Acceldata Open Source Data Platform
ODP 3.2.3.3-2
Release Notes
What is ODP
Installation
Advanced Installation
Configuration and Management
Upgrade
USER GUIDES
Security
Uninstall ODP
Title
Message
Create new category
What is the title of your new category?
Edit page index title
What is the title of the page index?
Edit category
What is the new title of your category?
Edit link
What is the new title and URL of your link?
Handle HDFS and YARN Permissions
Summarize Page
Copy Markdown
Open in ChatGPT
Open in Claude
Connect to Cursor
Connect to VS Code
To enable seamless interaction between JupyterHub, HDFS, and YARN in a Hadoop cluster, certain configurations must be applied.
- Update core-site.xml: Modify the Hadoop configuration file
core-site.xmlto allow the JupyterHub user to act as a proxy. Add the following properties.
These properties are auto-populated if you are using newer mpack.
Bash
<property> <name>hadoop.proxyuser.jupyterhub.groups<_name> <value>*<_value> <_property> <property> <name>hadoop.proxyuser.jupyterhub.hosts<_name> <value>*<_value> <_property> <property> <name>hadoop.proxyuser.jupyterhub.users<_name> <value>*<_value> <_property>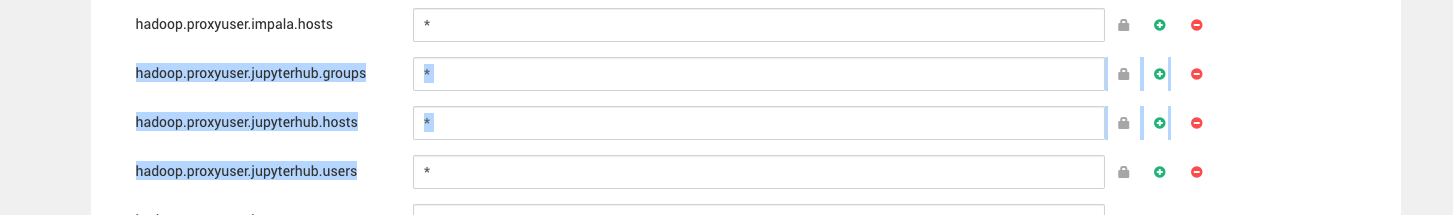
- Configure permissions for YARN
If you are using YarnSpawner, configure YARN to allow JupyterHub to submit applications. Use one of the following options:
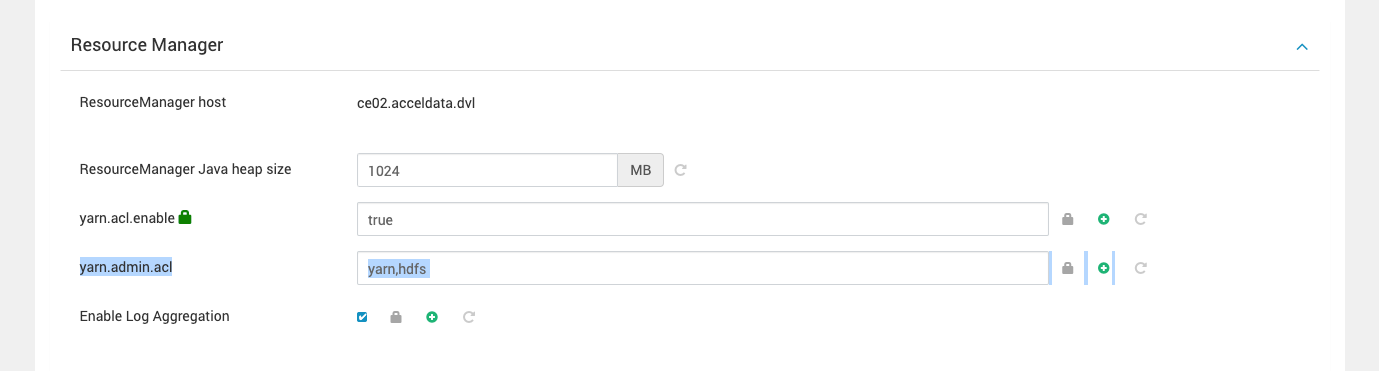
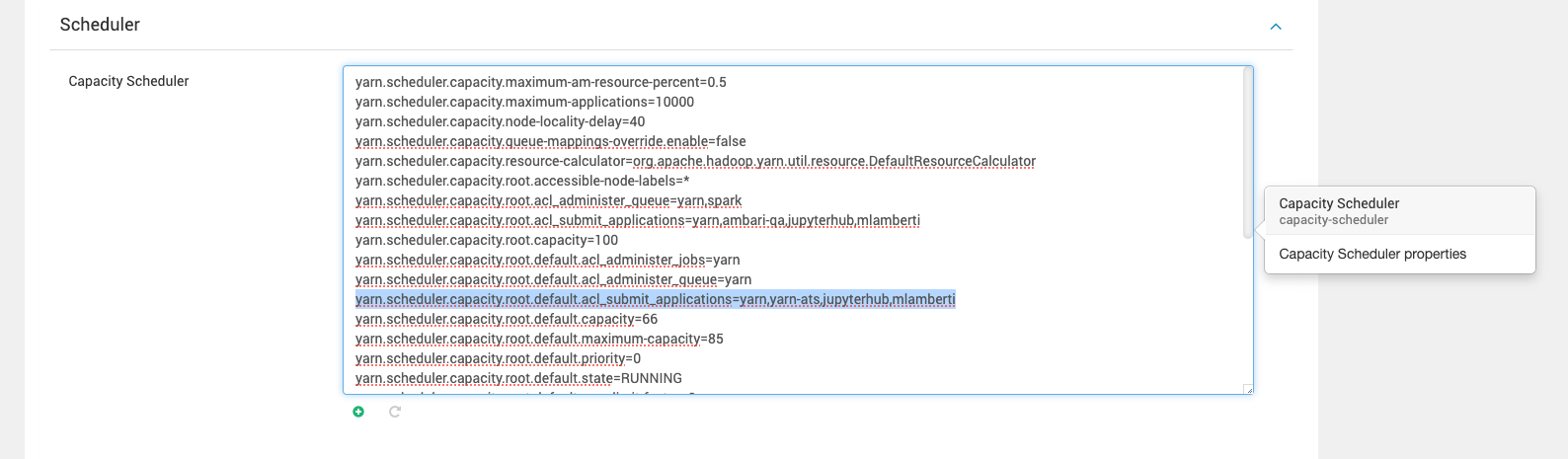
- If the Ranger plugin for YARN is not enabled or Ranger is not installed: Configure the YARN queue ACLs to grant the JupyterHub user permission to submit jobs. You can set these permissions in the YARN ResourceManager settings or in the queue configuration files.
