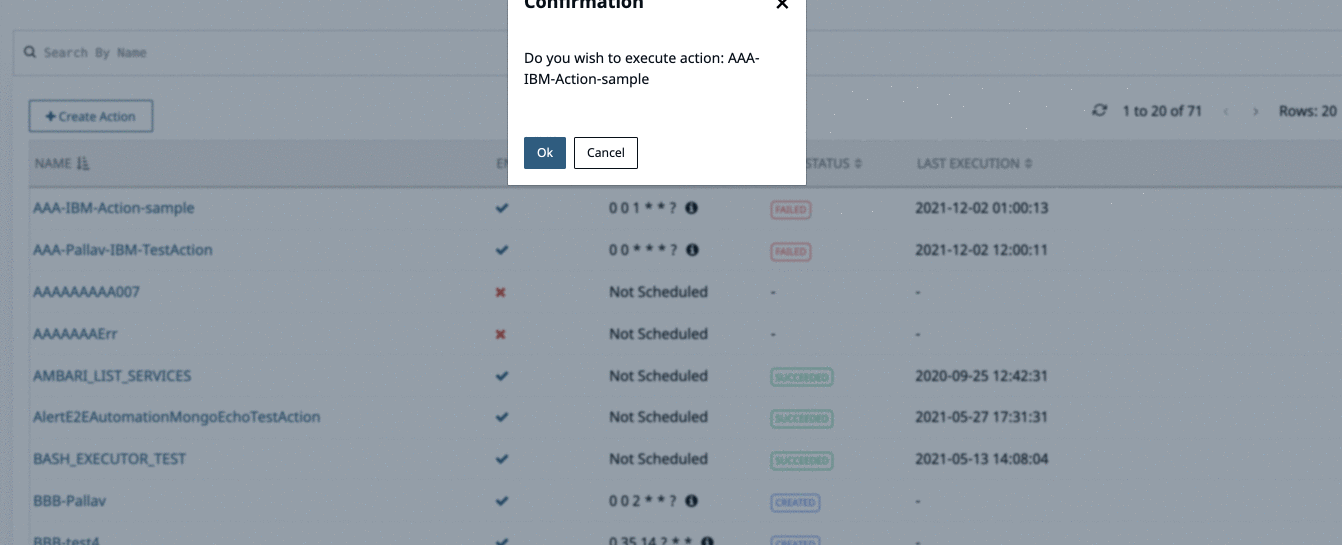
View Executions
To view the execution status, click
Edit Actions
From the Actions panel list, click the name of an action you want to edit. The action is displayed in the Actions