Acceldata Open Source Data Platform
ODP 3.2.3.3-2
Release Notes
What is ODP
Installation
Advanced Installation
Configuration and Management
Upgrade
USER GUIDES
Security
Uninstall ODP
Title
Message
Create new category
What is the title of your new category?
Edit page index title
What is the title of the page index?
Edit category
What is the new title of your category?
Edit link
What is the new title and URL of your link?
Documentation for Spark Notebook Examples
Summarize Page
Copy Markdown
Open in ChatGPT
Open in Claude
Connect to Cursor
Connect to VS Code
This page demonstrates how to use Jupyter notebooks with Spark, including Python 3 kernel options and related development tools.
Estimating Pi Using PySpark
This program uses the Monte Carlo method to estimate the value of Pi. It demonstrates how to use PySpark to parallelize computations.
Bash
x
from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionimport random# Initialize Spark sessionspark = SparkSession.builder \\ .appName("Estimate Pi") \\ .getOrCreate()# Function to check if a point is inside the unit circledef inside_circle(_): x = random.uniform(0, 1) y = random.uniform(0, 1) return x * x + y * y < 1# Function to estimate Pidef estimate_pi(num_samples): count_inside = spark.sparkContext.parallelize(range(num_samples)) \\ .filter(inside_circle) \\ .count() pi_estimate = 4 * count_inside _ num_samples return pi_estimate# Run estimationnum_samples = 100000pi_value = estimate_pi(num_samples)print(f"Estimated value of Pi: {pi_value}")# Stop the Spark sessionspark.stop()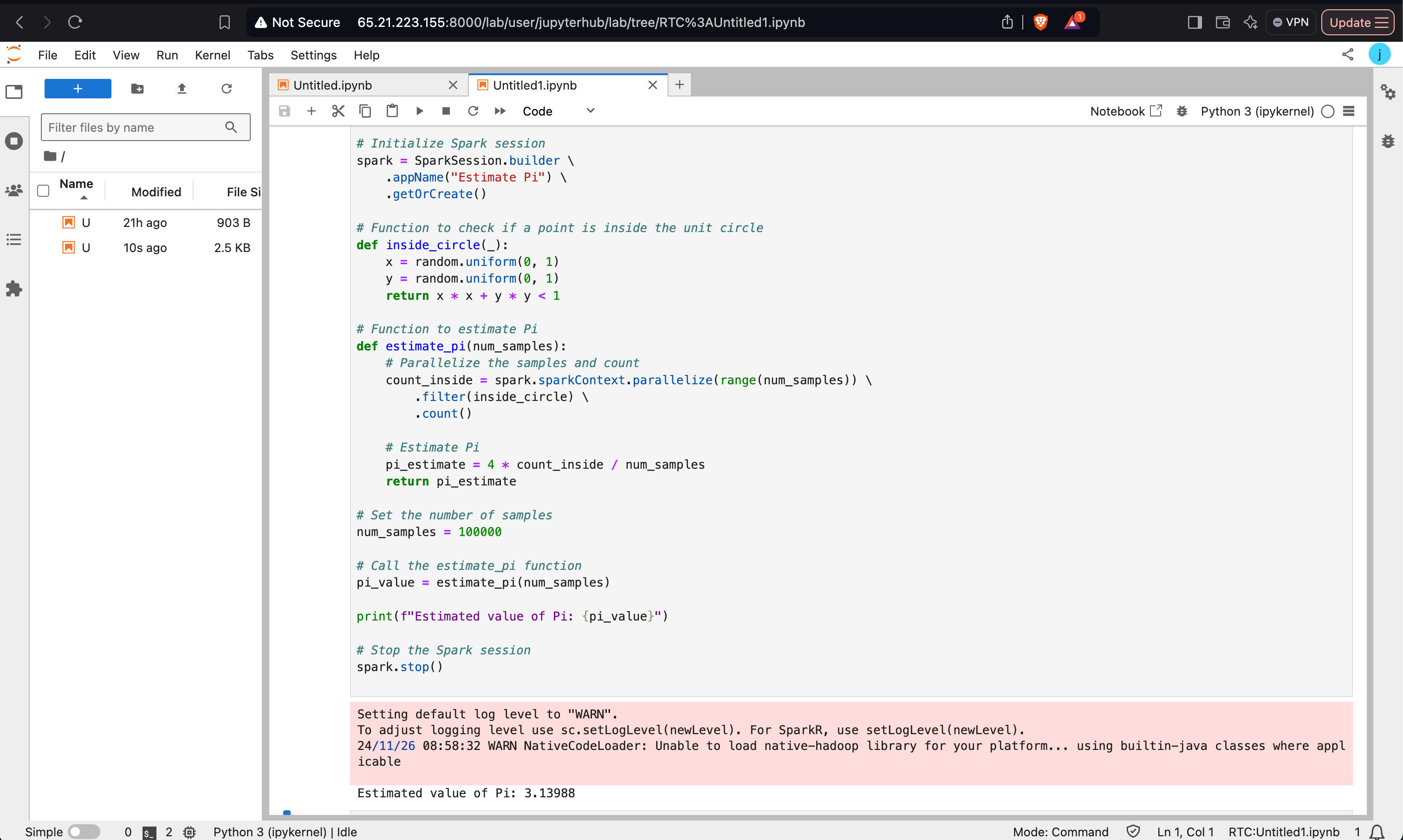
Creating and Displaying a DataFrame
This example showcases creating a Spark DataFrame using a list of Row objects and displaying it.
Bash
from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionfrom datetime import datetime, datefrom pyspark.sql import Row# Initialize Spark sessionspark = SparkSession.builder \\ .appName("MySparkApp") \\ .getOrCreate()# Create a DataFramedf = spark.createDataFrame([ Row(a=1, b=2.0, c='string1', d=date(2000, 1, 1), e=datetime(2000, 1, 1, 12, 0)), Row(a=2, b=3.0, c='string2', d=date(2000, 2, 1), e=datetime(2000, 1, 2, 12, 0)), Row(a=4, b=5.0, c='string3', d=date(2000, 3, 1), e=datetime(2000, 1, 3, 12, 0))])df.show()
Complex Operations with PySpark
This example demonstrates joining DataFrames, applying User-Defined Functions (UDFs), and executing SQL queries.
Data Preparation and Joining:
Bash
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession, Rowspark = SparkSession.builder \\ .appName("Complex Spark Example") \\ .master("yarn") \\ .config("spark.executor.memory", "2g") \\ .config("spark.driver.memory", "1g") \\ .getOrCreate()# Sample