- ** If Ranger is installed:
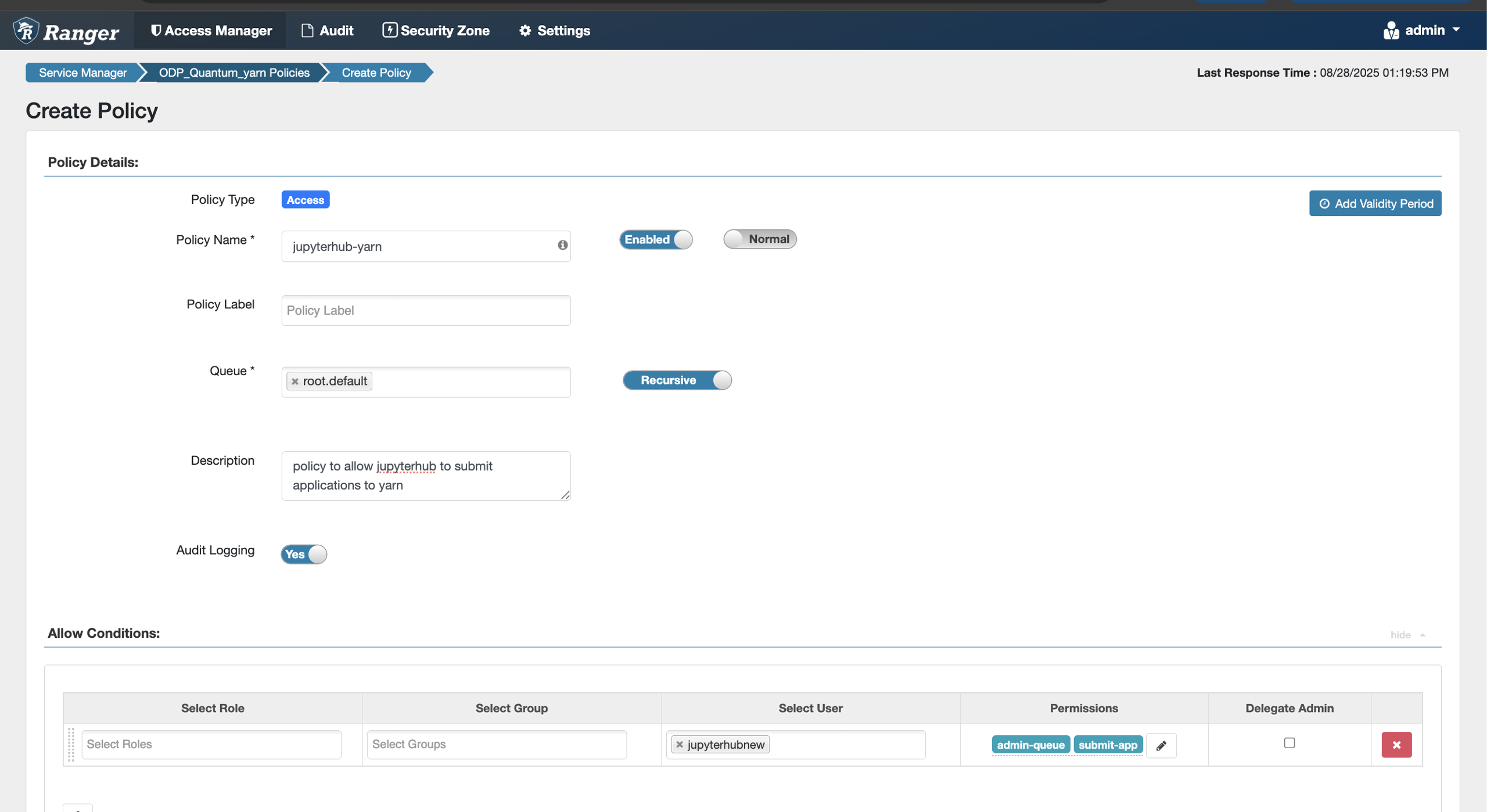
- *Create a Ranger policy that allows the JupyterHub user to submit applications to YARN. Select the target queue and assign permissions according to your requirements.
Why are these steps important?
Access Control:
- Configuring proxy permissions in
core-site.xmlallows JupyterHub to interact with HDFS on behalf of its users. - YARN ACLs ensure users can submit jobs through YarnSpawner without encountering permission issues.
- Configuring proxy permissions in
Seamless Execution:
- These configurations eliminate interruptions when users access files stored in HDFS or submit Spark jobs via YARN.
- Streamlined permissions simplify the setup and improve the user experience.
This document serves as a foundation for setting up JupyterHub in a distributed Hadoop environment. Following these steps ensures scalability, security, and smooth integration with essential components like HDFS and YARN.
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Type to search, ESC to discard
Last updated on Sep 2, 2025
Was this page helpful?
Next to read:
Configure YarnSpawner and HDFSCMDiscard Changes
Do you want to discard your current changes and overwrite with the template?
Archive Synced Block
Message
Create new Template
What is this template's title?
Delete Template
Message