page. Make your changes and click Save.
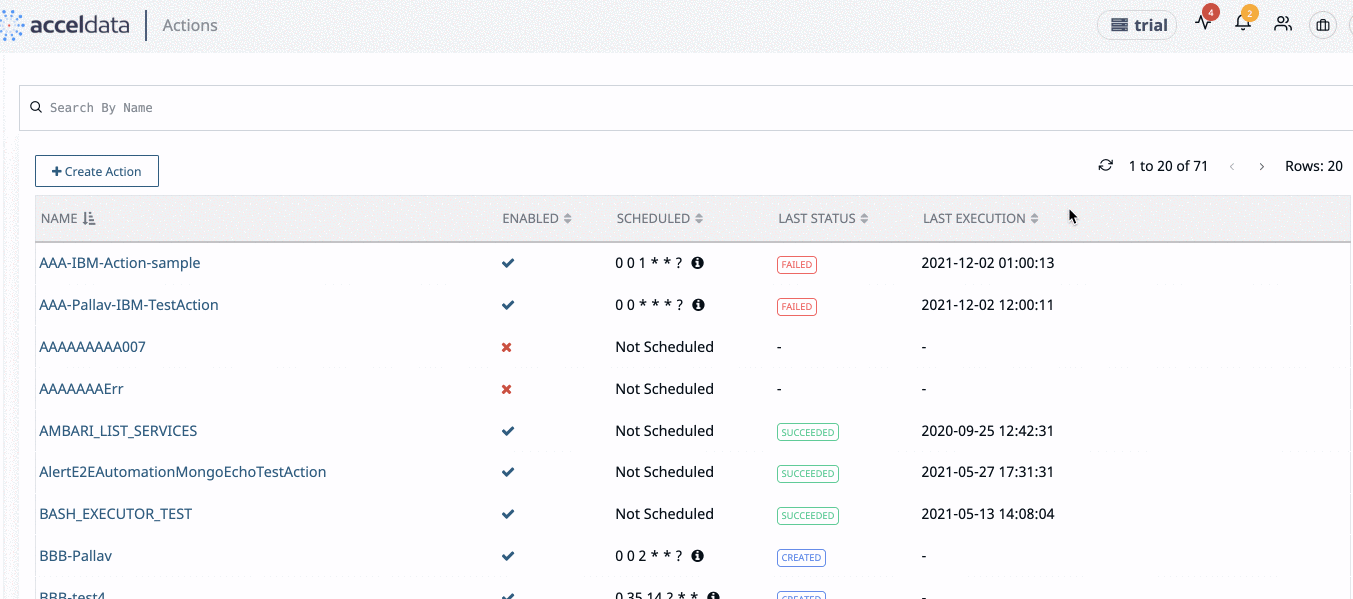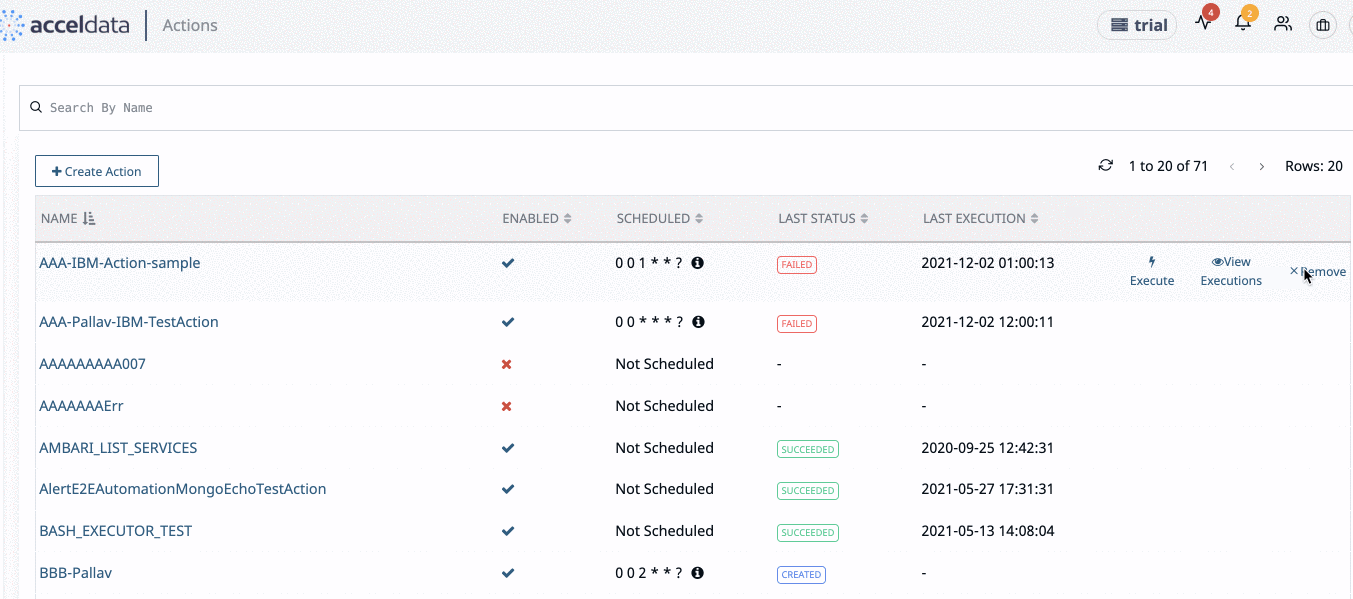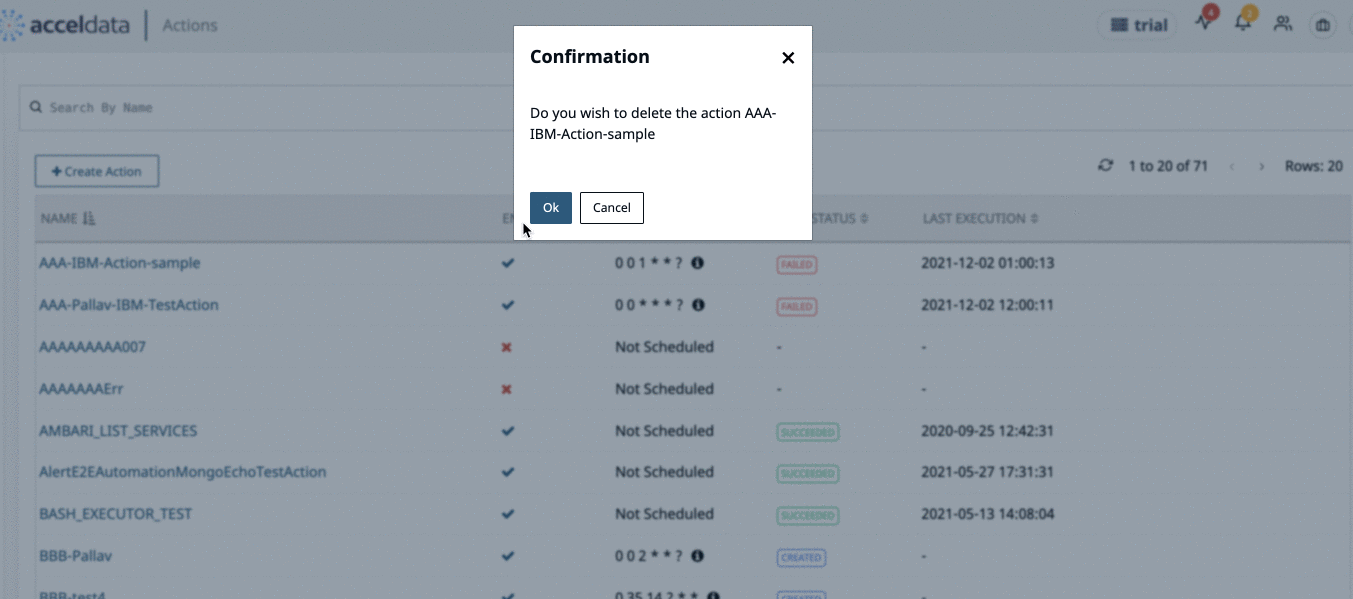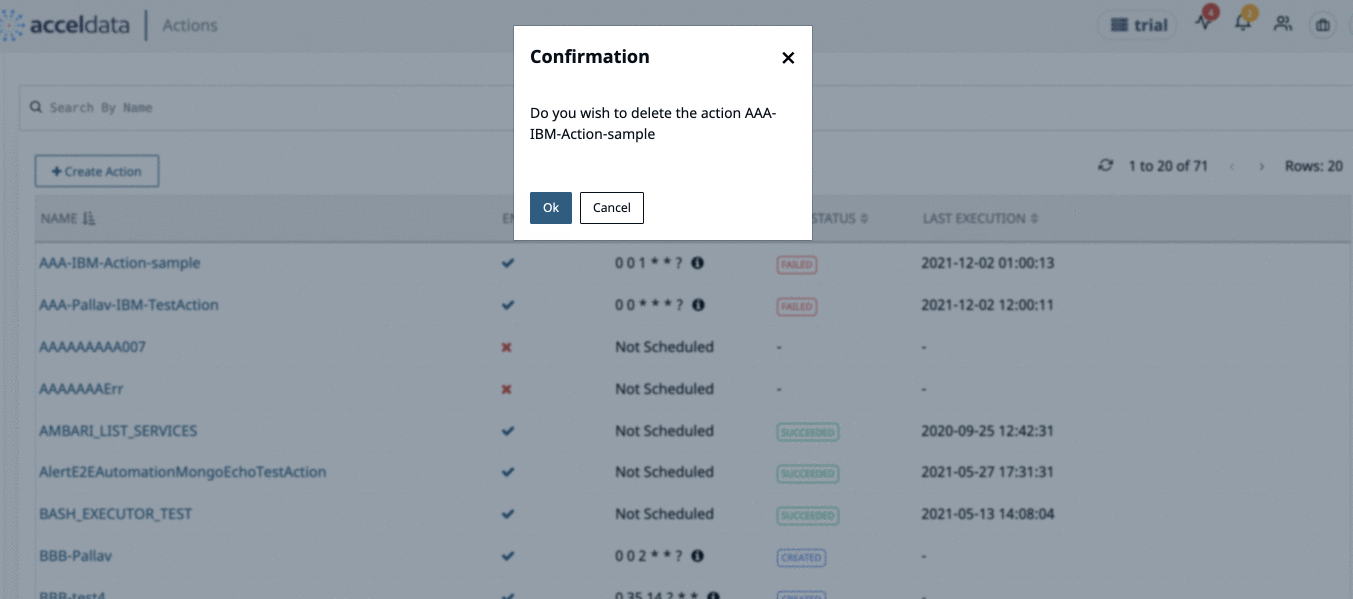
Delete Actions