dataemployee_data = [ Row(emp_id=1, name='John Doe', age=30, dept_id=1, salary=60000), Row(emp_id=2, name='Jane Smith', age=25, dept_id=2, salary=70000), Row(emp_id=3, name='Sam Brown', age=45, dept_id=1, salary=80000),]department_data = [ Row(dept_id=1, dept_name='HR'), Row(dept_id=2, dept_name='Engineering'),]employee_df = spark.createDataFrame(employee_data)department_df = spark.createDataFrame(department_data)joined_df = employee_df.join(department_df, on='dept_id', how='inner')joined_df.show()Using UDFs:
Bash
from pyspark.sql.functions import colfrom pyspark.sql.types import StringTypedef salary_category(salary): if salary < 70000: return 'Low' elif 70000 <= salary < 100000: return 'Medium' else: return 'High'salary_category_udf = spark.udf.register("salary_category", salary_category, StringType())categorized_df = joined_df.withColumn("salary_category", salary_category_udf(col("salary")))categorized_df.select("name", "dept_name", "salary", "salary_category").show()SQL Queries:
Bash
categorized_df.createOrReplaceTempView("employee_view")avg_salary_query = spark.sql(""" SELECT dept_name, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary FROM employee_view GROUP BY dept_name""")avg_salary_query.show()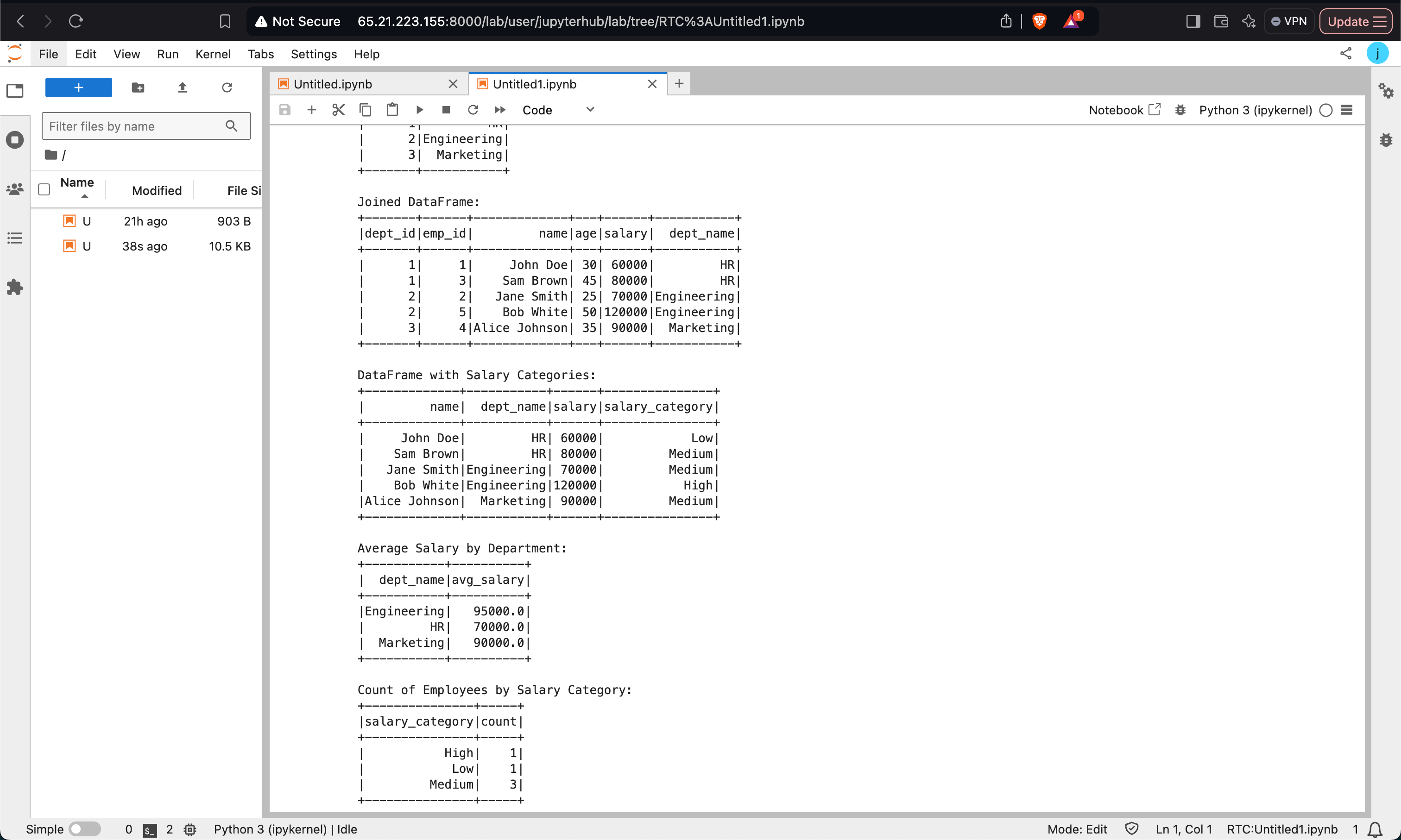
Performing Word Count
A simple word count example demonstrating Spark RDD transformations.
Bash
from pyspark.sql import SparkSessionspark = SparkSession.builder \\ .appName("Word Count Example") \\ .master("local[*]") \\ .getOrCreate()# Sample datadata = ["hello world", "hello spark", "spark is awesome", "hello world again"]# Word count using RDDrdd = spark.sparkContext.parallelize(data)word_counts = rdd.flatMap(lambda line: line.split(" ")) \\ .map(lambda word: (word, 1)) \\ .reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b)# Display resultsresult = word_counts.collect()for word, count in result: print(f"{word}: {count}")spark.stop()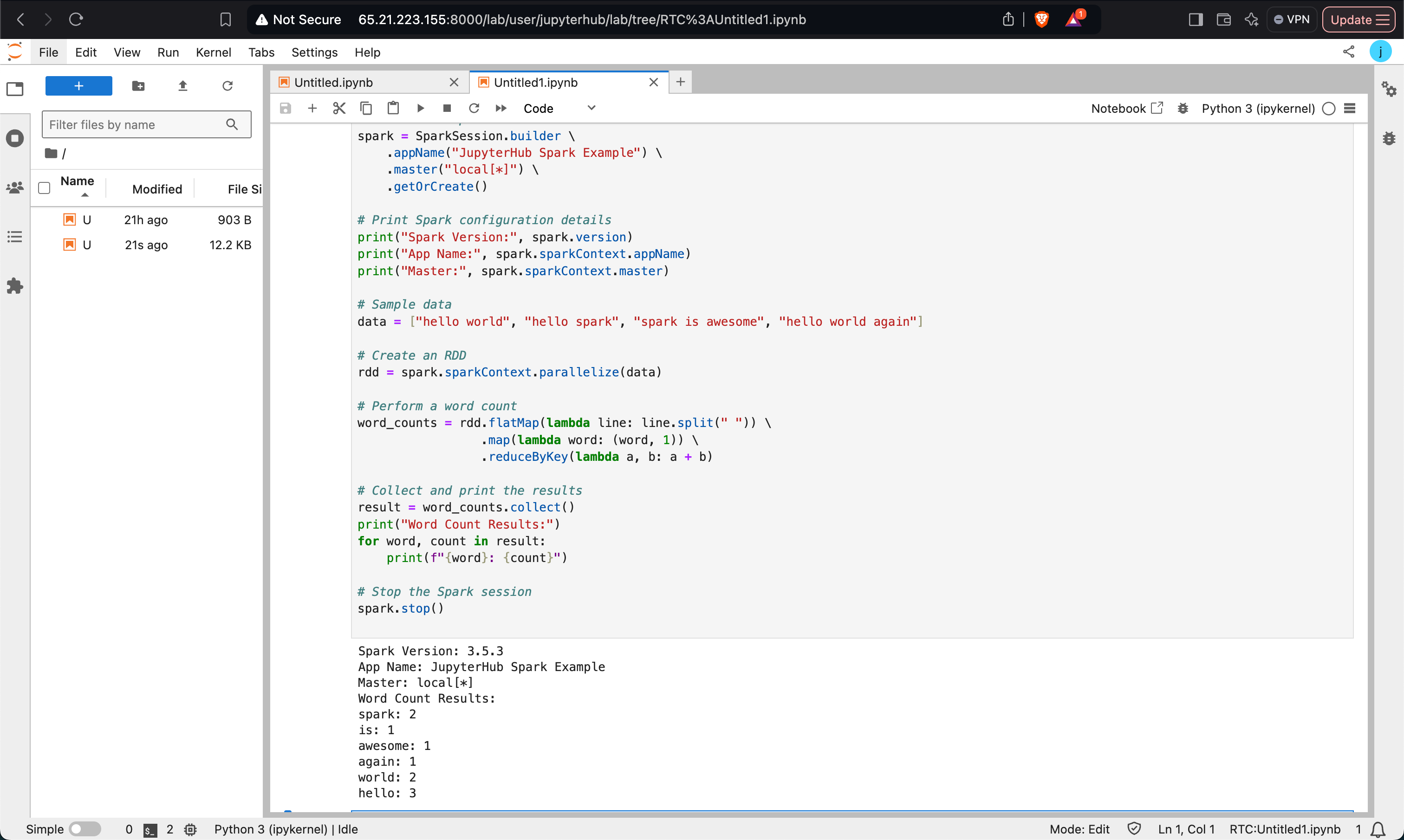
Using ODP’s Spark version
Bash
import osimport findspark# Set environment variables for Sparkos.environ['SPARK_HOME'] = '_usr_odp_3.2.3.2-3_spark3'os.environ['PYSPARK_PYTHON'] = '_usr_bin_python3'os.environ['PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON'] = 'python3'# Initialize findsparkfindspark.init('_usr_odp_3.2.3.2-3_spark3')from pyspark import SparkContext# Initialize SparkContextsc = SparkContext.getOrCreate()Bash