To delete an Action perform the following:
- From the Actions list, click the Remove link from the end of an action row. A confirmation pop-up dialog box is displayed.
- Click Ok. The Action will be deleted.
When the action is deleted, all executions associated with it are deleted as well.
Searching an Action
You can search an Action from the list by using the Search bar. Enter part name or full name of the Action.
Export and Import Actions
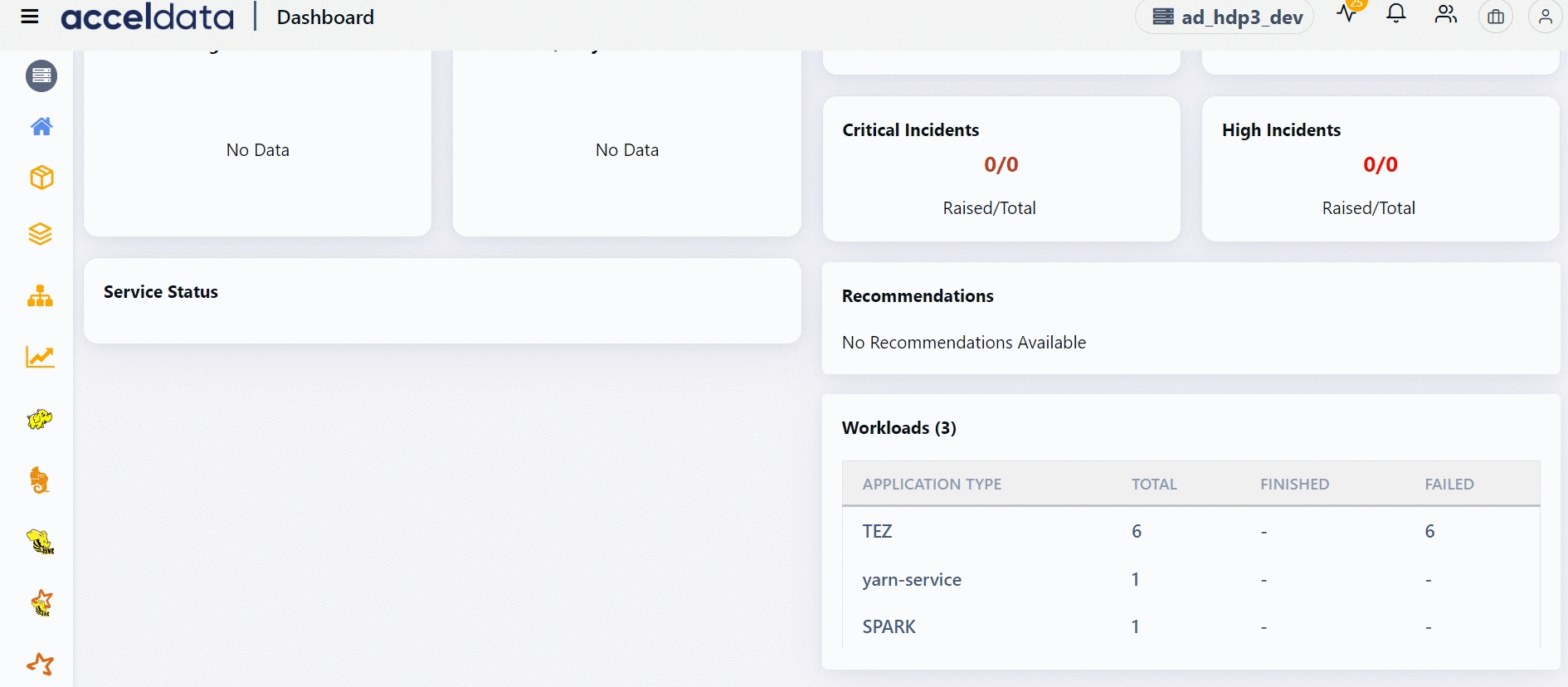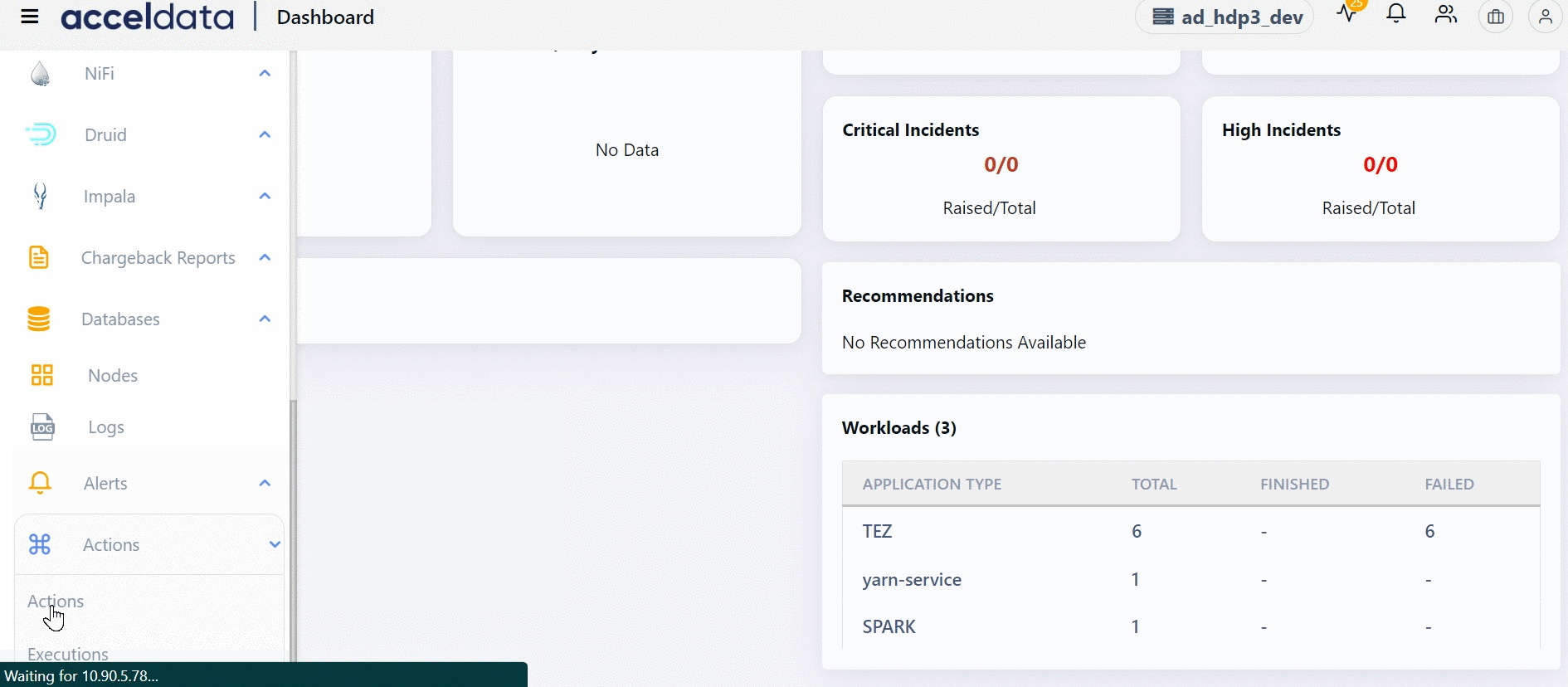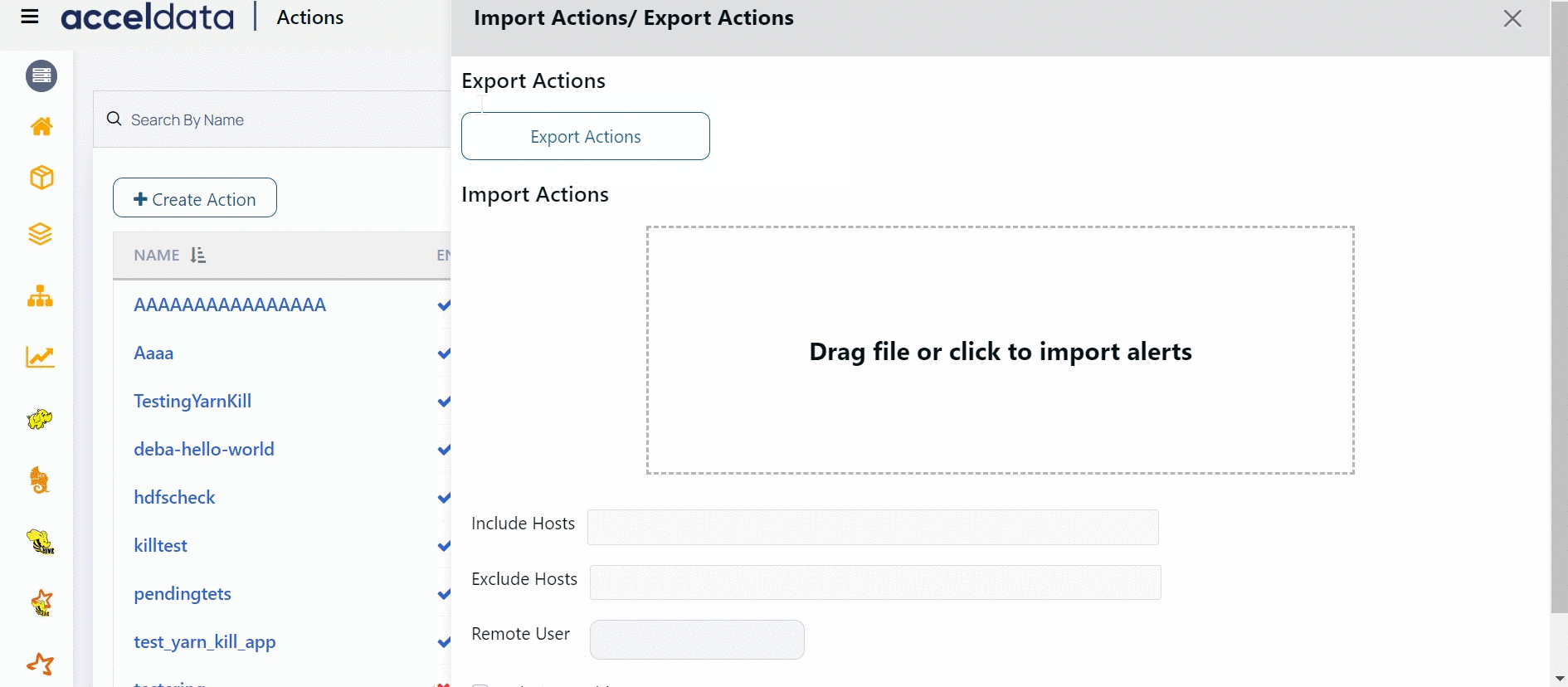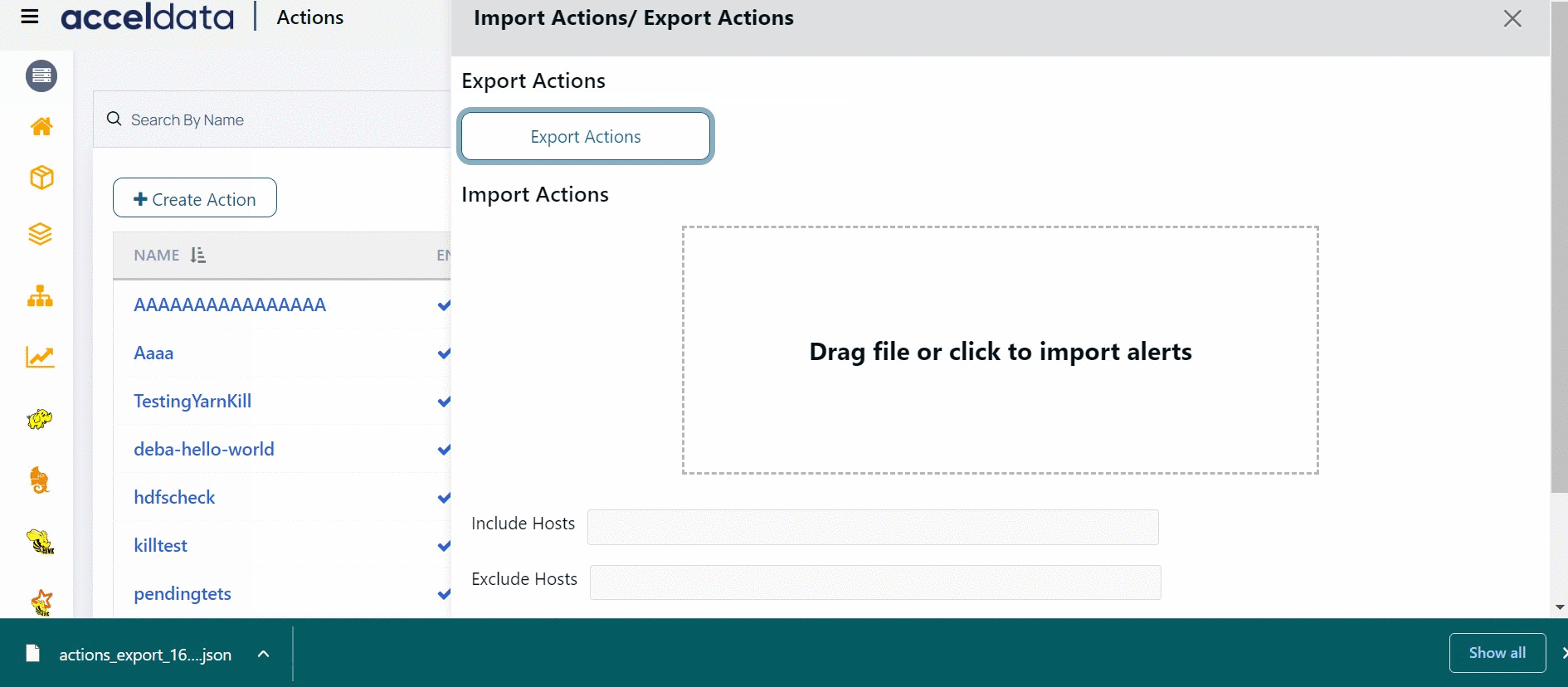
You can export and import actions in Pulse. You can use this feature to export and import actions from one cluster to another. The Actions are exported as a JSON format file. Once you export the Actions from a cluster, you can use the import option on another cluster, to import the Actions. Pulse allows you to import JSON format files as Actions. While importing the Action, you must specify various details like list of hosts to be included, list of hosts to be excluded, remote host details, and Kerberos configuration.