import random# Define the number of samplesnum_samples = 100000# Function to check if a point is inside the unit circledef inside_unit_circle(_): return (random.random() ** 2 + random.random() ** 2) < 1# Perform the estimation by running a parallel computationrdd = sc.parallelize(range(num_samples))count = rdd.map(inside_unit_circle).filter(lambda x: x).count()# Estimate the value of Pipi_estimate = 4.0 * count _ num_samplesprint("Estimated value of Pi:", pi_estimate)# Stop SparkContext after use (optional in a notebook environment)# sc.stop()Submit the Job to a Cluster (Optional)
If you’re using a cluster manager like YARN with JupyterHub, you need to adjust the configurations accordingly:
Bash
from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContextconf = SparkConf() \\ .setAppName("Pi Estimation") \\ .setMaster("yarn") \\ .set("spark.executor.memory", "4g") \\ .set("spark.executor.cores", "2")sc = SparkContext(conf=conf)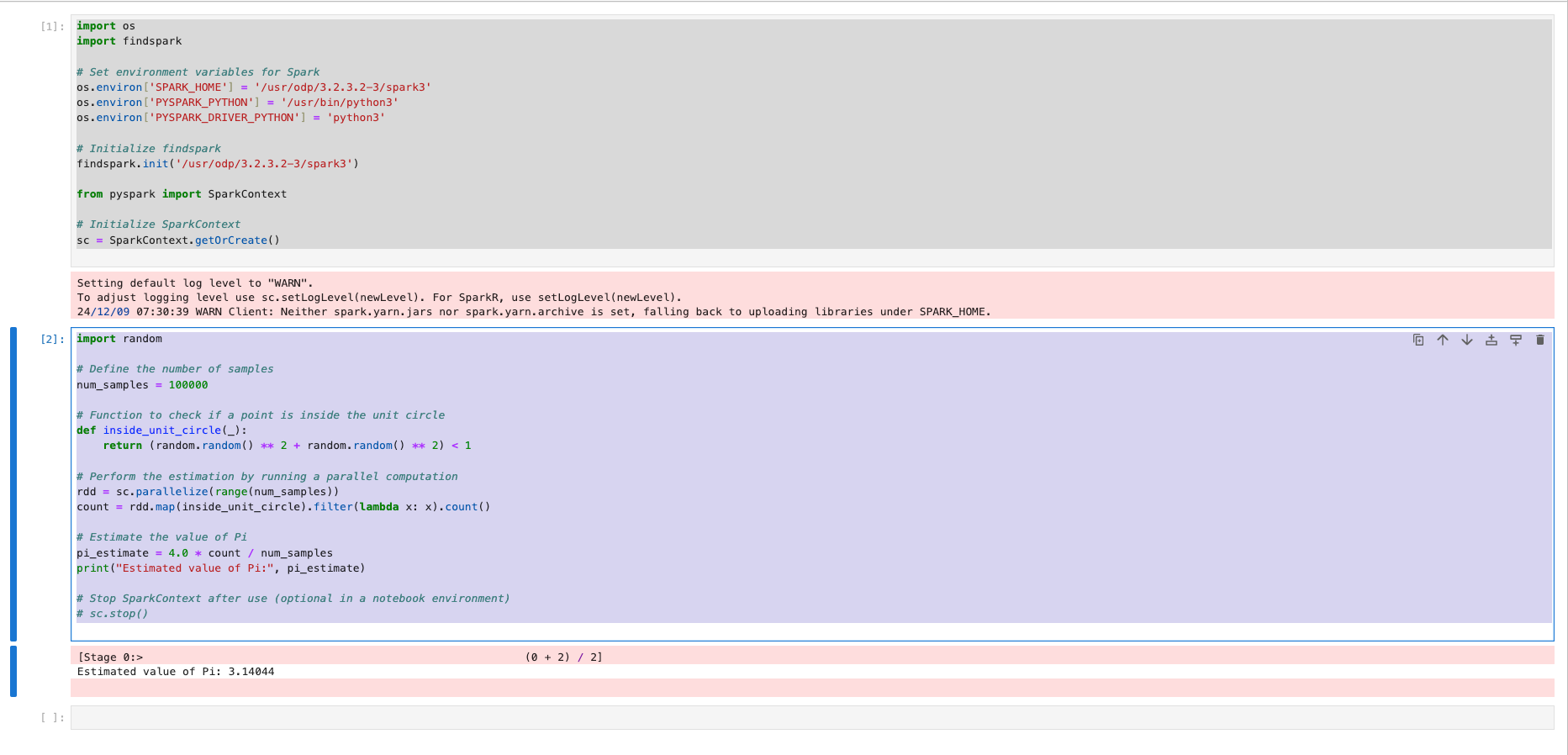
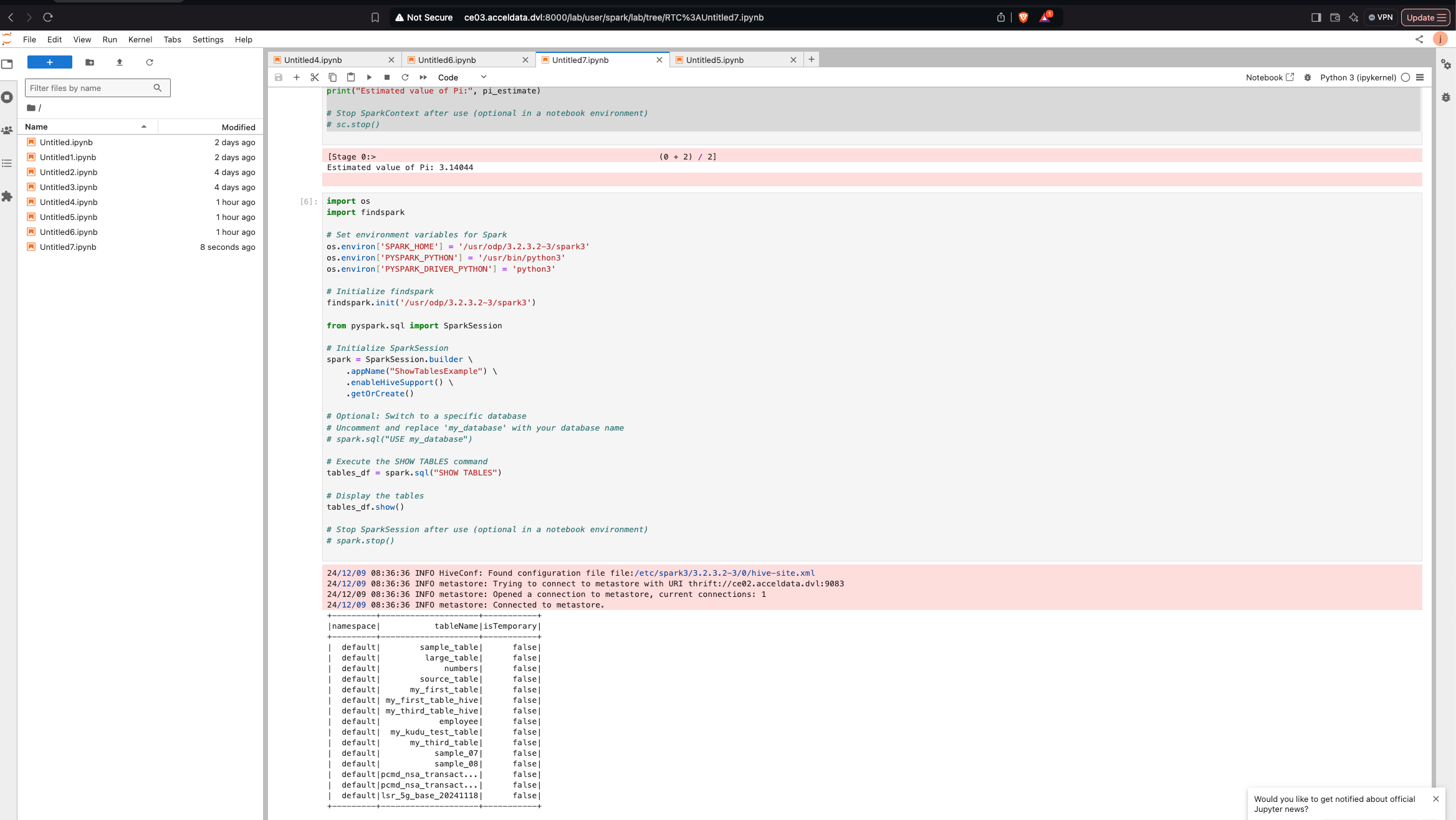
Show Hive Tables in Spark
Bash
import osimport findspark# Set environment variables for Sparkos.environ['SPARK_HOME'] = '_usr_odp_3.2.3.2-3_spark3'os.environ['PYSPARK_PYTHON'] = '_usr_bin_python3'os.environ['PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON'] = 'python3'# Initialize findsparkfindspark.init('_usr_odp_3.2.3.2-3_spark3')from pyspark.sql import SparkSession# Initialize SparkSessionspark = SparkSession.builder \\ .appName("ShowTablesExample") \\ .enableHiveSupport() \\ # Optional if you use Hive .getOrCreate()# Optional: Switch to a specific database# Uncomment and replace 'my_database' with your database name# spark.sql("USE my_database")# Execute the SHOW TABLES commandtables_df = spark.sql("SHOW TABLES")# Display the tablestables_df.show()# Stop SparkSession after use (optional in a notebook environment)# spark.stop()How It Works:
- Environment Setup: Configures the necessary Spark environment variables.
- SparkSession: Initializes a
SparkSessionwith Hive support (if needed). - Switch Database (Optional): You can switch to a specific database if you want to list tables from it.
- Show Tables: Executes the SQL command
SHOW TABLES, which returns a DataFrame of tables. - Display Output: Displays the list of tables in the output.
Expected Output:

Note
- Dependencies: Ensure Spark is correctly set up and configured for
localoryarnmode depending on the example. - UDFs: Register user-defined functions (UDFs) as required for custom transformations.
- SQL Queries: Use
createOrReplaceTempViewto run SQL queries on DataFrames. - Data Source: Replace hardcoded data with external sources like HDFS, databases, or files for real-world applications.
- Resource Configurations: Tune
spark.executor.memoryandspark.driver.memorybased on the cluster size and workload requirements.
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Last updated on Sep 2, 2025
Was this page helpful?
Next to read:
Error in Submitting YARN JobDiscard Changes
Do you want to discard your current changes and overwrite with the template?
Archive Synced Block
Message
Create new Template
What is this template's title?
Delete Template
Message