To export Actions:
- Navigate to Actions.
- Click the Import & Export Alerts button.
- Click Export Action.
To import Actions:
- Navigate to Actions.
- Click the Import & Export Alerts button.
- Get the JSON file containing the Actions to the Drag file or click to import alerts section by either dragging and dropping the JSON file or by importing it.
- (Optional) Provide the list of hosts whose Actions must be included, in the Include Hosts field. If you have multiple hosts, separate each host with comma.
- (Optional) Provide the list of hosts whose Actions must be excluded, in the Exclude Hosts field. If you have multiple hosts, separate each host with comma.
- (Optional) Select the remote user on whose behalf the Actions must be executed, in the Remote User field.
- (Optional) Select the Kerberos Enable field and provide Kerberos details if you have setup Kerberos.
- Click Submit.
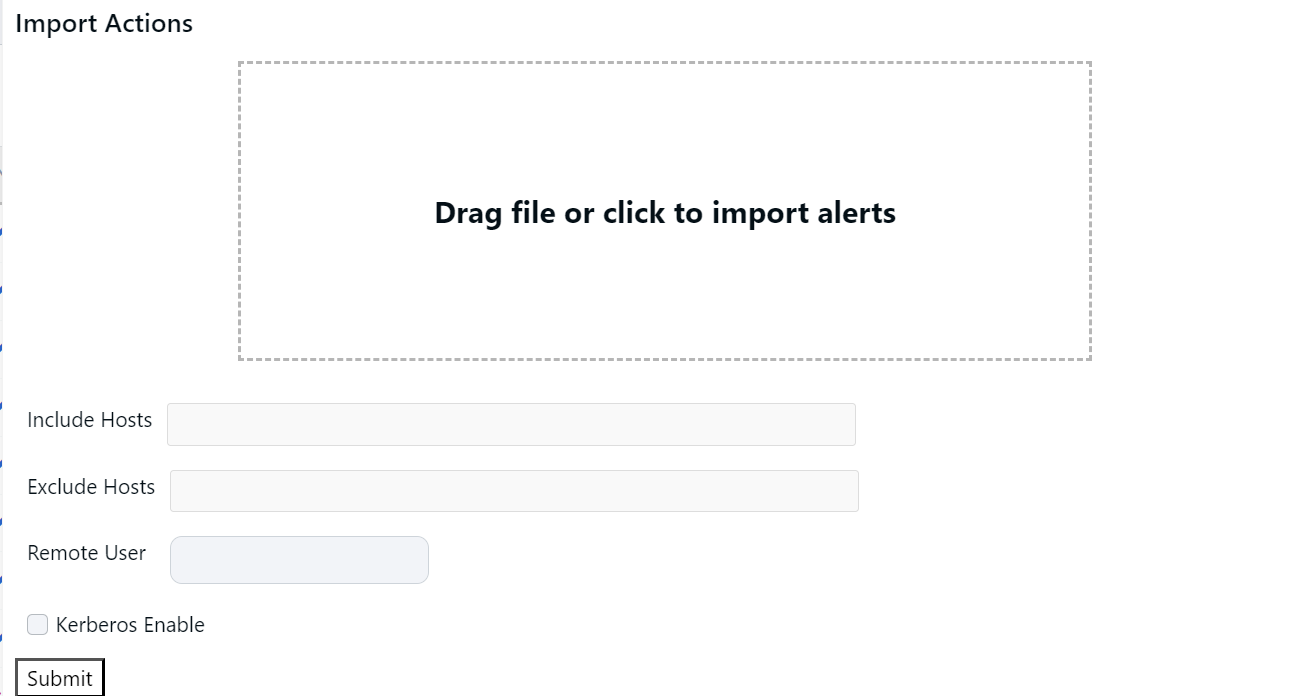
Option to export and import the created playbooks.